Page 1290 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1290
1136 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
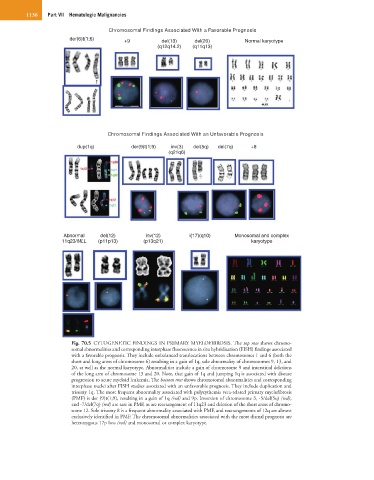
Chromosomal Findings Associated With a Favorable Prognosis
der(6)t(1;6) +9 del(13) del(20) Normal karyotype
(q12q14.2) (q11q13)
Chromosomal Findings Associated With an Unfavorable Prognosis
dup(1q) der(9)t(1;9) inv(3) del(5q) del(7q) +8
(q21q6)
Abnormal del(12) inv(12) i(17)(q10) Monosomal and complex
11q23/MLL (p11p13) (p13q21) karyotype
Fig. 70.5 CYTOGENETIC FINDINGS IN PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. The top row shows chromo-
somal abnormalities and corresponding interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) findings associated
with a favorable prognosis. They include unbalanced translocations between chromosomes 1 and 6 (both the
short and long arms of chromosome 6) resulting in a gain of 1q, sole abnormality of chromosomes 9, 13, and
20, as well as the normal karyotype. Abnormalities include a gain of chromosome 9 and interstitial deletions
of the long arm of chromosome 13 and 20. Note, that gain of 1q and jumping 1q is associated with disease
progression to acute myeloid leukemia. The bottom row shows chromosomal abnormalities and corresponding
interphase nuclei after FISH studies associated with an unfavorable prognosis. They include duplication and
trisomy 1q. The most frequent abnormality associated with polycythemia vera-related primary myelofibrosis
(PMF) is der (9)t(1;9), resulting in a gain of 1q (red) and 9p. Inversion of chromosome 3, -5/del(5q) (red),
and -7/del(7q) (red) are rare in PMF, as are rearrangement of 11q23 and deletion of the short arms of chromo-
some 12. Sole trisomy 8 is a frequent abnormality associated with PMF, and rearrangements of 12q are almost
exclusively identified in PMF. The chromosomal abnormalities associated with the most dismal prognosis are
heterozygous 17p loss (red) and monosomal or complex karyotype.