Page 2108 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2108
Chapter 125 Molecular Basis of Platelet Function 1871
A B
ADP TxA 2 Thrombin
C D
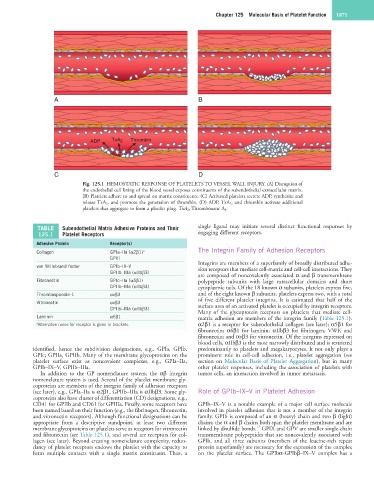
Fig. 125.1 HEMOSTATIC RESPONSE OF PLATELETS TO VESSEL WALL INJURY. (A) Disruption of
the endothelial cell lining of the blood vessel exposes constituents of the subendothelial extracellular matrix.
(B) Platelets adhere to and spread on matrix constituents. (C) Activated platelets secrete ADP, synthesize and
release TxA 2, and promote the generation of thrombin. (D) ADP, TxA 2, and thrombin activate additional
platelets that aggregate to form a platelet plug. TxA 2, Thromboxane A 2.
TABLE Subendothelial Matrix Adhesive Proteins and Their single ligand may initiate several distinct functional responses by
125.1 Platelet Receptors engaging different receptors.
Adhesive Protein Receptor(s)
Collagen GPIa–IIa (α2β1) a The Integrin Family of Adhesion Receptors
GPVI
Integrins are members of a superfamily of broadly distributed adhe-
von Willebrand factor GPIb–IX–V sion receptors that mediate cell-matrix and cell-cell interactions. They
GPIIb–IIIa (αIIbβ3)
are composed of noncovalently associated α and β transmembrane
Fibronectin GPIc–IIa (α5β1) polypeptide subunits with large extracellular domains and short
GPIIb–IIIa (αIIbβ3) cytoplasmic tails. Of the 18 known α subunits, platelets express five,
Thrombospondin-1 αvβ3 and of the eight known β subunits, platelets express two, with a total
of five different platelet integrins. It is estimated that half of the
Vitronectin αvβ3 surface area of an activated platelet is occupied by integrin receptors.
GPIIb–IIIa (αIIbβ3)
Many of the glycoprotein receptors on platelets that mediate cell-
Laminin α6β1 matrix adhesion are members of the integrin family (Table 125.1).
a Alternative name for receptor is given in brackets. α2β1 is a receptor for subendothelial collagen (see later); α5β1 for
fibronectin; α6β1 for laminin; αIIbβ3 for fibrinogen, VWF, and
fibronectin; and αvβ3 for vitronectin. Of the integrins expressed on
blood cells, αIIbβ3 is the most narrowly distributed and is restricted
identified, hence the subdivision designations, e.g., GPIa, GPIb, predominantly to platelets and megakaryocytes. It not only plays a
GPIc; GPIIa, GPIIb. Many of the membrane glycoproteins on the prominent role in cell-cell adhesion, i.e., platelet aggregation (see
platelet surface exist as noncovalent complexes, e.g., GPIa–IIa, section on Molecular Basis of Platelet Aggregation), but in many
GPIb–IX–V, GPIIb–IIIa. other platelet responses, including the association of platelets with
In addition to the GP nomenclature system, the αβ integrin tumor cells, an interaction involved in tumor metastasis.
nomenclature system is used. Several of the platelet membrane gly-
coproteins are members of the integrin family of adhesion receptors
(see later), e.g., GPIa–IIa is α2β1, GPIIb–IIIa is αIIbβ3. Some gly- Role of GPIb–IX–V in Platelet Adhesion
coproteins also have cluster of differentiation (CD) designations, e.g.,
CD41 for GPIIb and CD61 for GPIIIa. Finally, some receptors have GPIb–IX–V is a notable example of a major cell surface molecule
been named based on their function (e.g., the fibrinogen, fibronectin, involved in platelet adhesion that is not a member of the integrin
and vitronectin receptors). Although functional designations can be family. GPIb is composed of an α (heavy) chain and two β (light)
appropriate from a descriptive standpoint, at least two different chains; the α and β chains both span the platelet membrane and are
17
membrane glycoproteins on platelets serve as receptors for vitronectin linked by disulfide bonds. GPIX and GPV are smaller single-chain
and fibronectin (see Table 125.1), and several are receptors for col- transmembrane polypeptides that are noncovalently associated with
lagen (see later). Beyond creating nomenclature complexity, redun- GPIb, and all three subunits (members of the leucine-rich repeat
dancy of platelet receptors endows the platelet with the capacity to protein superfamily) are necessary for the expression of the complex
form multiple contacts with a single matrix constituent. Thus, a on the platelet surface. The GPIbα-GPIbβ–IX–V complex has a