Page 48 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 48
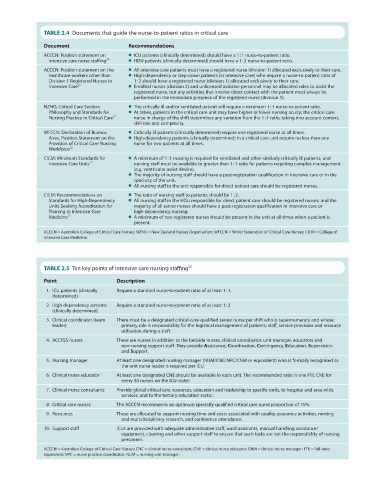
TABLE 2.4 Documents that guide the nurse-to-patient ratios in critical care
Document Recommendations
ACCCN: Position statement on ● ICU patients (clinically determined) should have a 1 : 1 nurse-to-patient ratio.
intensive care nurse staffing 30 ● HDU patients (clinically determined) should have a 1 : 2 nurse-to-patient ratio.
ACCCN: Position statement on the ● All intensive care patients must have a registered nurse (division 1) allocated exclusively to their care.
healthcare workers other than ● High-dependency or step-down patients (in intensive care) who require a nurse-to-patient ratio of
Division 1 Registered Nurses in 1 : 2 should have a registered nurse (division 1) allocated exclusively to their care.
Intensive Care 35 ● Enrolled nurses (division 2) and unlicensed assistive personnel may be allocated roles to assist the
registered nurse, but any activities that involve direct contact with the patient must always be
performed in the immediate presence of the registered nurse (division 1).
NZNO, Critical Care Section: ● The critically ill and/or ventilated patient will require a minimum 1 : 1 nurse-to-patient ratio.
Philosophy and Standards for ● At times, patients in the critical care unit may have higher or lower nursing acuity; the critical care
Nursing Practice in Critical Care 32 nurse in charge of the shift determines any variation from the 1 : 1 ratio, taking into account context,
skill mix and complexity.
WFCCN: Declaration of Buenos ● Critically ill patients (clinically determined) require one registered nurse at all times.
Aires, Position Statement on the ● High-dependency patients (clinically determined) in a critical care unit require no less than one
Provision of Critical Care Nursing nurse for two patients at all times.
Workforce 36
CICM: Minimum Standards for ● A minimum of 1 : 1 nursing is required for ventilated and other similarly critically ill patients, and
Intensive Care Units 27 nursing staff must be available to greater than 1 : 1 ratio for patients requiring complex management
(e.g. ventricular assist device).
● The majority of nursing staff should have a post-registration qualification in intensive care or in the
specialty of the unit.
● All nursing staff in the unit responsible for direct patient care should be registered nurses.
CICM: Recommendations on ● The ratio of nursing staff to patients should be 1 : 2.
Standards for High-Dependency ● All nursing staff in the HDU responsible for direct patient care should be registered nurses, and the
Units Seeking Accreditation for majority of all senior nurses should have a post-registration qualification in intensive care or
Training in Intensive Care high-dependency nursing.
Medicine 37 ● A minimum of two registered nurses should be present in the unit at all times when a patient is
present.
ACCCN = Australian College of Critical Care Nurses; NZNO = New Zealand Nurses Organisation; WFCCN = World Federation of Critical Care Nurses; CICM = College of
Intensive Care Medicine.
TABLE 2.5 Ten key points of intensive care nursing staffing 30
Point Description
1. ICU patients (clinically Require a standard nurse-to-patient ratio of at least 1 : 1.
determined)
2. High dependency patients Require a standard nurse-to-patient ratio of at least 1 : 2
(clinically determined)
3. Clinical coordinator (team There must be a designated critical-care-qualified senior nurse per shift who is supernumerary and whose
leader) primary role is responsibility for the logistical management of patients, staff, service provision and resource
utilisation during a shift.
4. ACCESS nurses These are nurses in addition to the bedside nurses, clinical coordinator, unit manager, educators and
non-nursing support staff. They provide Assistance, Coordination, Contingency, Education, Supervision
and Support.
5. Nursing manager At least one designated nursing manager (NUM/CNC/NPC/CNM or equivalent) who is formally recognised as
the unit nurse leader is required per ICU.
6. Clinical nurse educator At least one designated CNE should be available in each unit. The recommended ratio is one FTE CNE for
every 50 nurses on the ICU roster.
7. Clinical nurse consultants Provide global critical care resources, education and leadership to specific units, to hospital and area-wide
services, and to the tertiary education sector.
8. Critical care nurses The ACCCN recommends an optimum specialty qualified critical care nurse proportion of 75%.
9. Resources These are allocated to support nursing time and costs associated with quality assurance activities, nursing
and multidisciplinary research, and conference attendance.
10. Support staff ICUs are provided with adequate administrative staff, ward assistants, manual handling assistance/
equipment, cleaning and other support staff to ensure that such tasks are not the responsibility of nursing
personnel.
ACCCN = Australian College of Critical Care Nurses; CNC = clinical nurse consultant; CNE = clinical nurse educator; CNM = clinical nurse manager; FTE = full-time
equivalent; NPC = nurse practice coordinator; NUM = nursing unit manager.