Page 2113 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2113
1876 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Lysosomal Granules that bring the vesicular and target membranes into close proximity
(Fig. 125.3B). SNARE function is tightly regulated by chaperone
Platelets have small numbers of primary and secondary lysosomes proteins. NSF regulates membrane interaction by disassembling
that contain enzymes involved in degradation of proteins, carbohy- SNARE complexes on the same membrane so that they are avail-
drates, and lipids. These enzymes include cathepsins, elastase, colla- able to form complexes with proteins on opposing membranes. The
genases, galactosidase, glucuronidase, and acid phosphatase. Sec1/Munc proteins (Munc18a, b, and c, and Munc13-4) and Rab
51
GTPases regulate granule docking, a preliminary step to granule
membrane fusion (Fig. 125.3B).
Mechanism of Granule Secretion Activation pathways involving intracellular Ca , Rab GTPase,
2+
and PKC isoforms regulate the SNARE complex interactions. PKC
The secretion of platelet granule contents occurs through mechanisms isoforms phosphorylate several of the SNARE proteins and their
analogous to those required for the exocytosis of granules from regulators including Munc18c, syntaxin 4, and SNAP-23. The PKC
neurons and mast cells. Platelet secretion is triggered by a variety of substrate pleckstrin is also a critical mediator of granule exocytosis:
strong agonists such as thrombin. Induction of secretion by weak pleckstrin-deficient mice show markedly impaired platelet secretion. 52
agonists (e.g., ADP) occurs when the cells are brought into close The important role of granule releasates in hemostasis is under-
50
contact, such as during aggregation, and is dependent on TxA 2 to lined by the bleeding diathesis in people with granule deficiencies or
amplify the effect of the primary agonist. defects of granule exocytosis. α Granules secrete fibrinogen and VWF,
In most cells, exocytosis occurs when vesicles fuse with the plasma which mediate platelet-platelet and platelet-ECM interactions. Of
membrane and release their contents into the extracellular milieu. the total VWF, 20% is contained in α granules, which are enriched
In platelets, granules clustered centrally by platelet shape change in the most potent high-molecular-weight VWF multimers. ADP
also fuse with one another and with the open canalicular system released from dense granules is essential for recruitment of additional
(OCS), a system of invaginations of the plasma membrane extend- platelets to the primary plug. Other mediators released from α
ing into the interior of the platelet; the granule contents diffuse granules play key roles in additional functions including wound
to the external environment. Membrane fusion is driven by the repair, angiogenesis, and host defense. However, these modulators can
soluble N-ethylmaleimide–sensitive factor (NSF) attachment protein also be pathogenic, contributing to the inflammatory response and
receptors (SNAREs). Platelets have the three basic components of atherosclerosis (Fig. 125.3A).
SNARE machinery: tSNAREs (target receptors associated with
open canalicular system and plasma membrane), vSNAREs (vesicle-
associated receptors associated with the granule membranes), and Procoagulant Surface Exposure and Microparticles
soluble regulators (including NSF and NSF-attachment proteins). 48,51
vSNAREs including vesicle-associated membrane proteins (VAMPs) The phospholipids of the plasma membrane of resting platelets are
interact with syntaxin isoforms and synaptosomal-associated protein asymmetrically distributed between the leaflets of the membrane
(SNAP)-23 on the target membranes to form four helix bundles bilayer, with choline-containing phospholipids predominating in the
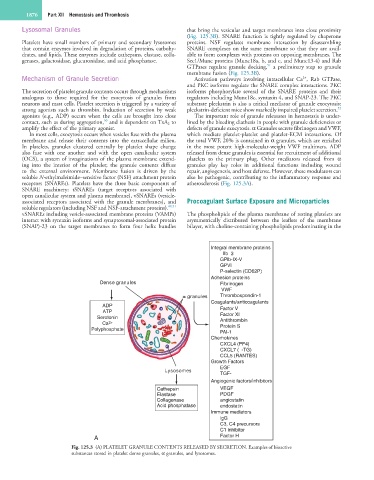
Integral membrane proteins
αllbβ3
GPlb-IX-V
GPVI
P-selectin (CD62P)
Adhesion proteins
Dense granules Fibrinogen
VWF
granules Thrombospondin-1
Coagulants/anticoagulants
ADP Factor V
ATP
Serotonin Factor XI
Antithrombin
Ca 2+ Protein S
Polyphosphate
PAI-1
Chemokines
CXCL4 (PF4)
CXCL7 (β-TG)
CCL5 (RANTES)
Growth Factors
EGF
Lysosomes
TGF-β
Angiogenic factors/inhibitors
Cathepsin VEGF
Elastase PDGF
Collagenase angiostatin
Acid phosphatase endostatin
Immune mediators
lgG
C3, C4 precursors
C1 inhibitor
A Factor H
Fig. 125.3 (A) PLATELET GRANULE CONTENTS RELEASED BY SECRETION. Examples of bioactive
substances stored in platelet dense granules, α granules, and lysosomes.