Page 1736 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1736
Chapter 97 Graft Engineering and Cell Processing 1541
Flow Cytometry effects). Stimulation of cells with interleukin-2 (IL-2) and ex vivo
culture also has been used to detect functional residual T lympho-
Accurate enumeration of very small numbers of target cells by cytes. In some cases, this method has shown a correlation between
cytometry requires rare event analysis. In this technique, large the numbers of T lymphocytes in the cultured sample and the
numbers of events must be accumulated and carefully analyzed if development of clinical GVHD in the graft recipient.
reliable data are to be obtained. This approach has been widely
+
adopted for counting CD34 cells in unfractionated grafts but is
often neglected when enumerating T lymphocytes in depleted grafts. Tetramer Analysis
The choice of MAb for detection of the T-lymphocyte population
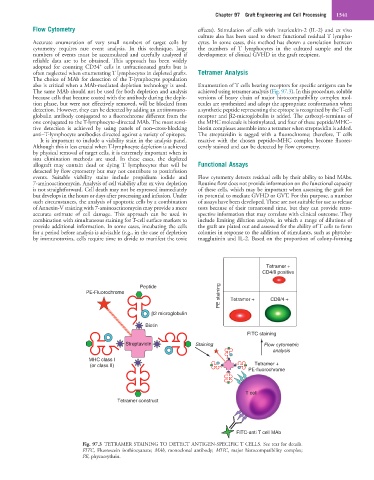
also is critical when a MAb-mediated depletion technology is used. Enumeration of T cells bearing receptors for specific antigens can be
The same MAb should not be used for both depletion and analysis achieved using tetramer analysis (Fig. 97.3). In this procedure, soluble
because cells that became coated with the antibody during the deple- versions of heavy chain of major histocompatibility complex mol-
tion phase, but were not effectively removed, will be blocked from ecules are synthesized and adopt the appropriate conformation when
detection. However, they can be detected by adding an antiimmuno- a synthetic peptide representing the epitope is recognized by the T-cell
globulin antibody conjugated to a fluorochrome different from the receptor and β2-microglobulin is added. The carboxyl-terminus of
one conjugated to the T-lymphocyte–directed MAb. The most sensi- the MHC molecule is biotinylated, and four of these peptide/MHC–
tive detection is achieved by using panels of non–cross-blocking biotin complexes assemble into a tetramer when streptavidin is added.
anti–T-lymphocyte antibodies directed against a variety of epitopes. The streptavidin is tagged with a fluorochrome; therefore, T cells
It is important to include a viability stain in the analysis panel. reactive with the chosen peptide–MHC complex become fluores-
Although this is less crucial when T-lymphocyte depletion is achieved cently stained and can be detected by flow cytometry.
by physical removal of target cells, it is extremely important when in
situ elimination methods are used. In these cases, the depleted
allograft may contain dead or dying T lymphocytes that will be Functional Assays
detected by flow cytometry but may not contribute to postinfusion
events. Suitable viability stains include propidium iodide and Flow cytometry detects residual cells by their ability to bind MAbs.
7-aminoactinomycin. Analysis of cell viability after ex vivo depletion Routine flow does not provide information on the functional capacity
is not straightforward. Cell death may not be expressed immediately of these cells, which may be important when assessing the graft for
but develops in the hours or days after processing and infusion. Under its potential to mediate GVHD or GVT. For this purpose, a number
such circumstances, the analysis of apoptotic cells by a combination of assays have been developed. These are not suitable for use as release
of Annexin-V staining with 7-aminoactinomycin may provide a more tests because of their turnaround time, but they can provide retro-
accurate estimate of cell damage. This approach can be used in spective information that may correlate with clinical outcome. They
combination with simultaneous staining for T-cell surface markers to include limiting dilution analysis, in which a range of dilutions of
provide additional information. In some cases, incubating the cells the graft are plated out and assessed for the ability of T cells to form
for a period before analysis is advisable (e.g., in the case of depletion colonies in response to the addition of stimulants, such as phytohe-
by immunotoxins, cells require time to divide to manifest the toxic magglutinin and IL-2. Based on the proportion of colony-forming
Tetramer +
CD4/8 positive
PE staining Tetramer + CD8/4 +
Peptide
PE-Fluorochrome
β2 microglobulin
Biotin
FITC staining
Streptavidin Staining Flow cytometric
analysis
MHC class I
(or class II) Tetramer +
PE-fluorochrome
T cell
Tetramer construct
FITC-anti T cell MAb
Fig. 97.3 TETRAMER STAINING TO DETECT ANTIGEN-SPECIFIC T CELLS. See text for details.
FITC, Fluorescein isothiocyanate; MAb, monoclonal antibody; MHC, major histocompatibility complex;
PE, phycoerythrin.