Page 510 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 510
Support of Renal Function 487
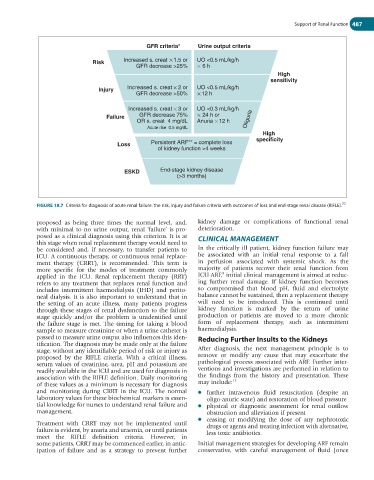
GFR criteria* Urine output criteria
Risk Increased s. creat 1.5 or UO <0.5 mL/kg/h
GFR decrease >25% 6 h
High
sensitivity
Injury Increased s. creat 2 or UO <0.5 mL/kg/h
GFR decrease >50% 12 h
Increased s. creat 3 or UO <0.3 mL/kg/h
Failure GFR decrease 75% 24 h or
OR s. creat 4 mg/dL Anuria 12 h Oliguria
Acute rise 0.5 mg/dL
High
specificity
Loss Persistent ARF** = complete loss
of kidney function >4 weeks
ESKD End-stage kidney disease
(>3 months)
32
FIGURE 18.7 Criteria for diagnosis of acute renal failure: the risk, injury and failure criteria with outcomes of loss and end-stage renal disease (RIFLE).
proposed as being three times the normal level, and, kidney damage or complications of functional renal
with minimal to no urine output, renal ‘failure’ is pro- deterioration.
posed as a clinical diagnosis using this criterion. It is at CLINICAL MANAGEMENT
this stage when renal replacement therapy would need to
be considered and, if necessary, to transfer patients to In the critically ill patient, kidney function failure may
ICU. A continuous therapy, or continuous renal replace- be associated with an initial renal response to a fall
ment therapy (CRRT), is recommended. This term is in perfusion associated with systemic shock. As the
more specific for the modes of treatment commonly majority of patients recover their renal function from
8
applied in the ICU. Renal replacement therapy (RRT) ICU ARF, initial clinical management is aimed at reduc-
refers to any treatment that replaces renal function and ing further renal damage. If kidney function becomes
includes intermittent haemodialysis (IHD) and perito- so compromised that blood pH, fluid and electrolyte
neal dialysis. It is also important to understand that in balance cannot be sustained, then a replacement therapy
the setting of an acute illness, many patients progress will need to be introduced. This is continued until
through these stages of renal dysfunction to the failure kidney function is marked by the return of urine
stage quickly and/or the problem is unidentified until production or patients are moved to a more chronic
the failure stage is met. The timing for taking a blood form of replacement therapy, such as intermittent
sample to measure creatinine or when a urine catheter is haemodialysis.
passed to measure urine output also influences this iden- Reducing Further Insults to the Kidneys
tification. The diagnosis may be made only at the failure
stage, without any identifiable period of risk or injury as After diagnosis, the next management principle is to
proposed by the RIFLE criteria. With a critical illness, remove or modify any cause that may exacerbate the
serum values of creatinine, urea, pH and potassium are pathological process associated with ARF. Further inter-
readily available in the ICU and are used for diagnosis in ventions and investigations are performed in relation to
association with the RIFLE definition. Daily monitoring the findings from the history and presentation. These
13
of these values as a minimum is necessary for diagnosis may include:
and monitoring during CRRT in the ICU. The normal ● further intravenous fluid resuscitation (despite an
laboratory values for these biochemical markers is essen- oligo-anuric state) and restoration of blood pressure
tial knowledge for nurses to understand renal failure and ● physical or diagnostic assessment for renal outflow
management. obstruction and alleviation if present
● ceasing or modifying the dose of any nephrotoxic
Treatment with CRRT may not be implemented until drugs or agents and treating infection with alternative,
failure is evident, by anuria and uraemia, or until patients less toxic antibiotics.
meet the RIFLE definition criteria. However, in
some patients, CRRT may be commenced earlier, in antic- Initial management strategies for developing ARF remain
ipation of failure and as a strategy to prevent further conservative, with careful management of fluid (once