Page 216 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 216
168 Part II Cellular Basis of Hematology
Pseudo-
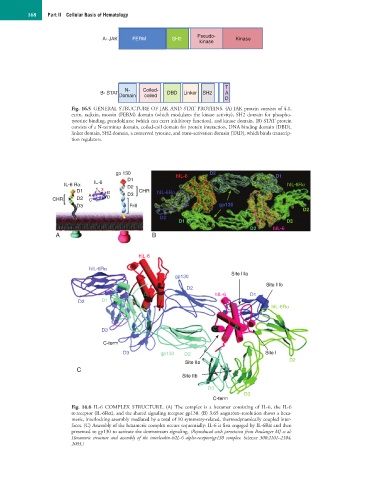
A- JAK FERM SH2 Kinase
kinase
T
N- Coiled-
B- STAT DBD Linker SH2 A
Domain coiled
D
Fig. 16.5 GENERAL STRUCTURE OF JAK AND STAT PROTEINS. (A) JAK protein consists of 4.1,
ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM) domain (which modulates the kinase activity), SH2 domain for phospho-
tyrosine binding, pseudokinase (which can exert inhibitory function), and kinase domain. (B) STAT protein
consists of a N-terminus domain, coiled-coil domain for protein interaction, DNA binding domain (DBD),
linker domain, SH2 domain, a conserved tyrosine, and trans-activation domain (TAD), which binds transcrip-
tion regulators.
gp 130 hIL-6 D2 D1
D1
IL-6 Rα IL-6 D2 hIL-6Rα
D1 1 3 B CHR hIL-6Rα
A D3
CHR D2 C D
D3 Frill gp130
D2
D2
D1 D3
D2 hIL-6
A B
hIL-6
hIL-6Rα B
Site IIIa
gp130
Site IIIb
D2
D C hIL-6 D1
D2 D1
A D hIL-6Rα
D3 C B
A
C-term
D3 gp130 D2 Site I
Site IIa D2
C
Site IIb
D3
D3
C-term
Fig. 16.6 IL-6 COMPLEX STRUCTURE. (A) The complex is a hexamer consisting of IL-6, the IL-6
α-receptor (IL-6Rα), and the shared signaling receptor gp130. (B) 3.65 angström–resolution shows a hexa-
meric, interlocking assembly mediated by a total of 10 symmetry-related, thermodynamically coupled inter-
faces. (C) Assembly of the hexameric complex occurs sequentially: IL-6 is first engaged by IL-6Rα and then
presented to gp130 to activate the downstream signaling. (Reproduced with permission from Boulanger MJ et al:
Hexameric structure and assembly of the interleukin-6/IL-6 alpha-receptor/gp130 complex. Science 300:2101–2104,
2003.)