Page 2217 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2217
1964 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
66 F: Admission for prosthetic valve endocarditis
300
Plt
250
tfns
200 IVIg
Platelet count (mean × 10 9 /L) 100 4 × 10 /L
x 2
150
Nadir
9
50
0
Heparin
Heparin
Ranitidine
Omeprazole
Carbamazepine, phenytoin Carbamazepine, valproate
Gentamicin and vancomycin Teicoplanin
Digoxin Digoxin
–2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
A Days after starting multiple drugs
Normal serum Normal serum
60 + buffer 60 + drug (vancomycin)
Events 40 Events 40
20 20
0 0
1 10 100 1000 1 10 100 1000
Fluorescence Fluorescence
Patient serum Patient serum
60 + buffer 60 + drug (vancomycin)
Events 40 Events 40
20 20
0 0
1 10 100 1000 1 10 100 1000
B Fluorescence Fluorescence
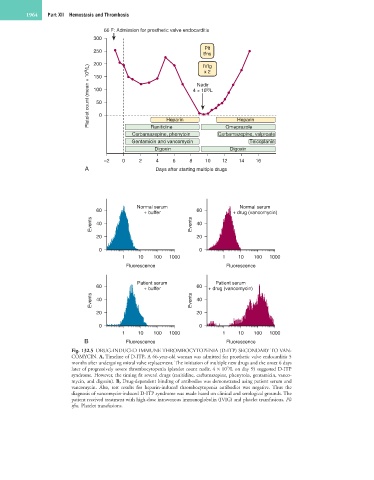
Fig. 132.5 DRUG-INDUCED IMMUNE THROMBOCYTOPENIA (D-ITP) SECONDARY TO VAN-
COMYCIN. A, Timeline of D-ITP. A 66-year-old woman was admitted for prosthetic valve endocarditis 5
months after undergoing mitral valve replacement. The initiation of multiple new drugs and the onset 6 days
later of progressively severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count nadir, 4 × 10 /L on day 9) suggested D-ITP
9
syndrome. However, the timing fit several drugs (ranitidine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, gentamicin, vanco-
mycin, and digoxin). B, Drug-dependent binding of antibodies was demonstrated using patient serum and
vancomycin. Also, test results for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies was negative. Thus the
diagnosis of vancomycin-induced D-ITP syndrome was made based on clinical and serological grounds. The
patient received treatment with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and platelet transfusions. Plt
tfns, Platelet transfusions.