Page 1197 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1197
Chapter 66 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults 1045
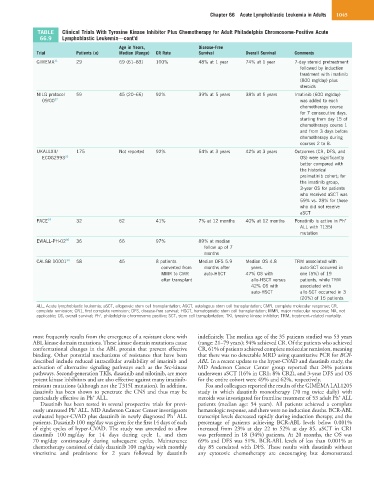
TABLE Clinical Trials With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Plus Chemotherapy for Adult Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute
66.9 Lymphoblastic Leukemia—cont’d
Age in Years, Disease-Free
Trial Patients (n) Median (Range) CR Rate Survival Overall Survival Comments
GIMEMA 31 29 69 (61–83) 100% 48% at 1 year 74% at 1 year 7-day steroid pretreatment
followed by induction
treatment with imatinib
(800 mg/day) plus
steroids
NILG protocol 59 45 (20–66) 92% 39% at 5 years 38% at 5 years Imatinib (600 mg/day)
09/00 32 was added to each
chemotherapy course
for 7 consecutive days,
starting from day 15 of
chemotherapy course 1
and from 3 days before
chemotherapy during
courses 2 to 8.
UKALLXII/ 175 Not reported 92% 54% at 3 years 42% at 3 years Outcomes (CR, DFS, and
ECOG2993 33 OS) were significantly
better compared with
the historical
preimatinib cohort; for
the imatinib group,
3-year OS for patients
who received aSCT was
59% vs. 28% for those
who did not receive
aSCT
+
PACE 34 32 62 41% 7% at 12 months 40% at 12 months Ponatinib is active in Ph
ALL with T135I
mutation
EWALL-PH-02 35 36 66 97% 89% at median
follow up of 7
months
CALGB 10001 36 58 45 8 patients Median DFS 5.9 Median OS 4.8 TRM associated with
converted from months after years. auto-SCT occurred in
MMR to CMR auto-HSCT 47% OS with one (5%) of 19
after transplant allo-HSCT versus patients, while TRM
42% OS with associated with
auto-HSCT allo-SCT occurred in 3
(20%) of 15 patients
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; aSCT, allogeneic stem cell transplantation; ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; CMR, complete molecular response; CR,
complete remission; CR1, first complete remission; DFS, disease-free survival; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; MMR, major molecular response; NA, not
+
applicable; OS, overall survival; Ph , philadelphia chromosome positive; SCT, stem cell transplantation; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; TRM, treatment–related mortality.
most frequently results from the emergence of a resistant clone with indefinitely. The median age of the 35 patients studied was 53 years
ABL kinase domain mutations. These kinase domain mutations cause (range: 21–79 years); 94% achieved CR. Of the patients who achieved
conformational changes in the ABL protein that prevent effective CR, 61% of patients achieved complete molecular remission, meaning
binding. Other potential mechanisms of resistance that have been that there was no detectable MRD using quantitative PCR for BCR-
described include reduced intracellular availability of imatinib and ABL. In a recent update to the hyper-CVAD and dasatinib study, the
activation of alternative signaling pathways such as the Src-kinase MD Anderson Cancer Center group reported that 24% patients
pathways. Second-generation TKIs, dasatinib and nilotinib, are more underwent aSCT (16% in CR1; 8% CR2), and 3-year DFS and OS
potent kinase inhibitors and are also effective against many imatinib- for the entire cohort were 49% and 62%, respectively.
resistant mutations (although not the T315I mutation). In addition, Foa and colleagues reported the results of the GIMEMA LAL1205
dasatinib has been shown to penetrate the CNS and thus may be study in which dasatinib monotherapy (70 mg twice daily) with
+
+
particularly effective in Ph ALL. steroids was investigated for frontline treatment of 53 adult Ph ALL
Dasatinib has been tested in several prospective trials for previ- patients (median age: 54 years). All patients achieved a complete
+
ously untreated Ph ALL. MD Anderson Cancer Center investigators hematologic response, and there were no induction deaths. BCR-ABL
+
evaluated hyper-CVAD plus dasatinib in newly diagnosed Ph ALL transcript levels decreased rapidly during induction therapy, and the
patients. Dasatinib 100 mg/day was given for the first 14 days of each percentage of patients achieving BCR-ABL levels below 0.001%
of eight cycles of hyper-CVAD. The study was amended to allow increased from 23% at day 22 to 52% at day 85. aSCT in CR1
dasatinib 100 mg/day for 14 days during cycle 1, and then was performed in 18 (34%) patients. At 20 months, the OS was
70 mg/day continuously during subsequent cycles. Maintenance 69% and DFS was 51%. BCR-ABL levels of less than 0.001% at
chemotherapy consisted of daily dasatinib 100 mg/day with monthly day 85 correlated with DFS. These results with dasatinib without
vincristine and prednisone for 2 years followed by dasatinib any cytotoxic chemotherapy are encouraging but demonstrated