Page 1464 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1464
Chapter 81 Mantle Cell Lymphoma 1301
other criteria; therefore, SOX11 is a very useful tool in cyclin
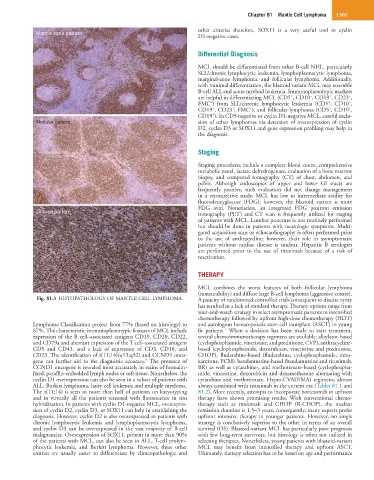
Mantle zone pattern
D1-negative cases.
Differential Diagnosis
MCL should be differentiated from other B-cell NHL, particularly
SLL/chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma,
marginal-zone lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma. Additionally,
with minimal differentiation, the blastoid variant MCL may resemble
B-cell ALL and acute myeloid leukemia. Immunophenotypic markers
+
−
+
−
are helpful in differentiating MCL (CD5 , CD10 , CD19 , CD23 ,
+
−
+
FMC ) from SLL/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CD5 , CD10 ,
−
−
+
+
+
CD19 , CD23 , FMC ), and follicular lymphoma (CD5 , CD10 ,
+
CD19 ). In CD5 negative or cyclin D1-negative MCL, careful exclu-
Nodular pattern sion of other lymphomas via detection of overexpression of cyclin
D2, cyclin D3 or SOX11 and gene expression profiling may help in
the diagnosis.
Staging
Staging procedures include a complete blood count, comprehensive
metabolic panel, lactate dehydrogenase, evaluation of a bone marrow
biopsy, and computed tomography (CT) of chest, abdomen, and
pelvis. Although endoscopies of upper and lower GI tracts are
frequently positive, such evaluation did not change management
in a retrospective study. MCL has low to intermediate avidity for
fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG); however, the blastoid variant is more
FDG avid. Nonetheless, an integrated FDG positron emission
Diffuse pattern tomography (PET) and CT scan is frequently utilized for staging
of patients with MCL. Lumbar puncture is not routinely performed
but should be done in patients with neurologic symptoms. Multi-
gated acquisition scan or echocardiography is often performed prior
to the use of anthracycline; however, their role in asymptomatic
patients without cardiac disease is unclear. Hepatitis B serologies
are performed prior to the use of rituximab because of a risk of
reactivation.
THERAPY
MCL combines the worst features of both follicular lymphoma
(noncurability) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (aggressive course).
Fig. 81.3 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA. A paucity of randomized controlled trials consequent to disease rarity
has resulted in a lack of standard therapy. Therapy options range from
wait-and-watch strategy in select asymptomatic patients to intensified
chemotherapy followed by upfront high-dose chemotherapy (HDT)
Lymphoma Classification project from 77% (based on histology) to and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (ASCT) in young
1
87%. The characteristic immunophenotypic features of MCL include fit patients. When a decision has been made to start treatment,
expression of the B cell–associated antigens CD19, CD20, CD22, several chemoimmunotherapy regimens are available: alkylator-based
and CD79a and aberrant expression of the T cell–associated antigens (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone, CVP), anthracycline-
CD5 and CD43, and a lack of expression of CD3, CD10, and based (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone,
CD23. The identification of t(11;14)(q13;q32) and CCND1 onco- CHOP), fludarabine-based (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, mito-
3
gene can further aid to the diagnostic accuracy. The presence of xantrone, FCM), bendamustine-based (bendamustine and rituximab,
CCND1 oncogene is revealed most accurately in stains of formalin- BR) as well as cytarabine-, and methotrexate-based (cyclophospha-
fixed, paraffin-embedded lymph nodes or soft tissue. Nonetheless, the mide, vincristine, doxorubicin and dexamethasone alternating with
cyclin D1 overexpression can also be seen in a subset of patients with cytarabine and methotrexate, Hyper-CVAD/MA) regimens, almost
ALL, Burkitt lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia and multiple myeloma. always combined with rituximab in the current era (Tables 81.1 and
The t(11;14) is seen in more than half of patients on karyotyping 81.2). More recently, attempts to incorporate bortezomib in upfront
and in virtually all the patients screened with fluorescence in situ therapy have shown promising results. With conventional chemo-
hybridization. In patients with cyclin D1-negative MCL, overexpres- therapy such as rituximab and CHOP (R-CHOP), the median
sion of cyclin D2, cyclin D3, or SOX11 can help in establishing the remission duration is 1.5–3 years; consequently, many experts prefer
diagnosis. However, cyclin D2 is also overexpressed in patients with upfront intensive therapy in younger patients. However, no single
chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, strategy is conclusively superior to the other in terms of an overall
and cyclin D3 can be overexpressed in the vast majority of B-cell survival (OS). Blastoid-variant MCL has particularly poor prognosis
malignancies. Overexpression of SOX11, present in more than 90% with few long-term survivors, but histology is often not utilized in
of the patients with MCL, can also be seen in ALL, T-cell prolym- selecting therapies. Nonetheless, young patients with blastoid-variant
phocytic leukemia, and Burkitt lymphoma. However, these other MCL may benefit from intensified therapy and upfront ASCT.
entities are usually easier to differentiate by clinicopathologic and Ultimately, therapy selection has to be based on age and performance