Page 1688 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1688
1506 Part VIII Comprehensive Care of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
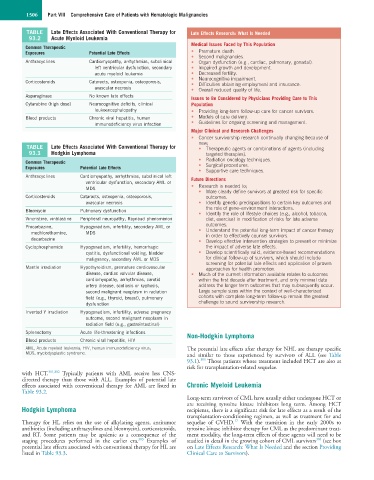
TABLE Late Effects Associated With Conventional Therapy for Late Effects Research: What Is Needed
93.2 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Medical Issues Faced by This Population
Common Therapeutic
Exposures Potential Late Effects • Premature death.
• Second malignancies.
Anthracyclines Cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, subclinical • Organ dysfunction (e.g., cardiac, pulmonary, gonadal).
left ventricular dysfunction, secondary • Impaired growth and development.
acute myeloid leukemia • Decreased fertility.
• Neurocognitive impairment.
Corticosteroids Cataracts, osteopenia, osteoporosis, • Difficulties obtaining employment and insurance.
avascular necrosis • Overall reduced quality of life.
Asparaginase No known late effects Issues to Be Considered by Physicians Providing Care to This
Cytarabine (high dose) Neurocognitive deficits, clinical Population
leukoencephalopathy • Providing long-term follow-up care for cancer survivors.
Blood products Chronic viral hepatitis, human • Models of care delivery.
immunodeficiency virus infection • Guidelines for ongoing screening and management.
Major Clinical and Research Challenges
• Cancer survivorship research continually changing because of
new;
TABLE Late Effects Associated With Conventional Therapy for • Therapeutic agents or combinations of agents (including
93.3 Hodgkin Lymphoma targeted therapies).
• Radiation oncology techniques.
Common Therapeutic
Exposures Potential Late Effects • Surgical procedures.
• Supportive care techniques.
Anthracyclines Cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, subclinical left Future Directions
ventricular dysfunction, secondary AML or
MDS • Research is needed to;
• More clearly define survivors at greatest risk for specific
Corticosteroids Cataracts, osteopenia, osteoporosis, outcomes.
avascular necrosis • Identify genetic predispositions to certain key outcomes and
the role of gene–environment interactions.
Bleomycin Pulmonary dysfunction
• Identify the role of lifestyle choices (e.g., alcohol, tobacco,
Vincristine, vinblastine Peripheral neuropathy, Raynaud phenomenon diet, exercise) in modification of risks for late adverse
Procarbazine, Hypogonadism, infertility, secondary AML or outcomes.
mechlorethamine, MDS • Understand the potential long-term impact of cancer therapy
in order to effectively counsel survivors.
dacarbazine
• Develop effective intervention strategies to prevent or minimize
Cyclophosphamide Hypogonadism, infertility, hemorrhagic the impact of adverse late effects.
cystitis, dysfunctional voiding, bladder • Develop scientifically valid, evidence-based recommendations
malignancy, secondary AML or MDS for clinical follow-up of survivors, which should include
screening for potential late effects and application of proven
Mantle irradiation Hypothyroidism, premature cardiovascular approaches for health promotion.
disease, cardiac valvular disease, • Much of the current information available relates to outcomes
cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, carotid within the first decade after treatment, and only minimal data
artery disease, scoliosis or kyphosis, address the longer term outcomes that may subsequently occur.
second malignant neoplasm in radiation Large sample sizes within the context of well-characterized
field (e.g., thyroid, breast), pulmonary cohorts with complete long-term follow-up remain the greatest
dysfunction challenge to sound survivorship research.
Inverted Y irradiation Hypogonadism, infertility, adverse pregnancy
outcome, second malignant neoplasm in
radiation field (e.g., gastrointestinal)
Splenectomy Acute life-threatening infections Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Blood products Chronic viral hepatitis, HIV
AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; The potential late effects after therapy for NHL are therapy specific
MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome. and similar to those experienced by survivors of ALL (see Table
303
93.1). Those patients whose treatment included HCT are also at
risk for transplantation-related sequelae.
with HCT. 301,302 Typically patients with AML receive less CNS-
directed therapy than those with ALL. Examples of potential late
effects associated with conventional therapy for AML are listed in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Table 93.2.
Long-term survivors of CML have usually either undergone HCT or
are receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors long term. Among HCT
Hodgkin Lymphoma recipients, there is a significant risk for late effects as a result of the
transplantation-conditioning regimen, as well as treatment for and
17
Therapy for HL relies on the use of alkylating agents, antitumor sequelae of GVHD. With the transition in the early 2000s to
antibiotics (including anthracyclines and bleomycin), corticosteroids, tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for CML as the predominant treat-
and RT. Some patients may be apslenic as a consequence of the ment modality, the long-term effects of these agents will need to be
304
303
staging procedures performed in the earlier era. Examples of studied in detail in the growing cohort of CML survivors (see box
potential late effects associated with conventional therapy for HL are on Late Effects Research: What Is Needed and the section Providing
listed in Table 93.3. Clinical Care to Survivors).