Page 1049 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1049
932 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A A C D
BB E
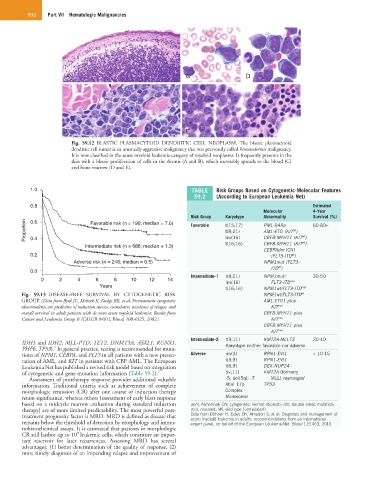
Fig. 59.12 BLASTIC PLASMACYTOID DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASM. The blastic plasmacytoid
dendritic cell tumor is an unusually aggressive malignancy that was previously called hematodermic malignancy.
It is now classified in the acute myeloid leukemia category of myeloid neoplasms. It frequently presents in the
skin with a blastic proliferation of cells in the dermis (A and B), which inevitably spreads to the blood (C)
and bone marrow (D and E).
1.0 TABLE Risk Groups Based on Cytogenetic-Molecular Features
59.2 (According to European Leukemia Net)
0.8 Estimated
Molecular 4-Year
Risk Group Karyotype Abnormality Survival (%)
Proportion 0.4 Favorable t(15;17) PML-RARa wt wt 60-80+
0.6
Favorable risk (n = 190; median = 7.6)
AML-ETO (KIT )
t(8;21)
CBFB-MYH11 (KIT )
inv(16)
wt
Intermediate risk (n = 686; median = 1.3) t(16;16) CBFB-MYH11 (KIT )
CEBPAdm (CN)
0.2 (FLT3-ITD )
wt
Adverse risk (n = 248; median = 0.5) NPM1mut (FLT3-
ITD )
wt
0.0
Intermediate-1 t(8;21) NPM1mut/ 30-50
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 inv(16) FLT3-ITD mut
Years mut
t(16;16) NPM1wt/FLT3-ITD
Fig. 59.13 DISEASE-FREE SURVIVAL BY CYTOGENETIC RISK NPM1wt/FLT3-ITD wt
GROUP. (Data from Byrd JC, Mrózek K, Dodge RK, et al: Pretreatment cytogenetic AML-ETO1 plus
abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and KIT mut
overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: Results from CBFB-MYH11 plus
Cancer and Leukemia Group B [CALGB 8461], Blood 100:4325, 2002.) KIT mut
CBFB-MYH11 plus
KIT mut
Intermediate-2 t(9;11) KMT2A-MLLT3 20-40
IDH1 and IDH2, MLL-PTD, TET2, DNMT3A, ASXL1, RUNX1, Karyotype neither favorable nor adverse
6
PHF6, TP53). In general practice, testing is recommended for muta-
tions of NPM1, CEBPA, and FLT3 in all patients with a new presen- Adverse inv(3) RPN1-EVI1 < 10-15
tation of AML, and KIT in patients with CBF AML. The European t(3;3) RPN1-EVI1
Leukemia Net has published a revised risk model based on integration t(6;9) DEK-NUP24
of cytogenetic and gene mutation information (Table 59.2). 7 t(v;11) KMT2A (formerly
Assessment of posttherapy response provides additional valuable -5; del(5q); -7 MLL) rearranged
information. Traditional criteria such as achievement of complete Abnl 17p TP53
morphologic remission (CR) after one course of induction therapy Complex
retain significance, whereas others (assessment of early blast response Monosomal
based on a midcycle marrow evaluation during standard induction abnl, Abnormal; CN, cytogenetic normal (diploid); dm, double allelic mutation;
therapy) are of more limited predictability. The most powerful post- mut, mutated; Wt, wild type (unmutated).
treatment prognostic factor is MRD. MRD is defined as disease that Data from Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al: Diagnosis and management of
acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international
remains below the threshold of detection by morphology and immu- expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 115:453, 2010.
nohistochemical assays. It is estimated that patients in morphologic
9
CR still harbor up to 10 leukemic cells, which constitute an impor-
tant reservoir for later recurrences. Assessing MRD has several
advantages: (1) better determination of the quality of response, (2)
more timely diagnosis of an impending relapse and improvement of