Page 1288 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1288
1134 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A B
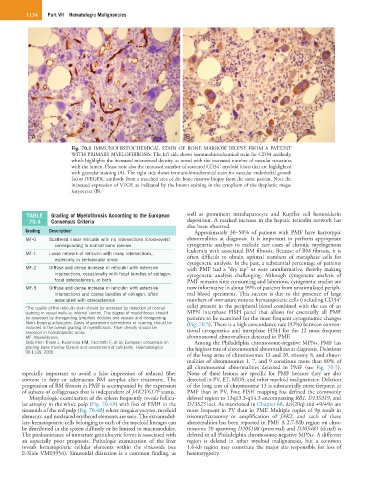
Fig. 70.3 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STAIN OF BONE MARROW BIOPSY FROM A PATIENT
WITH PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. The left side shows immunohistochemical stain for CD34 antibody,
which highlights the increased microvessel density, as noted with the increased number of vascular structures
+
with the lumen. Please note also the increased number of scattered CD34 myeloid blasts that are highlighted
with granular staining (A). The right side shows immunohistochemical stain for vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF)C antibody from a matched area of the bone marrow biopsy from the same patient. Note the
increased expression of VEGF, as indicated by the brown staining in the cytoplasm of the dysplastic mega-
karyocytes (B).
TABLE Grading of Myelofibrosis According to the European well as prominent intrahepatocyte and Kupffer cell hemosiderin
70.4 Consensus Criteria deposition. A marked increase in the hepatic reticulin network has
also been observed.
Grading Description a Approximately 30–50% of patients with PMF have karyotypic
MF-0 Scattered linear reticulin with no intersections (cross-overs) abnormalities at diagnosis. It is important to perform appropriate
corresponding to normal bone marrow cytogenetic analyses to exclude rare cases of chronic myelogenous
leukemia with associated BM fibrosis. Because of BM fibrosis, it is
MF-1 Loose network of reticulin with many intersections, often difficult to obtain optimal numbers of metaphase cells for
especially in perivascular areas
cytogenetic analysis. In the past, a substantial percentage of patients
MF-2 Diffuse and dense increase in reticulin with extensive with PMF had a “dry tap” or were uninformative, thereby making
intersections, occasionally with focal bundles of collagen, cytogenetic analysis challenging. Although cytogenetic analysis of
focal osteosclerosis, or both PMF remains time consuming and laborious, cytogenetic studies are
MF-3 Diffuse and dense increase in reticulin with extensive now informative in about 99% of patients from unstimulated periph-
intersections and coarse bundles of collagen, often eral blood specimens. This success is due to the presence of large
+
associated with osteosclerosis numbers of immature mitotic hematopoietic cells (including CD34
a The quality of the reticulin stain should be assessed by detection of normal cells) present in the peripheral blood combined with the use of an
staining in vessel walls as internal control. The degree of myelofibrosis should MPN interphase FISH panel that allows for essentially all PMF
be assessed by disregarding lymphoid nodules and vessels and disregarding patients to be examined for the most frequent cytogenomic changes
fibers framing adipocytes. Areas of prominent scleredema or scarring should be (Fig. 70.5). There is a high concordance rate (92%) between conven-
included in the overall grading of myelofibrosis. Fiber density should be tional cytogenetics and interphase FISH for the 12 most frequent
assessed in hematopoietic areas.
MF, Myelofibrosis. chromosomal abnormalities detected in PMF.
Data from Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM, Facchetti F, et al: European consensus on Among the Philadelphia chromosome-negative MPNs, PMF has
grading bone marrow fibrosis and assessment of cellularity. Haematologica the highest rate of chromosomal abnormalities at diagnosis. Deletions
90:1128, 2005.
of the long arms of chromosomes 13 and 20, trisomy 8, and abnor-
malities of chromosomes 1, 7, and 9 constitute more than 80% of
all chromosomal abnormalities detected in PMF (see Fig. 70.5).
especially important to avoid a false impression of reduced fiber None of these lesions are specific for PMF because they are also
content in fatty or edematous BM samples after treatment. The detected in PV, ET, MDS, and other myeloid malignancies. Deletion
progression of BM fibrosis in PMF is accompanied by the expression of the long arm of chromosome 13 is substantially more frequent in
of subsets of collagenases that is independent of JAK2V617F status. PMF than in PV. Fine FISH mapping has defined the commonly
Morphologic examination of the spleen frequently reveals follicu- deleted region to 13q13.3-q14.3 encompassing RB1, D13S319, and
lar atrophy in the white pulp (Fig. 70.4A) with foci of EMH in the D13S25 loci. As mentioned in Chapter 68, del(20q) and +9/+9p are
sinusoids of the red pulp (Fig. 70.4B) where megakaryocytes, myeloid more frequent in PV than in PMF. Multiple copies of 9p result in
elements, and nucleated erythroid elements are seen. The extramedul- trisomy/tetrasomy or amplification of JAK2, and each of these
lary hematopoietic cells belonging to each of the myeloid lineages can abnormalities has been reported in PMF. A 2.7-Mb region on chro-
be distributed in the spleen diffusely or be limited to macronodules. mosome 20 spanning D20S108 (proximal) and D20S481 (distal) is
The predominance of immature granulocytic forms is associated with deleted in all Philadelphia chromosome-negative MPNs. A different
an especially poor prognosis. Pathologic examination of the liver region is deleted in other myeloid malignancies, but a common
reveals hematopoietic cellular elements within the sinusoids (see 1.6-kb region may constitute the major site responsible for loss of
E-Slide VM03954). Sinusoidal dilatation is a common finding, as heterozygosity.