Page 1463 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1463
1300 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
BCR
BCR/BTK LYN P CD19
SYK P
P BCL-2 family
NF-κB PKCβ PI3Kδ (BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1)
BTK
IKKγ
IKKα AKT Apoptosis
IKKβ P BAD
NFAT
P P
IκBα NF-κB
P AKT
mTOR
IκBα Cell cycle
CyclinD1 PI3K/ALT/mTOR
E2F CDK4/6
E2F
B-Catenin
Defective RB1 RB1
DNA damage P P P
CyclinD1 CDK2 G5K3β G5K3β
BMI-1 CDK4 P27 P27 CyclinE
p14/ARF MDM2 P21 P CyclinD1 FZD
CRM1
WNT
CHK2 P
P53 CyclinD1 LRP
CHK1
ATM E3 ligase SCF
P53
CyclinD1 AKT Ub-Ub-Ub Protein degradation
HSP90 Proteasome Ub-Ub-Ub
Protein homeostasis
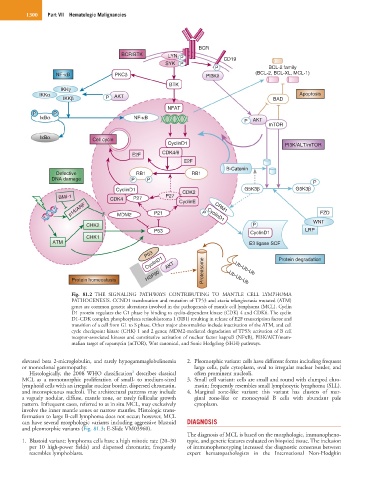
Fig. 81.2 THE SIGNALING PATHWAYS CONTRIBUTING TO MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA
PATHOGENESIS. CCND1 translocation and mutation of TP53 and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM)
genes are common genetic alterations involved in the pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Cyclin
D1 protein regulates the G1 phase by binding to cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and CDK6. The cyclin
D1-CDK complex phosphorylates retinoblastoma 1 (RB1) resulting in release of E2F transcription factor and
transition of a cell from G1 to S phase. Other major abnormalities include inactivation of the ATM, and cell
cycle checkpoint kinase (CHK) 1 and 2 genes; MDM2-mediated degradation of TP53; activation of B cell
receptor-associated kinases and constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NFκB), PI3K/AKT/mam-
malian target of rapamycin (mTOR), Wnt canonical, and Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) pathways.
elevated beta 2-microglobulin, and rarely hypogammaglobulinemia 2. Pleomorphic variant: cells have different forms including frequent
or monoclonal gammopathy. large cells, pale cytoplasm, oval to irregular nuclear border, and
3
Histologically, the 2008 WHO classification describes classical often prominent nucleoli.
MCL as a monomorphic proliferation of small- to medium-sized 3. Small cell variant: cells are small and round with clumped chro-
lymphoid cells with an irregular nuclear border, dispersed chromatin, matin; frequently resembles small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).
and inconspicuous nucleoli. The architectural patterns may include 4. Marginal zone-like variant: this variant has clusters of mar-
a vaguely nodular, diffuse, mantle zone, or rarely follicular growth ginal zone-like or monocytoid B cells with abundant pale
pattern. Infrequent cases, referred to as in situ MCL, may exclusively cytoplasm.
involve the inner mantle zones or narrow mantles. Histologic trans-
formation to large B-cell lymphoma does not occur; however, MCL
can have several morphologic variants including aggressive blastoid DIAGNOSIS
and pleomorphic variants (Fig. 81.3; E-Slide VM03960).
The diagnosis of MCL is based on the morphologic, immunopheno-
1. Blastoid variant: lymphoma cells have a high mitotic rate (20–30 typic, and genetic features evaluated on biopsied tissue. The inclusion
per 10 high-power fields) and dispersed chromatin; frequently of immunophenotyping increased the diagnostic consensus between
resembles lymphoblasts. expert hematopathologists in the International Non-Hodgkin