Page 1289 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1289
Chapter 70 Primary Myelofibrosis 1135
A B
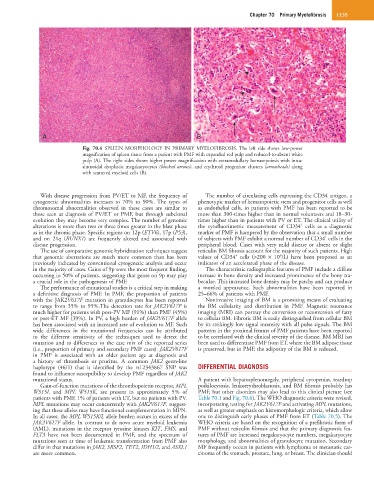
Fig. 70.4 SPLEEN MORPHOLOGY IN PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. The left side shows low-power
magnification of spleen tissue from a patient with PMF with expanded red pulp and reduced-to-absent white
pulp (A). The right sides shows higher power magnification with extramedullary hematopoiesis with intra-
sinusoidal dysplastic megakaryocytes (blocked arrows), and erythroid progenitor clusters (arrowheads) along
with scattered myeloid cells (B).
With disease progression from PV/ET to MF, the frequency of The number of circulating cells expressing the CD34 antigen, a
cytogenetic abnormalities increases to 70% to 90%. The types of phenotypic marker of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells as well
chromosomal abnormalities observed in these cases are similar to as endothelial cells, in patients with PMF has been reported to be
those seen at diagnosis of PV/ET or PMF, but through subclonal more than 300-times higher than in normal volunteers and 18–30-
evolution they may become very complex. The number of genomic times higher than in patients with PV or ET. The clinical utility of
+
alterations is more than two or three times greater in the blast phase the cytofluorimetric measurement of CD34 cells as a diagnostic
as in the chronic phase. Specific regions on 12p (ETV6), 17p (P53), marker of PMF is hampered by the observation that a small number
+
and on 21q (RUNX1) are frequently altered and associated with of subjects with PMF exhibit a normal number of CD34 cells in the
disease progression. peripheral blood. Cases with very mild disease or absent or slight
The use of comparative genomic hybridization techniques suggest reticulin BM fibrosis account for the majority of such patients. High
+
6
that genomic aberrations are much more common than has been values of CD34 cells (>200 × 10 /L) have been proposed as an
previously indicated by conventional cytogenetic analysis and occur indicator of an accelerated phase of the disease.
in the majority of cases. Gains of 9p were the most frequent finding, The characteristic radiographic features of PMF include a diffuse
occurring in 50% of patients, suggesting that genes on 9p may play increase in bone density and increased prominence of the bony tra-
a crucial role in the pathogenesis of PMF. beculae. This increased bone density may be patchy and can produce
The performance of mutational studies is a critical step in making a mottled appearance. Such abnormalities have been reported in
a definitive diagnosis of PMF. In PMF, the proportion of patients 25–66% of patients with PMF.
with the JAK2V617F mutation in granulocytes has been reported Noninvasive imaging of BM is a promising means of evaluating
to range from 35% to 95%.The detection rate for JAK2V617F is the BM cellularity and distribution in PMF. Magnetic resonance
much higher for patients with post-PV MF (91%) than PMF (45%) imaging (MRI) can portray the conversion or reconversion of fatty
or post-ET MF (39%). In PV, a high burden of JAK2V617F allele to cellular BM. Fibrotic BM is easily distinguished from cellular BM
has been associated with an increased rate of evolution to MF. Such by its strikingly low signal intensity with all pulse signals. The BM
wide differences in the mutational frequencies can be attributed patterns in the proximal femurs of PMF patients have been reported
to the different sensitivity of the techniques used to detect the to be correlated with the clinical severity of the disease. BM MRI has
mutation and to differences in the case mix of the reported series been used to differentiate PMF from ET, where the BM adipose tissue
(i.e., proportion of primary and secondary PMF cases). JAK2V617F is preserved, but in PMF, the adiposity of the BM is reduced.
in PMF is associated with an older patient age at diagnosis and
a history of thrombosis or pruritus. A common JAK2 germ-line
haplotype (46/1) that is identified by the rs12343867 SNP was DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
found to influence susceptibility to develop PMF regardless of JAK2
mutational status. A patient with hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral cytopenias, teardrop
Gain-of-function mutations of the thrombopoietin receptor, MPL poikilocytosis, leukoerythroblastosis, and BM fibrosis probably has
W515L and MPL W515K, are present in approximately 5% of PMF, but other disorders may also lead to this clinical picture (see
patients with PMF, 1% of patients with ET, but no patients with PV. Table 70.1 and Fig. 70.6). The WHO diagnostic criteria were revised,
MPL mutations may occur concurrently with JAK2V617F, suggest- incorporating testing for JAK2V617F and activating MPL mutations,
ing that these alleles may have functional complementation in MPN. as well as greater emphasis on histomorphologic criteria, which allow
In all cases, the MPL W515K/L allele burden occurs in excess of the one to distinguish early phases of PMF from ET (Table 70.5). The
JAK2V617F allele. In contrast to de novo acute myeloid leukemia WHO criteria are based on the recognition of a prefibrotic form of
(AML), mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinases KIT, FMS, and PMF without reticulin fibrosis and that the primary diagnostic fea-
FLT3 have not been documented in PMF, and the spectrum of tures of PMF are increased megakaryocyte numbers, megakaryocyte
mutations seen at time of leukemic transformation from PMF also morphology, and abnormalities of granulocyte mutation. Secondary
differ in that mutations in JAK2, SRSF2, TET2, IDH1/2, and ASXL1 MF frequently occurs in patients with lymphoma or metastatic car-
are more common. cinoma of the stomach, prostate, lung, or breast. The clinician should