Page 1249 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1249
Chapter 68 The Polycythemias 1095
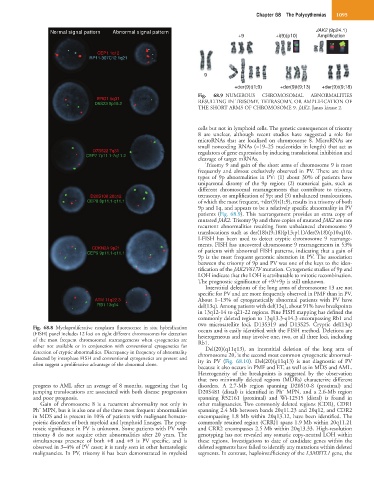
Normal signal pattern Abnormal signal pattern JAK2 (9p24.1)
+9 +i(9)(p10) Amplification
CEP1 1q12
RP11-307C12 1q21
9
+der(9)t(1;9) +der(9)t(9;13) +der(9)t(9;18)
Fig. 68.9 NUMEROUS CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES
ERG1 5q31
D5S23 5p15.2 RESULTING IN TRISOMY, TETRASOMY, OR AMPLIFICATION OF
THE SHORT ARMS OF CHROMOSOME 9. JAK2, Janus kinase 2.
cells but not in lymphoid cells. The genetic consequences of trisomy
8 are unclear, although recent studies have suggested a role for
microRNAs that are localized on chromosome 8. MicroRNAs are
small noncoding RNAs (≈19–25 nucleotides in length) that act as
D7S522 7q31 regulators of gene expression by inducing translational inhibition and
CEP7 7p11.1-7q11.2
cleavage of target mRNAs.
Trisomy 9 and gain of the short arms of chromosome 9 is most
frequently and almost exclusively observed in PV. There are three
types of 9p abnormalities in PV: (1) about 30% of patients have
uniparental disomy of the 9p region; (2) numerical gain, such as
different chromosomal rearrangements that contribute to trisomy,
D20S108 20q12 tetrasomy, or amplification of 9p; and (3) unbalanced translocations,
CEP8 8p11.1-q11.1 of which the most frequent, +der(9)t(1;9), results in a trisomy of both
9p and 1q, and appears to be a relatively specific abnormality in PV
patients (Fig. 68.9). This rearrangement provides an extra copy of
mutated JAK2. Trisomy 9p and three copies of mutated JAK2 are rare
recurrent abnormalities resulting from unbalanced chromosome 9
translocations such as der(18)t(9;18)(p13;p11)/der(9;18)(p10;q10).
I-FISH has been used to detect cryptic chromosome 9 rearrange-
ments. FISH has uncovered chromosome 9 rearrangements in 53%
CDKN2A 9p21
CEP9 9p11.1-q11.1 of patients with abnormal FISH patterns, indicating that a gain of
9p is the most frequent genomic alteration in PV. The association
between the trisomy of 9p and PV was one of the keys to the iden-
tification of the JAK2V617F mutation. Cytogenetic studies of 9p and
LOH indicate that the LOH is attributable to mitotic recombination.
The prognostic significance of +9/+9p is still unknown.
Interstitial deletions of the long arms of chromosome 13 are not
specific for PV and are more frequently observed in PMF than in PV.
ATM 11q22.3 About 1–13% of cytogenetically abnormal patients with PV have
RB1 13q14 del(13q). Among patients with del(13q), about 91% have breakpoints
in 13q12-14 to q21-22 regions. Fine FISH mapping has defined the
commonly deleted region to 13q13.3-q14.3 encompassing Rb1 and
two microsatellite loci, D13S319 and D13S25. Cryptic del(13q)
Fig. 68.8 Myeloproliferative neoplasm fluorescence in situ hybridization occurs and is easily identified with the FISH method. Deletions are
(FISH) panel includes 12 loci on eight different chromosomes for detection heterogeneous and may involve one, two, or all three loci, including
of the most frequent chromosomal rearrangements when cytogenetics are Rb1.
either not available or in conjunction with conventional cytogenetics for Del(20)(q11q13), an interstitial deletion of the long arm of
detection of cryptic abnormalities. Discrepancy in frequency of abnormality chromosome 20, is the second most common cytogenetic abnormal-
detected by interphase FISH and conventional cytogenetics are present and ity in PV (Fig. 68.10). Del(20)(q11q13) is not diagnostic of PV
often suggest a proliferative advantage of the abnormal clone.
because it also occurs in PMF and ET, as well as in MDS and AML.
Heterogeneity of the breakpoints is suggested by the observation
that two minimally deleted regions (MDRs) characterize different
progress to AML after an average of 8 months, suggesting that 1q disorders. A 2.7-Mb region spanning D20S10-8 (proximal) and
−
jumping translocations are associated with both disease progression D20S481 (distal) is identified in Ph MPN, and a 2.6-Mb region
and poor prognosis. spanning R52161 (proximal) and Wi-12515 (distal) is found in
Gain of chromosome 8 is a recurrent abnormality not only in other malignancies. Two commonly deleted regions (CDR), CDR1
−
Ph MPN, but it is also one of the three most frequent abnormalities spanning 2.4 Mb between bands 20q11.23 and 20q12, and CDR2
in MDS and is present in 10% of patients with malignant hemato- encompassing 1.8 Mb within 20q13.12, have been identified. The
poietic disorders of both myeloid and lymphoid lineages. The prog- commonly retained region (CRR)1 spans 1.9 Mb within 20q11.21
nostic significance in PV is unknown. Some patients with PV with and CRR2 encompasses 2.5 Mb within 20q13.33. High-resolution
trisomy 8 do not acquire other abnormalities after 20 years. The genotyping has not revealed any somatic copy-neutral LOH within
simultaneous presence of both +8 and +9 is PV specific, and is these regions. Investigations to date of candidate genes within the
observed in 3–4% of PV cases; it is rarely seen in other hematologic deleted segments have failed to identify any mutations within deleted
malignancies. In PV, trisomy 8 has been demonstrated in myeloid segments. In contrast, haploinsufficiency of the L3MBTL1 gene, the