Page 1287 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1287
Chapter 70 Primary Myelofibrosis 1133
A B C D E
H
F G I J
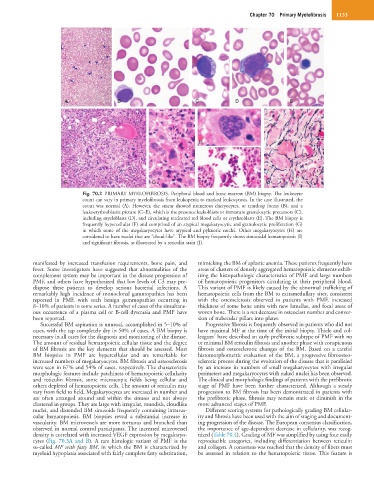
Fig. 70.2 PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. Peripheral blood and bone marrow (BM) biopsy. The leukocyte
count can vary in primary myelofibrosis from leukopenia to marked leukocytosis. In the case illustrated, the
count was normal (A). However, the smear showed numerous dacryocytes, or teardrop forms (B), and a
leukoerythroblastic picture (C–E), which is the presence leukoblasts or immature granulocytic precursors (C),
including myeloblasts (D), and circulating nucleated red blood cells or erythroblasts (E). The BM biopsy is
frequently hypercellular (F) and comprised of an atypical megakaryocytic and granulocytic proliferation (G)
in which some of the megakaryocytes have atypical and pyknotic nuclei. Other megakaryocytes (H) are
considered to have nuclei that are “cloud-like”. The BM biopsy frequently shows sinusoidal hematopoiesis (I)
and significant fibrosis, as illustrated by a reticulin stain (J).
manifested by increased transfusion requirements, bone pain, and mimicking the BM of aplastic anemia. These patients frequently have
fever. Some investigators have suggested that abnormalities of the areas of clusters of densely aggregated hematopoietic elements exhib-
complement system may be important in the disease progression of iting the histopathologic characteristics of PMF and large numbers
PMF, and others have hypothesized that low levels of C3 may pre- of hematopoietic progenitors circulating in their peripheral blood.
dispose these patients to develop serious bacterial infections. A This variant of PMF is likely caused by the abnormal trafficking of
remarkably high incidence of monoclonal gammopathies has been hematopoietic cells from the BM to extramedullary sites, consistent
reported in PMF, with such benign gammopathies occurring in with the osteosclerosis observed in patients with PMF, increased
8–10% of patients in some series. A number of cases of the simultane- thickness of some bone units with new lamellae, and focal areas of
ous occurrence of a plasma cell or B-cell dyscrasia and PMF have woven bone. There is a net decrease in osteoclast number and conver-
been reported. sion of trabecular pillars into plates.
Successful BM aspiration is unusual, accomplished in 5–10% of Progressive fibrosis is frequently observed in patients who did not
cases, with the tap completely dry in 50% of cases. A BM biopsy is have maximal MF at the time of the initial biopsy. Thiele and col-
7
necessary in all cases for the diagnosis and monitoring of the disease. leagues have described an early prefibrotic subtype of PMF with no
The amount of residual hematopoietic cellular tissue and the degree or minimal BM reticulin fibrosis and another phase with conspicuous
of BM fibrosis are the key elements that should be assessed. Most fibrosis and osteosclerotic changes of the BM. Based on a careful
BM biopsies in PMF are hypercellular and are remarkable for histomorphometric evaluation of the BM, a progressive fibroosteo-
increased numbers of megakaryocytes. BM fibrosis and osteosclerosis sclerotic process during the evolution of the disease that is paralleled
were seen in 67% and 54% of cases, respectively. The characteristic by an increase in numbers of small megakaryocytes with irregular
morphologic features include patchiness of hematopoietic cellularity perimeters and megakaryocytes with naked nuclei has been observed.
and reticulin fibrosis, some microscopic fields being cellular and The clinical and morphologic findings of patients with the prefibrotic
others depleted of hematopoietic cells. The amount of reticulin may stage of PMF have been further characterized. Although a steady
vary from field to field. Megakaryocytes are increased in number and progression to BM fibrosis has been demonstrated in patients with
are often arranged around and within the sinuses and not always the prefibrotic phase, fibrosis may remain static or diminish in the
clustered in groups. They are large with irregular, roundish, cloudlike more advanced stages of PMF.
nuclei, and distended BM sinusoids frequently containing intravas- Different scoring systems for pathologically grading BM cellular-
cular hematopoiesis. BM biopsies reveal a substantial increase in ity and fibrosis have been used with the aim of staging and document-
vascularity. BM microvessels are more tortuous and branched than ing progression of the disease. The European consensus classification,
observed in normal control participants. The increased microvessel the importance of age-dependent decrease in cellularity, was recog-
density is correlated with increased VEGF expression by megakaryo- nized (Table 70.4). Grading of MF was simplified by using four easily
cytes (Fig. 70.3A and B). A rare histologic variant of PMF is the reproducible categories, including differentiation between reticulin
so-called MF with fatty BM, in which the BM is characterized by and collagen. A consensus was reached that the density of fibers must
myeloid hypoplasia associated with fairly complete fatty substitution, be assessed in relation to the hematopoietic tissue. This feature is