Page 2232 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2232
Chapter 133 Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia 1979
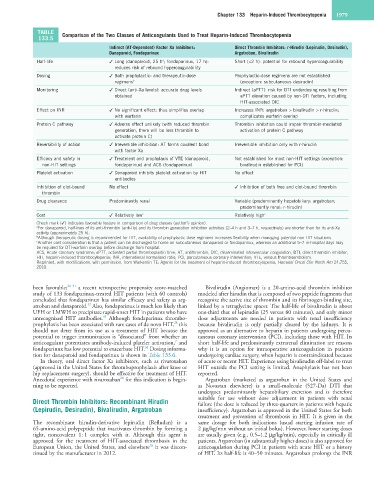
TABLE Comparison of the Two Classes of Anticoagulants Used to Treat Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
133.5
Indirect (AT-Dependent) Factor Xa Inhibitors: Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: r-Hirudin (Lepirudin, Desirudin),
Danaparoid, Fondaparinux Argatroban, Bivalirudin
a
Half-life ✓ Long (danaparoid, 25 h ; fondaparinux, 17 h): Short (<2 h): potential for rebound hypercoagulability
reduces risk of rebound hypercoagulability
Dosing ✓ Both prophylactic- and therapeutic-dose Prophylactic-dose regimens are not established
regimens b (exception: subcutaneous desirudin)
Monitoring ✓ Direct (anti-Xa levels): accurate drug levels Indirect (aPTT): risk for DTI underdosing resulting from
obtained aPTT elevation caused by non-DTI factors, including
HIT-associated DIC
Effect on INR ✓ No significant effect: thus simplifies overlap Increases INR: argatroban > bivalirudin > r-hirudin;
with warfarin complicates warfarin overlap
Protein C pathway ✓ Adverse effect unlikely (with reduced thrombin Thrombin inhibition could impair thrombin-mediated
generation, there will be less thrombin to activation of protein C pathway
activate protein C)
Reversibility of action ✓ Irreversible inhibition: AT forms covalent bond Irreversible inhibition only with r-hirudin
with factor Xa
Efficacy and safety in ✓ Treatment and prophylaxis of VTE (danaparoid, Not established for most non-HIT settings (exception:
non-HIT settings fondaparinux) and ACS (fondaparinux) bivalirudin established for PCI)
Platelet activation ✓ Danaparoid inhibits platelet activation by HIT No effect
antibodies
Inhibition of clot-bound No effect ✓ Inhibition of both free and clot-bound thrombin
thrombin
Drug clearance Predominantly renal Variable (predominantly hepatobiliary: argatroban;
predominantly renal: r-hirudin)
Cost ✓ Relatively low c Relatively high c
Check mark (✓) indicates favorable feature in comparison of drug classes (author’s opinion).
a For danaparoid, half-lives of its anti-thrombin (anti-IIa) and its thrombin generation inhibition activities (2–4 h and 3–7 h, respectively) are shorter than for its anti-Xa
activity (approximately 25 h).
b Although therapeutic dosing is recommended for HIT, availability of prophylactic-dose regimens increases flexibility when managing potential non-HIT situations.
c Another cost consideration is that a patient can be discharged to home on subcutaneous danaparoid or fondaparinux, whereas an additional 5–7 in-hospital days may
be required for DTI-warfarin overlap before discharge from hospital.
ACS, Acute coronary syndrome; aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; AT, antithrombin; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; DTI, direct thrombin inhibitor;
HIT, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; INR, international normalized ratio; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
Reprinted, with modifications, with permission, from Warkentin TE: Agents for the treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 24:755,
2010.
been favorable; 28–31 a recent retrospective propensity score-matched Bivalirudin (Angiomax) is a 20-amino-acid thrombin inhibitor
study of 133 fondaparinux-treated HIT patients (with 60 controls) modeled after hirudin that is composed of two peptide fragments that
concluded that fondaparinux has similar efficacy and safety as arg- recognize the active site of thrombin and its fibrinogen-binding site,
32
atroban and danaparoid. Also, fondaparinux is much less likely than linked by a tetraglycine spacer. The half-life of bivalirudin is about
UFH or LMWH to precipitate rapid-onset HIT in patients who have one-third that of lepirudin (25 versus 80 minutes), and only minor
33
unrecognized HIT antibodies. Although fondaparinux thrombo- dose adjustments are needed in patients with renal insufficiency
28
prophylaxis has been associated with rare cases of de novo HIT, this because bivalirudin is only partially cleared by the kidneys. It is
should not deter from its use as a treatment of HIT because the approved as an alternative to heparin in patients undergoing percu-
potential to trigger immunization is “dissociated” from whether an taneous coronary intervention (PCI), including those with HIT. Its
7
anticoagulant potentiates antibody-induced platelet activation, and short half-life and predominantly extrarenal elimination are reasons
33
fondaparinux has low potential to exacerbate HIT. Dosing informa- why it is an option for intraoperative anticoagulation in patients
tion for danaparoid and fondaparinux is shown in Table 133.6. undergoing cardiac surgery, when heparin is contraindicated because
In theory, oral direct factor Xa inhibitors, such as rivaroxaban of acute or recent HIT. Experience using bivalirudin off-label to treat
(approved in the United States for thromboprophylaxis after knee or HIT outside the PCI setting is limited. Anaphylaxis has not been
hip replacement surgery), should be effective for treatment of HIT. reported.
20
Anecdotal experience with rivaroxaban for this indication is begin- Argatroban (marketed as argatroban in the United States and
ning to be reported. as Novastan elsewhere) is a small-molecule (527-Da) DTI that
undergoes predominantly hepatobiliary excretion and is therefore
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: Recombinant Hirudin suitable for use without dose adjustment in patients with renal
failure (the dose is reduced by three-quarters in patients with hepatic
(Lepirudin, Desirudin), Bivalirudin, Argatroban insufficiency). Argatroban is approved in the United States for both
treatment and prevention of thrombosis in HIT. It is given in the
The recombinant hirudin-derivative lepirudin (Refludan) is a same dosage for both indications (usual starting infusion rate of
65-amino-acid polypeptide that inactivates thrombin by forming a 2 µg/kg/min without an initial bolus). However, lower starting doses
tight, noncovalent 1 : 1 complex with it. Although this agent is are usually given (e.g., 0.5–1.2 µg/kg/min), especially in critically ill
approved for the treatment of HIT-associated thrombosis in the patients. Argatroban (in substantially higher doses) is also approved for
26
European Union, the United States, and elsewhere it was discon- anticoagulation during PCI in patients with acute HIT or a history
tinued by the manufacturer in 2012. of HIT. Its half-life is 40–50 minutes. Argatroban prolongs the INR