Page 1692 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1692
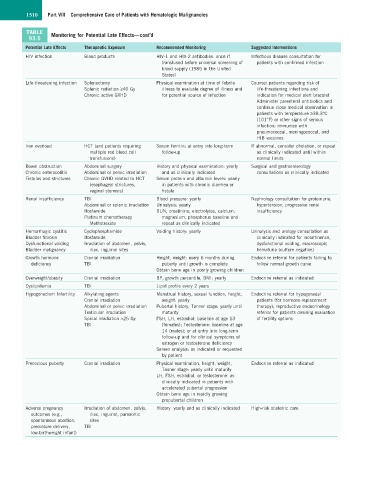
1510 Part VIII Comprehensive Care of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
TABLE Monitoring for Potential Late Effects—cont’d
93.5
Potential Late Effects Therapeutic Exposure Recommended Monitoring Suggested Interventions
HIV infection Blood products HIV-1 and HIV-2 antibodies: once if Infectious disease consultation for
transfused before universal screening of patients with confirmed infection
blood supply (1985 in the United
States)
Life-threatening infection Splenectomy Physical examination at time of febrile Counsel patients regarding risk of
Splenic radiation ≥40 Gy illness to evaluate degree of illness and life-threatening infections and
Chronic active GVHD for potential source of infection indication for medical alert bracelet
Administer parenteral antibiotics and
continue close medical observation in
patients with temperature ≥38.3°C
(101°F) or other signs of serious
infection; immunize with
pneumococcal, meningococcal, and
HIB vaccines
Iron overload HCT (and patients requiring Serum ferritin: at entry into long-term If abnormal, consider chelation, or repeat
multiple red blood cell follow-up as clinically indicated until within
transfusions) normal limits
Bowel obstruction Abdominal surgery History and physical examination: yearly Surgical and gastroenterology
Chronic enterocolitis Abdominal or pelvic irradiation and as clinically indicated consultations as clinically indicated
Fistulas and strictures Chronic GVHD related to HCT Serum protein and albumin levels: yearly
(esophageal strictures, in patients with chronic diarrhea or
vaginal stenosis) fistula
Renal insufficiency TBI Blood pressure: yearly Nephrology consultation for proteinuria,
Abdominal or splenic irradiation Urinalysis: yearly hypertension, progressive renal
Ifosfamide BUN, creatinine, electrolytes, calcium, insufficiency
Platinum chemotherapy magnesium, phosphorus baseline and
Methotrexate repeat as clinically indicated
Hemorrhagic cystitis Cyclophosphamide Voiding history: yearly Urinalysis and urology consultation as
Bladder fibrosis Ifosfamide clinically indicated for incontinence,
Dysfunctional voiding Irradiation of abdomen, pelvis, dysfunctional voiding, macroscopic
Bladder malignancy iliac, inguinal sites hematuria (culture negative)
Growth hormone Cranial irradiation Height, weight: every 6 months during Endocrine referral for patients failing to
deficiency TBI puberty until growth is complete follow normal growth curve
Obtain bone age in poorly growing children
Overweight/obesity Cranial irradiation BP, growth percentile, BMI: yearly Endocrine referral as indicated
Dyslipidemia TBI Lipid profile every 2 years
Hypogonadism Infertility Alkylating agents Menstrual history, sexual function, height, Endocrine referral for hypogonadal
Cranial irradiation weight: yearly patients (for hormone-replacement
Abdominal or pelvic irradiation Pubertal history, Tanner stage: yearly until therapy); reproductive endocrinology
Testicular irradiation maturity referral for patients desiring evaluation
Spinal irradiation >25 Gy FSH, LH, estradiol: baseline at age 13 of fertility options
TBI (females); Testosterone: baseline at age
14 (males); or at entry into long-term
follow-up and for clinical symptoms of
estrogen or testosterone deficiency
Semen analysis: as indicated or requested
by patient
Precocious puberty Cranial irradiation Physical examination, height, weight, Endocrine referral as indicated
Tanner stage: yearly until maturity
LH, FSH, estradiol, or testosterone: as
clinically indicated in patients with
accelerated pubertal progression
Obtain bone age in rapidly growing
prepubertal children
Adverse pregnancy Irradiation of abdomen, pelvis, History: yearly and as clinically indicated High-risk obstetric care
outcomes (e.g., iliac, inguinal, paraaortic
spontaneous abortion, sites
premature delivery, TBI
low-birthweight infant)