Page 508 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 508
Support of Renal Function 485
diabetes, advanced age, investigations requiring radio- before death in a response known as apoptosis (cell self-
21
opaque dye administration, potent and nephrotoxic drug death) (see Chapter 21). The response is aimed at organ
administration or major surgery with an inflammatory survival, with some individual cells ‘sacrificing’ them-
state due to an underlying infection. This is the context selves during a period of crisis. This protective response
of critical illness and ARF where, despite modulation of reduces oxygen demand by initiating cell death in some
the cause and support with artificial renal replacement tubules, while others differentiate and/or proliferate for
therapies, mortality ranges from 28–90% depending on repair, and allows continuation of some normal function.
diagnostic criteria or definition. 3,24,25 If the causative process abates, remaining cells regenerate
by differentiation and proliferation, tissue repair occurs
This type of kidney damage is of particular importance, with restoration of normal epithelium in some tubules
as ATN is abrupt in onset and causes a rapid cessation of and nephron function returns.
normal nephron function, a picture typical of any critical
illness and failure of other body organs. As this failure is During this period cellular ‘debris’ collects in the tubule
commonly mediated by a loss in total or regional blood loops, causing obstruction of tubular flow, with backleak
26
flow to the kidney, it is more pronounced in the kidney of filtrate occurring through the ‘patchy’ exposed tubular
medulla or outer regions sensitive to reduced blood flow. membrane surface. An inflammatory process is also
The cause of this loss in blood flow may be multifactorial stimulated due to release of cell adhesion factors and
27
but is commonly associated with shock and consequent leucocyte activation, which in turn causes further vaso-
28
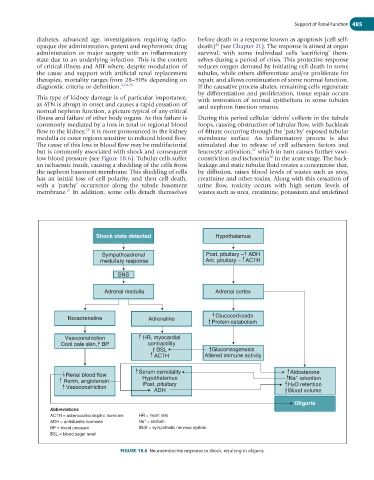
low blood pressure (see Figure 18.6). Tubular cells suffer constriction and ischaemia in the acute stage. The back-
an ischaemic insult, causing a shedding of the cells from leakage and static tubular fluid creates a concentrate that,
the nephron basement membrane. This shedding of cells by diffusion, raises blood levels of wastes such as urea,
has an initial loss of cell polarity, and then cell death, creatinine and other toxins. Along with this cessation of
with a ‘patchy’ occurrence along the tubule basement urine flow, toxicity occurs with high serum levels of
21
membrane. In addition, some cells detach themselves wastes such as urea, creatinine, potassium and undefined
Shock state detected Hypothalamus
Sympathoadrenal Post. pituitary – ADH
medullary response Ant. pituitary – ACTH
SNS
Adrenal medulla Adrenal cortex
Noradrenaline Adrenaline Glucocorticoids
Protein catabolism
Vasoconstriction HR, myocardial
Cool pale skin, BP contractility
BSL Gluconeogenesis
ACTH Altered immune activity
Serum osmolality Aldosterone
Renal blood flow +
Renin, angiotensin Hypothalamus Na retention
Post. pituitary
Vasoconstriction H2O retention
ADH Blood volume
Oliguria
Abbreviations
ACTH = adrenocorticotrophic hormone HR = heart rate
+
ADH = antidiuretic hormone Na = sodium
BP = blood pressure SNS = sympathetic nervous system.
BSL = blood sugar level
FIGURE 18.6 Neuroendocrine response to shock, resulting in oliguria.