Page 215 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 215
Chapter 16 Cytokine/Receptor Families and Signal Transduction 167
Cytokine
CD45
Cytoplasmic membrane
SHP-1
p
Y Y p
SOCS3
JAK JAK
p p JAK SOCS1 Y
Y Y CIS JAK
STAT
STAT
STAT STAT
p p p
Y Y Y
p p STAT
Y Y SHP-1 STAT
PIAS
p
p SOCS family of cytokine
signaling inhibitors
Nucleus
STAT
STAT
Transcription Proteasome
Cytokine response genes
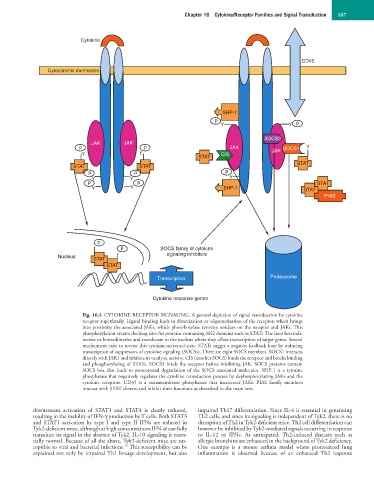
Fig. 16.4 CYTOKINE RECEPTOR SIGNALING. A general depiction of signal transduction by cytokine
receptor superfamily. Ligand binding leads to dimerization or oligomerization of the receptor, which brings
into proximity the associated JAKs, which phosphorylate tyrosine residues on the receptor and JAKs. This
.
phosphorylation creates docking sites for proteins containing SH2 domains such as STATs The later heterodi-
merize or homodimerize and translocate to the nucleus where they affect transcription of target genes. Several
mechanisms exist to reverse this cytokine-activated state. STATs trigger a negative feedback loop by inducing
transcription of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCSs). There are eight SOCS members. SOCS1 interacts
directly with JAK1 and inhibits its catalytic activity. CIS (another SOCS) binds the receptor and blocks binding
and phosphorylating of STATs. SOCS3 binds the receptor before inhibiting JAK. SOCS proteins contain
SOCS box that leads to proteosomal degradation of the SOCS associated molecules. SHP-1 is a tyrosine
phosphatase that negatively regulates the cytokine transduction process by dephosphorylating JAKs and the
cytokine receptors. CD45 is a transmembrane phosphatase that inactivates JAKs. PIAS family members
interact with STAT dimers and inhibit their functions as described in the main text.
downstream activation of STAT3 and STAT4 is clearly reduced, impaired Th17 differentiation. Since IL-4 is essential in generating
resulting in the inability of IFN-γ production by T cells. Both STAT3 Th2 cells, and since its signaling is independent of Tyk2, there is no
and STAT1 activation by type I and type II IFNs are reduced in disruption of Th2 in Tyk2-deficient mice. Th2 cell differentiation can
Tyk2-deficient mice, although at high concentrations IFN-α can fully however be inhibited by Tyk2-mediated signals occurring in response
transduce its signal in the absence of Tyk2. IL-10 signaling is essen- to IL-12 or IFNs. As anticipated, Th2-induced diseases such as
tially normal. Because of all the above, Tyk2-deficient mice are sus- allergic bronchitis are enhanced in the background of Tyk2 deficiency.
18
ceptible to viral and bacterial infections. This susceptibility can be One example is a mouse asthma model where pronounced lung
explained not only by impaired Th1 lineage development, but also inflammation is observed because of an enhanced Th2 response