Page 1294 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1294
1140 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
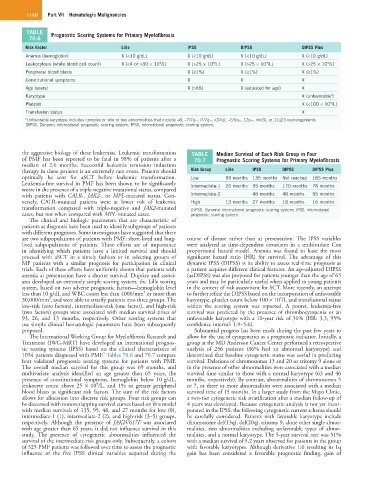
TABLE Prognostic Scoring Systems for Primary Myelofibrosis
70.6
Risk Factor Lille IPSS DIPSS DIPSS Plus
Anemia (hemoglobin) X (<10 g/dL) X (<10 g/dL) X (<10 g/dL) X (<10 g/dL)
9
9
9
Leukocytosis (white blood cell count) X (<4 or >30 × 10 /L) X (>25 × 10 /L) X (>25 × 10 /L) X (>25 × 10 /L)
9
Peripheral blood blasts X (≥1%) X (≥1%) X (≥1%)
Constitutional symptoms X X X
Age (years) X (>65) X (adjusted for age) X
a
Karyotype X (unfavorable )
Platelet X (<100 × 10 /L)
9
Transfusion status X
a Unfavorable karyotype includes complex or sole or two abnormalities that include +8, −7/7q−, i7/7q−, i(17q), −5/5q−, 12p−, inv(3), or 11q23 rearrangements.
DIPSS, Dynamic international prognostic scoring system; IPSS, international prognostic scoring system.
the aggressive biology of these leukemias. Leukemic transformation TABLE Median Survival of Each Risk Group in Four
of PMF has been reported to be fatal in 98% of patients after a 70.7 Prognostic Scoring Systems for Primary Myelofibrosis
median of 2.6 months. Successful leukemia remission induction
therapy in these patients is an extremely rare event. Patients should Risk Group Lille IPSS DIPSS DIPSS Plus
optimally be sent for aSCT before leukemic transformation. Low 93 months 135 months Not reached 185 months
Leukemia-free survival in PMF has been shown to be significantly Intermediate-1 26 months 95 months 170 months 78 months
worse in the presence of a triple-negative mutational status, compared
with patients with CALR-, JAK2-, or MPL-mutated status. Con- Intermediate-2 48 months 48 months 35 months
versely, CALR-mutated patients were at lower risk of leukemic High 13 months 27 months 18 months 16 months
transformation compared with triple-negative and JAK2-mutated DIPSS, Dynamic international prognostic scoring system; IPSS, international
cases, but not when compared with MPL-mutated cases. prognostic scoring system.
The clinical and biologic parameters that are characteristic of
patients at diagnosis have been used to identify subgroups of patients
with different prognoses. Some investigators have suggested that there
are two subpopulations of patients with PMF; short-lived and long- course of disease rather than at presentation. The IPSS variables
lived subpopulations of patients. These efforts are of importance were analyzed as time-dependent covariates in a multivariate Cox
in identifying which patients have a limited survival and should proportional hazard model. Anemia was found to have the most
proceed with aSCT in a timely fashion or in selecting groups of significant hazard ratio (HR) for survival. The advantage of this
MF patients with a similar prognosis for participation in clinical dynamic IPSS (DIPSS) is its ability to assess real-time prognosis as
trials. Each of these efforts have uniformly shown that patients with a patient acquires different clinical features. An age-adjusted DIPSS
anemia at presentation have a shorter survival. Dupriez and associ- (aaDIPSS) was also proposed for patients younger than the age of 65
ates developed an extremely simple scoring system, the Lille scoring years and may be particularly useful when applied to young patients
system, based on two adverse prognostic factors—hemoglobin level in the context of risk assessment for SCT. More recently, an attempt
3
less than 10 g/dL and WBC count less than 4000/mm or more than to further refine the DIPSS based on the incorporation of unfavorable
3
9
30,000/mm , and were able to stratify patients into three groups. The karyotype, platelet count below 100 × 10 /L and transfusional status
low-risk (zero factors), intermediate-risk (one factor), and high-risk within the scoring system was reported. A poorer, leukemia-free
(two factors) groups were associated with median survival times of survival was predicted by the presence of thrombocytopenia or an
93, 26, and 13 months, respectively. Other scoring systems that unfavorable karyotype with a 10-year risk of 31% (HR: 3.3; 95%
use simple clinical hematologic parameters have been subsequently confidence interval: 1.9–5.6).
proposed. Substantial progress has been made during the past few years to
The International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and allow for the use of cytogenetics as a prognostic indicator. Initially, a
Treatment (IWG-MRT) have developed an international prognos- group at the MD Anderson Cancer Center performed a retrospective
tic scoring systems (IPSS) based on the clinical characteristics of analysis of 256 patients (36% had an abnormal karyotype) and
9
1054 patients diagnosed with PMF. Tables 70.6 and 70.7 compare determined that baseline cytogenetic status was useful in predicting
four validated prognostic scoring systems for patients with PMF. survival. Deletions of chromosomes 13 and 20 or trisomy 9 alone or
The overall median survival for this group was 69 months, and in the presence of other abnormalities were associated with a median
multivariate analysis identified an age greater than 65 years, the survival time similar to those with a normal karyotype (63 and 46
presence of constitutional symptoms, hemoglobin below 10 g/dL, months, respectively). By contrast, abnormalities of chromosomes 5
9
leukocyte count above 25 × 10 /L, and 1% or greater peripheral or 7, or three or more abnormalities were associated with a median
blood blasts as significant risk factors. The sum of the risk factors survival time of 15 months. In a larger study from the Mayo Clinic,
allows for allocation into discrete risk groups. Four risk groups can a two-tier cytogenetic risk stratification after a median follow-up of
be discerned with nonoverlapping survival curves based on this model 4 years was developed. Because cytogenetic analysis is not yet incor-
with median survivals of 135, 95, 48, and 27 months for low (0), porated in the IPSS, the following cytogenetic current schema should
intermediate-1 (1), intermediate-2 (2), and high-risk (3–5) groups, be carefully considered. Patients with favorable karyotype include
respectively. Although the presence of JAK2V617F was associated chromosome del(13q), del(20q), trisomy 9, alone other single abnor-
with age greater than 65 years, it did not influence survival in this malities, two abnormalities excluding unfavorable types of abnor-
study. The presence of cytogenetic abnormalities influenced the malities, and a normal karyotype. The 5-year survival rate was 51%
survival of the intermediate-risk groups only. Subsequently, a cohort with a median survival of 5.2 years observed for patients in the group
of 525 PMF patients was followed over time to assess the prognostic with favorable karyotypes. Although derivative 1;6 resulting in 1q
influence of the five IPSS clinical variables acquired during the gain has been considered a favorable prognostic finding, gain of