Page 1051 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1051
934 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
in 2010; decitabine, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, was approved the marrow continues to show blasts and is cellular, a reinduction is
in 2013 for older patients with AML in Europe, but not in the United usually given. The reinduction may be an attenuated repetition of the
States). induction (“2 + 5”) or an intensification with intermediate-dose
cytarabine (IDAC) or high-dose cytarabine (HiDAC). If the day 14
Induction Therapy or 21 marrow is hypoplastic and hence appropriately chemoablated,
hematopoietic growth factors (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
[G-CSF]) are initiated and supportive care continues. Marrow studies
Patients Less Than 60 Years of Age are repeated 2 weeks later and then weekly if necessary until it becomes
clear whether the patient is going into CR or not. If in CR, postremis-
Induction therapy is still built on the same two drugs as 40 years ago: sion therapy starts shortly thereafter, whereas in case of no response
cytarabine and anthracycline. Cytarabine, an analogue of a physiologic (“primary refractory”), treatment is often changed. Remissions fol-
pyrimidine nucleoside, is an antimetabolite that requires intracellular lowing reinductions are usually shorter lasting than remission after
conversion to its triphosphate compound, ara-CTP, and incorpora- one induction cycle. The degree of neutrophil and platelet recovery
tion into DNA to become active. When given by itself at standard at the time of remission has prognostic significance. Higher neutrophil
2
doses of 100–200 mg/m intravenously (IV) daily for 5–7 days, it and platelet counts at the time of remission are predictive of better
produces CR rates of around 40%. Anthracyclines (daunorubicin, relapse-free survival. In some cases a regenerating marrow may have
idarubicin, mitoxantrone, aclarubicin) act by stabilizing the normally an increased number of blasts, which may look like persistent leuke-
occurring complex between DNA and the enzyme topoisomerase II, mia. Immunophenotyping by flow cytometry often helps to make
thereby leading to apoptotic cell death. Daunorubicin, the anthracy- that distinction. Further follow-up marrow studies will show reduc-
cline that was first available, achieves similar CR rates as does cyta- tion in blasts concomitant with a rise of neutrophils and platelets.
2
rabine alone. The combination of cytarabine 100–200 mg/m as a Many modifications to the 3 + 7 regimen have been tried over the
continuous IV infusion (its serum half-life is only 15 minutes) daily years. Giving 10 instead of 7 days of cytarabine (3 + 10), increasing
2
2
2
for 7 days and daunorubicin 45–60 mg/m IV daily for 3 days on the dose of cytarabine from 100 mg/m /day to 200 mg/m /day,
days 1–3 has become known as the “3 + 7” regimen and, for more adding a third drug (e.g., etoposide, thioguanine, topotecan, fluda-
than 40 years, has been the standard induction combination for most rabine) or modulators of drug resistance, and priming leukemic blasts
patients with AML. Remission rates range from 60% to 80%, and with hematopoietic growth factors (G-CSF and granulocyte-
long-term disease-free survival is about 35%. 9 macrophage colony stimulating factor) have not proven superior.
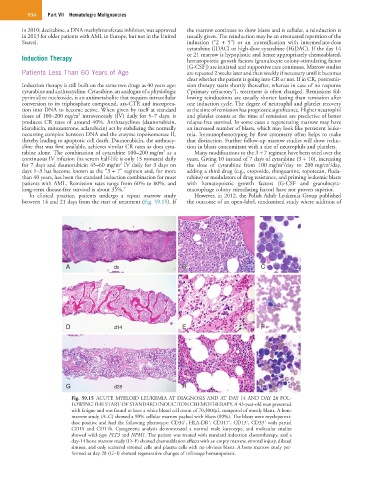
In clinical practice, patients undergo a repeat marrow study However, in 2012, the Polish Adult Leukemia Group published
between 14 and 21 days from the start of treatment (Fig. 59.15). If the outcome of an open-label, randomized study where addition of
A dx B B C
D d14 E F
G d28 H I I
Fig. 59.15 ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AT DIAGNOSIS AND AT DAY 14 AND DAY 28 FOL-
LOWING THE START OF STANDARD INDUCTION CHEMOTHERAPY. A 43-year-old man presented
with fatigue and was found to have a white blood cell count of 70,300/µL composed of mostly blasts. A bone
marrow study (A–C) showed a 90% cellular marrow packed with blasts (80%). The blasts were myeloperoxi-
+
+
+
+
+
dase positive and had the following phenotype: CD34 , HLA-DR , CD117 , CD13 , CD33 with partial
CD15 and CD11b. Cytogenetic analysis demonstrated a normal male karyotype, and molecular studies
showed wild-type FLT3 and NPM1. The patient was treated with standard induction chemotherapy, and a
day-14 bone marrow study (D–F) showed chemoablation effects with an empty marrow, stromal injury, dilated
sinuses, and only scattered stromal cells and plasma cells with no obvious blasts. A bone marrow study per-
formed at day 28 (G–I) showed regenerative changes of trilineage hematopoiesis.