Page 1194 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1194
1042 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
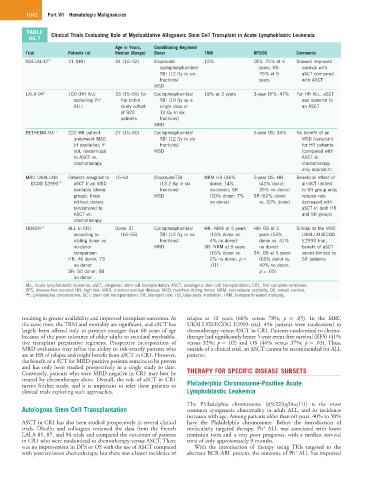
TABLE Clinical Trials Evaluating Role of Myeloablative Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
66.7
Age in Years, Conditioning Regimen/
Trial Patients (n) Median (Range) Donor TRM DFS/OS Comments
GOELAL02 13 41 (HR) 34 (15–52) Etoposide/ 15% DFS: 75% at 6 Showed improved
cyclophosphamide/ years; OS: survival with
TBI (12 Gy in six 75% at 6 aSCT compared
fractions) years with ASCT
MSD
LALA 94 6 100 (HR ALL 33 (15–55) for Cyclophosphamide/ 18% at 3 years 3-year DFS: 47% For HR ALL, aSCT
excluding Ph + the entire TBI (10 Gy as a was superior to
ALL) study cohort single dose or an ASCT
of 922 12 Gy in six
patients fractions)
MRD
PETHEMA-93 11 222 HR patient 27 (15–50) Cyclophosphamide/ 5-year OS: 35% No benefit of an
underwent MSD TBI (12 Gy in six MSD transplant
(if available); if fractions) for HR patients
not, randomized MSD (compared with
to ASCT vs. ASCT or
chemotherapy chemotherapy
only approach)
MRC UKALLXII/ Patients assigned to 15–64 Etoposide/TBI NRM HR (36% 5-year OS: HR Beneficial effect of
ECOG E2993 10 aSCT if an MSD (13.2 Gy in six donor; 14% (41% donor, all-SCT limited
available (donor fractions) no-donor); SR 35% no donor) to SR group only;
group); those MSD (20% donor; 7% SR (62% donor relapse rate
without donors no donor) vs. 52% donor) decreased with
randomized to aSCT in both HR
ASCT vs. and SR groups
chemotherapy
HOVON 14 ALL in CR1 Donor 31 Cyclophosphamide/ HR: NRM at 5 years HR: OS at 5 Similar to the MRC
according to (16–55) TBI (12 Gy in six (15% donor vs. years (53% UKALLXII/ECOG
sibling donor vs. fractions) 4% no-donor) donor vs. 41% E2993 trial,
no-donor MRD SR: NRM at 5 years no donor) benefit of aSCT
comparison (16% donor vs. SR: OS at 5 years seems limited to
HR: 46 donor; 73 2% no-donor, p = (69% donor vs. SR patients
no donor .01) 49% no donor,
SR: 50 donor; 88 p = .05)
no donor
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; aSCT, allogeneic stem cell transplantation; ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CR1, first complete remission;
DFS, disease-free survival; HR, high risk; MRD, minimal residual disease; MSD, matched sibling donor; NRM, non-relapse mortality; OS, overall survival;
Ph, philadelphia chromosome; SCT, stem cell transplantation; SR, standard risk; TBI, total-body irradiation; TRM, transplant-related mortality.
resulting in greater availability and improved transplant outcomes. At relapse at 10 years (66% versus 78%; p = .05). In the MRC
the same time, the TRM and mortality are significant, and aSCT has UKALLXII/ECOG E2993 trial, 456 patients were randomized to
largely been offered only to patients younger than 60 years of age chemotherapy versus ASCT in CR1. Patients randomized to chemo-
because of the poor tolerance of older adults to standard myeloabla- therapy had significantly better 5-year event-free survival (EFS) (41%
tive transplant preparative regimens. Prospective incorporation of versus 32%; p = .02) and OS (46% versus 37%; p = .03). Thus,
MRD evaluation may refine the ability to risk-stratify patients who outside of a clinical trial, an ASCT cannot be recommended for ALL
are at HR of relapse and might benefit from aSCT in CR1. However, patients.
the benefit of a SCT for MRD-positive patients remains to be proven
and has only been studied prospectively in a single study to date.
Conversely, patients who were MRD negative in CR1 may best be THERAPY FOR SPECIFIC DISEASE SUBSETS
treated by chemotherapy alone. Overall, the role of aSCT in CR1
merits further study, and it is important to refer these patients to Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute
clinical trials exploring such approaches. Lymphoblastic Leukemia
The Philadelphia chromosome [t(9;22)(q34;q11)] is the most
Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation common cytogenetic abnormality in adult ALL, and its incidence
increases with age. Among patients older than 60 years, 40% to 50%
ASCT in CR1 has also been studied prospectively in several clinical have the Philadelphia chromosome. Before the introduction of
+
trials. Dhedin and colleagues reviewed the data from the French molecularly targeted therapy, Ph ALL was associated with lower
LALA 85, 87, and 94 trials and compared the outcomes of patients remission rates and a very poor prognosis, with a median survival
in CR1 who were randomized to chemotherapy versus ASCT. There time of only approximately 9 months.
was no improvement in DFS or OS with the use of ASCT compared With the introduction of therapy using TKIs targeted to the
+
with postremission chemotherapy, but there was a lower incidence of aberrant BCR-ABL protein, the outcome of Ph ALL has improved