Page 1293 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1293
Chapter 70 Primary Myelofibrosis 1139
may present with MF in the setting of established SLE or in patients transformation at 1 and 5 years after diagnosis has been reported to
with minimal manifestations of an autoimmune disorder, as in be 2% and 16%, respectively. Immunologic and morphologic char-
primary AIMF. The presence of teardrop erythrocytes or leukoeryth- acterization of the blast cell phenotypes comprising these leukemias
roblastosis in a patient with lupus suggests autoimmune MF. Such reveals that a typical myeloid phenotype is most commonly detected;
patients universally have a positive ANA test result or an elevated other cell lineages, such as megakaryocytic, erythroid, lymphoid, and
anti-DNA titer. Because the physical manifestations of an auto- even stem cell phenotype, may also be involved, leading to the exis-
immune disease may not be evident, all patients with MF should have tence of mixed myeloid and hybrid transformations. Megakaryoblastic
an ANA test to exclude an autoimmune etiology. Primary AIMF transformations have been detected in one-third of cases in one series,
patients lack MPN mutations such as JAK2V617F, MPL W515L/K, an incidence higher than that found in de novo AML. In 50% of
and CALR, or marker cytogenetic abnormalities consistent with cases of JAK2V617F MPNs, the blast cells that represent the progeny
polyclonal rather than clonal hematopoiesis of the leukemia initiating clone are JAK2V617F negative, suggesting
that the leukemia originates from a clone distinct from the
JAK2V617F-positive clone. This coexistent JAK2V617F-negative
PROGNOSIS clone appears to have a higher propensity to undergo leukemic
transformation. JAK2V617F therefore does not appear to be a pre-
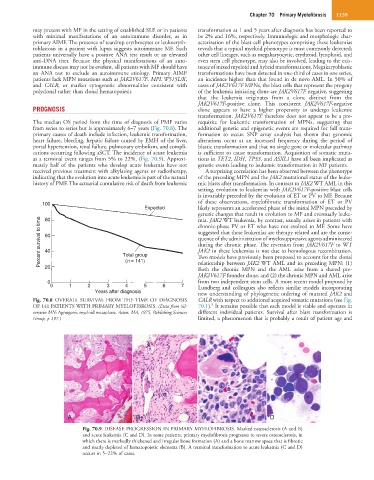
The median OS period from the time of diagnosis of PMF varies requisite for leukemic transformation of MPNs, suggesting that
from series to series but is approximately 6–7 years (Fig. 70.8). The additional genetic and epigenetic events are required for full trans-
primary causes of death include infection, leukemic transformation, formation to occur. SNP array analysis has shown that genomic
heart failure, bleeding, hepatic failure caused by EMH of the liver, alterations occur at an increased frequency during the period of
portal hypertension, renal failure, pulmonary embolism, and compli- blastic transformation and that no single gene or molecular pathway
cations occurring following aSCT. The incidence of acute leukemia is sufficient to cause transformation. Acquisition of somatic muta-
as a terminal event ranges from 5% to 22%, (Fig. 70.9). Approxi- tions in TET2, IDH, TP53, and ASXL1 have all been implicated as
mately half of the patients who develop acute leukemia have not genetic events leading to leukemic transformation in MF patients.
received previous treatment with alkylating agents or radiotherapy, A surprising correlation has been observed between the phenotype
indicating that the evolution into acute leukemia is part of the natural of the preceding MPN and the JAK2 mutational status of the leuke-
history of PMF. The actuarial cumulative risk of death from leukemic mic blasts after transformation. In contrast to JAK2 WT AML in this
setting, evolution to leukemias with JAK2V617F-positive blast cells
is invariably preceded by the evolution of ET or PV to MF. Because
100 of these observations, myelofibrotic transformation of ET or PV
Expected likely represents an accelerated phase of the initial MPN preceded by
genetic changes that result in evolution to MF and eventually leuke-
80
Percent survival to time 60 Total group suggested that these leukemias are therapy related and are the conse-
mia. JAK2 WT leukemia, by contrast, usually arises in patients with
chronic-phase PV or ET who have not evolved to MF. Some have
quence of the administration of myelosuppressive agents administered
during the chronic phase. The reversion from JAK2V617F to WT
40
JAK2 in these leukemias is not due to homologous recombination.
Two models have previously been proposed to account for the clonal
(n = 141)
relationship between JAK2 WT AML and its preceding MPN: (1)
20
Both the chronic MPN and the AML arise from a shared pre-
JAK2V617F founder clone, and (2) the chronic MPN and AML arise
0 from two independent stem cells. A more recent model proposed by
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Lundberg and colleagues also reflects similar models incorporating
Years after diagnosis new understanding of phylogenetic ordering of mutated JAK2 and
Fig. 70.8 OVERALL SURVIVAL FROM THE TIME OF DIAGNOSIS CALR with respect to additional acquired somatic mutations (see Fig.
8
OF 141 PATIENTS WITH PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. (Data from Sil- 70.1). It remains possible that each model is viable and operates in
verstein MN: Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia, Acton, MA, 1975, Publishing Sciences different individual patients. Survival after blast transformation is
Group, p 197.) limited, a phenomenon that is probably a result of patient age and
A B C D
Fig. 70.9 DISEASE PROGRESSION IN PRIMARY MYELOFIBROSIS. Marked osteosclerosis (A and B)
and acute leukemia (C and D). In some patients, primary myelofibrosis progresses to severe osteosclerosis, in
which there is markedly thickened and irregular bone formation (A) and a bone marrow space that is fibrotic
and nearly depleted of hematopoietic elements (B). A terminal transformation to acute leukemia (C and D)
occurs in 5–22% of cases.