Page 1284 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1284
1130 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
Hematopoietic MPN initiation MPN diagnosis Chronic MPN
stem cells
Unknown driver No observed mutations
20/197(10%)
CALR CALR only
22/197(11%)
JAK2 V617F JAK2 only
84/197(43%)
CALR with additional
CALR mutations
7/197(4%)
Mutations in other
Fertile ground genes, e.g., TET2, DNMT3A
EZH2 or ASXL1
Unknown driver JAK2/CALR negative
with other mutations
13/197(7%)
Early mutations:
e.g., TET2, DNMT3A
JAK2 V617F Increasing risk JAK2 with
additional mutations
37197(19%)
e.g., ASXL1, EZH2
CBL or TP53 etc
High-risk MPN
Leukemogenic
hits, e.g., TP53 Several non-driver
mutations
14/197(7%)
e.g., TP53 LOH
or additional hits
Transformation
to AML
JAK2 V617F- JAK2 V617F-positive
negative AML AML with late hits
JAK2 V617F-
positive AML
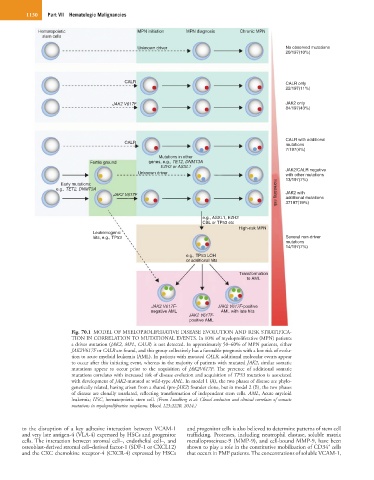
Fig. 70.1 MODEL OF MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE EVOLUTION AND RISK STRATIFICA-
TION IN CORRELATION TO MUTATIONAL EVENTS. In 10% of myeloproliferative (MPN) patients
a driver mutation (JAK2, MPL, CALR) is not detected. In approximately 50–60% of MPN patients, either
JAK2V617F or CALR are found, and this group collectively has a favorable prognosis with a low risk of evolu-
tion to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In patients with mutated CALR, additional molecular events appear
to occur after this initiating event, whereas in the majority of patients with mutated JAK2, similar somatic
mutations appear to occur prior to the acquisition of JAK2V617F. The presence of additional somatic
mutations correlates with increased risk of disease evolution and acquisition of TP53 mutation is associated
with development of JAK2-mutated or wild-type AML. In model 1 (A), the two phases of disease are phylo-
genetically related, having arisen from a shared (pre-JAK2) founder clone, but in model 2 (B), the two phases
of disease are clonally unrelated, reflecting transformation of independent stem cells. AML, Acute myeloid
leukemia; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell. (From Lundberg et al: Clonal evolution and clinical correlates of somatic
mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 123:2220, 2014.)
to the disruption of a key adhesive interaction between VCAM-1 and progenitor cells is also believed to determine patterns of stem cell
and very late antigen-4 (VLA-4) expressed by HSCs and progenitor trafficking. Proteases, including neutrophil elastase, soluble matrix
cells. The interaction between stromal cell–, endothelial cell–, and metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and cell-bound MMP-9, have been
+
osteoblast-derived stromal cell–derived factor-1 (SDF-1 or CXCL12) shown to play a role in the constitutive mobilization of CD34 cells
and the CXC chemokine receptor-4 (CXCR-4) expressed by HSCs that occurs in PMF patients. The concentrations of soluble VCAM-1,