Page 1195 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1195
Chapter 66 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults 1043
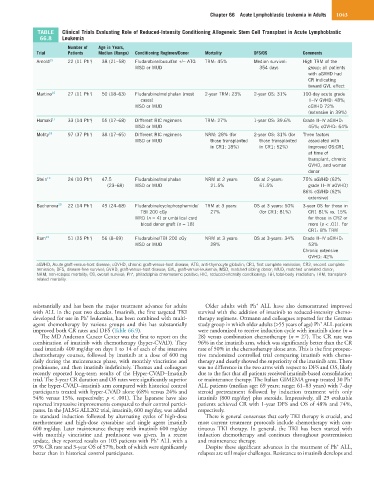
TABLE Clinical Trials Evaluating Role of Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant in Acute Lymphoblastic
66.8 Leukemia
Number of Age in Years,
Trial Patients Median (Range) Conditioning Regimen/Donor Mortality DFS/OS Comments
+
Arnold 15 22 (11 Ph ) 38 (21–58) Fludarabine/busulfan +/− ATG TRM: 45% Median survival: High TRM of the
MSD or MUD 354 days group; all patients
with aGVHD had
CR indicating
toward GVL effect
+
Martino 16 27 (11 Ph ) 50 (18–63) Fludarabine/melphalan (most 2-year TRM: 23% 2-year OS: 31% 100-day acute grade
cases) II–IV GVHD: 48%;
MSD or MUD cGVHD 72%
(extensive in 39%)
+
Hamaki 17 33 (14 Ph ) 55 (17–68) Different RIC regimens TRM: 27% 1-year OS: 39.6% Grade II–IV aGVHD:
MSD or MUD 45%; cGVHD: 64%
+
Mohty 18 97 (37 Ph ) 38 (17–65) Different RIC regimens NRM: 28% (for 2-year OS: 31% (for Three factors
MSD or MUD those transplanted those transplanted associated with
in CR1: 18%) in CR1: 52%) improved OS:CR1
at time of
transplant, chronic
GVHD, and woman
donor
+
Stein 19 24 (10 Ph ) 47.5 Fludarabine/melphalan NRM at 2 years: OS at 2-years: 75% aGVHD (62%
(23–68) MSD or MUD 21.5% 61.5% grade II–IV aGVHD)
86% cGVHD (62%
extensive)
+
Bachanova 20 22 (14 Ph ) 49 (24–68) Fludarabine/cyclophosphamide/ TRM at 3 years: OS at 3 years: 50% 3-year OS for those in
TBI 200 cGy 27% (for CR1: 81%) CR1 81% vs. 15%
MRD (n = 4) or umbilical cord for those in CR2 or
blood donor graft (n = 18) more (p < .01). For
CR1: 8% TRM
+
Ram 21 51 (25 Ph ) 56 (8–69) Fludarabine/TBI 200 cGy NRM at 3 years: OS at 3-years: 34% Grade II–IV aGVHD:
MSD or MUD 28% 53%
Chronic extensive
GVHD: 42%
aGVHD, Acute graft-versus-host disease; cGVHD, chronic graft-versus-host disease; ATG, anti-thymocyte globulin; CR1, first complete remission; CR2, second complete
remission; DFS, disease-free survival; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; GVL, graft-versus-leukemia; MSD, matched sibling donor; MUD, matched unrelated donor;
+
NRM, non-relapse mortality; OS, overall survival; Ph , philadelphia chromosome positive; RIC, reduced-intensity conditioning; TBI, total-body irradiation; TRM, transplant-
related mortality.
+
substantially and has been the major treatment advance for adults Older adults with Ph ALL have also demonstrated improved
with ALL in the past two decades. Imatinib, the first targeted TKI survival with the addition of imatinib to reduced-intensity chemo-
+
developed for use in Ph leukemias, has been combined with multi- therapy regimens. Ottmann and colleagues reported for the German
+
agent chemotherapy by various groups and this has substantially study group in which older adults (>55 years of age) Ph ALL patients
improved both CR rates and DFS (Table 66.9). were randomized to receive induction cycle with imatinib alone (n =
The MD Anderson Cancer Center was the first to report on the 28) versus combination chemotherapy (n = 27). The CR rate was
combination of imatinib with chemotherapy (hyper-CVAD). They 96% in the imatinib arm, which was significantly better than the CR
used imatinib 400 mg/day on days 1 to 14 of each of the intensive rate of 50% in the chemotherapy alone arm. This is the first prospec-
chemotherapy courses, followed by imatinib at a dose of 600 mg tive randomized controlled trial comparing imatinib with chemo-
daily during the maintenance phase, with monthly vincristine and therapy and clearly showed the superiority of the imatinib arm. There
prednisone, and then imatinib indefinitely. Thomas and colleagues was no difference in the two arms with respect to DFS and OS, likely
recently reported long-term results of the Hyper-CVAD–Imatinib due to the fact that all patients received imatinib-based consolidation
+
trial. The 3-year CR duration and OS rates were significantly superior or maintenance therapy. The Italian GIMEMA group treated 30 Ph
in the hyper-CVAD–imatinib arm compared with historical control ALL patients (median age: 69 years; range: 61–83 years) with 7-day
participants treated with hyper-CVAD alone (68% versus 24% and steroid pretreatment followed by induction treatment with only
54% versus 15%, respectively; p < .001). The Japanese have also imatinib (800 mg/day) plus steroids. Impressively, all 29 evaluable
reported impressive improvements compared to their control partici- patients achieved CR with 1-year DFS and OS of 48% and 74%,
pants. In the JALSG ALL202 trial, imatinib, 600 mg/day, was added respectively.
to standard induction followed by alternating cycles of high-dose There is general consensus that early TKI therapy is crucial, and
methotrexate and high-dose cytarabine and single agent imatinib most current treatment protocols include chemotherapy with con-
600 mg/day. Later maintenance therapy with imatinib 600 mg/day tinuous TKI therapy. In general, the TKI has been started with
with monthly vincristine and prednisone was given. In a recent induction chemotherapy and continues throughout postremission
+
update, they reported results on 103 patients with Ph ALL with a and maintenance therapy.
+
97% CR rate and 3-year OS of 57%, both of which were significantly Despite these significant advances in the treatment of Ph ALL,
better than in historical control participants. relapses are still major challenges. Resistance to imatinib develops and