Page 1691 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1691
Chapter 93 Late Complications of Hematologic Diseases and Their Therapies 1509
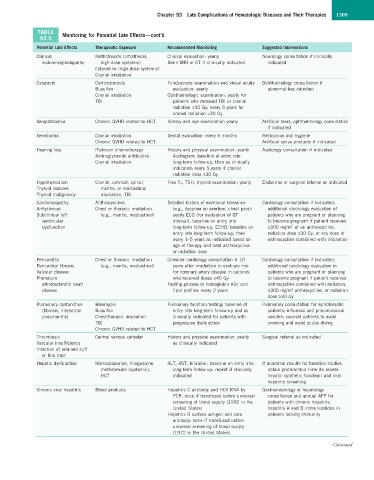
TABLE Monitoring for Potential Late Effects—cont’d
93.5
Potential Late Effects Therapeutic Exposure Recommended Monitoring Suggested Interventions
Clinical Methotrexate (intrathecal, Clinical evaluation: yearly Neurology consultation if clinically
leukoencephalopathy high-dose systemic) Brain MRI or CT if clinically indicated indicated
Cytarabine (high-dose systemic)
Cranial irradiation
Cataracts Corticosteroids Funduscopic examination and visual acuity Ophthalmology consultation if
Busulfan evaluation: yearly abnormalities detected
Cranial irradiation Ophthalmologic examination: yearly for
TBI patients who received TBI or cranial
radiation ≥30 Gy; every 3 years for
cranial radiation <30 Gy
Xerophthalmia Chronic GVHD related to HCT History and eye examination yearly Artificial tears, ophthalmology consultation
if indicated
Xerostomia Cranial irradiation Dental evaluation: every 6 months Meticulous oral hygiene
Chronic GVHD related to HCT Artificial saliva products if indicated
Hearing loss Platinum chemotherapy History and physical examination: yearly Audiology consultation if indicated
Aminoglycoside antibiotics Audiogram: baseline at entry into
Cranial irradiation long-term follow-up, then as clinically
indicated; every 5 years if cranial
radiation dose ≥30 Gy
Hypothyroidism Cranial, cervical, spinal, Free T 4 , TSH, thyroid examination: yearly Endocrine or surgical referral as indicated
Thyroid nodules mantle, or mediastinal
Thyroid malignancy irradiation; TBI
Cardiomyopathy Anthracyclines Detailed history of exertional tolerance Cardiology consultation if indicated;
Arrhythmias Chest or thoracic irradiation (e.g., dyspnea on exertion, chest pain): additional cardiology evaluation of
Subclinical left (e.g., mantle, mediastinal) yearly ECG (for evaluation of QT patients who are pregnant or planning
ventricular interval): baseline on entry into to become pregnant if patient received
2
dysfunction long-term follow-up; ECHO: baseline on ≥300 mg/m of an anthracycline,
entry into long-term follow-up, then radiation dose ≥30 Gy, or any dose of
every 1–5 years as indicated based on anthracycline combined with irradiation
age at therapy and total anthracycline
or radiation dose
Pericarditis Chest or thoracic irradiation Consider cardiology consultation 5–10 Cardiology consultation if indicated;
Pericardial fibrosis (e.g., mantle, mediastinal) years after irradiation to evaluate risk additional cardiology evaluation in
Valvular disease for coronary artery disease in patients patients who are pregnant or planning
Premature who received doses ≥40 Gy to become pregnant if patient received
atherosclerotic heart Fasting glucose or hemoglobin A1c and anthracycline combined with radiation,
disease lipid profiles: every 2 years ≥300 mg/m anthracycline, or radiation
2
dose ≥30 Gy
Pulmonary dysfunction Bleomycin Pulmonary function testing: baseline at Pulmonary consultation for symptomatic
(fibrosis, interstitial Busulfan entry into long-term follow-up and as patients; influenza and pneumococcal
pneumonitis) Chest/thoracic irradiation clinically indicated for patients with vaccine; counsel patients to avoid
TBI progressive dysfunction smoking and avoid scuba diving
Chronic GVHD related to HCT
Thrombosis Central venous catheter History and physical examination: yearly Surgical referral as indicated
Vascular insufficiency as clinically indicated
Infection of retained cuff
or line tract
Hepatic dysfunction Mercaptopurine, thioguanine, ALT, AST, bilirubin: baseline on entry into If abnormal results for baseline studies,
methotrexate (systemic), long-term follow-up; repeat if clinically obtain prothrombin time (to assess
HCT indicated hepatic synthetic function) and viral
hepatitis screening
Chronic viral hepatitis Blood products Hepatitis C antibody and HCV RNA by Gastroenterology or hepatology
PCR: once if transfused before universal consultation and annual AFP for
screening of blood supply (1992 in the patients with chronic hepatitis;
United States) hepatitis A and B immunizations in
Hepatitis B surface antigen and core patients lacking immunity
antibody: once if transfused before
universal screening of blood supply
(1972 in the United States)
Continued