Page 2233 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2233
1980 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
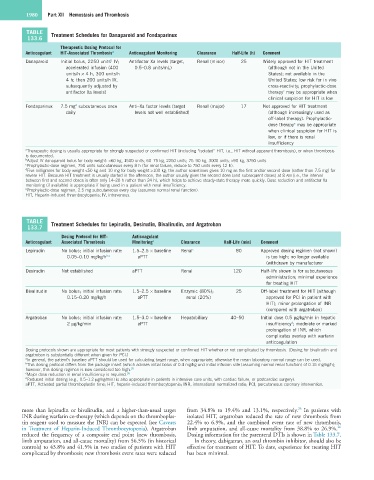
TABLE Treatment Schedules for Danaparoid and Fondaparinux
133.6
Therapeutic Dosing Protocol for
Anticoagulant HIT-Associated Thrombosis a Anticoagulant Monitoring Clearance Half-Life (h) Comment
b
Danaparoid Initial bolus, 2250 units IV; Antifactor Xa levels (target, Renal (minor) 25 Widely approved for HIT treatment
accelerated infusion (400 0.5–0.8 units/mL) (although not in the United
units/h × 4 h, 300 units/h States); not available in the
4 h; then 200 units/h IV, United States; low risk for in vivo
subsequently adjusted by cross-reactivity; prophylactic-dose
antifactor Xa levels) therapy may be appropriate when
c
clinical suspicion for HIT is low
Fondaparinux 7.5 mg subcutaneous once Anti–Xa factor levels (target Renal (major) 17 Not approved for HIT treatment
d
daily levels not well established) (although increasingly used as
off-label therapy). Prophylactic-
dose therapy may be appropriate
e
when clinical suspicion for HIT is
low, or if there is renal
insufficiency
a Therapeutic dosing is usually appropriate for strongly suspected or confirmed HIT (including “isolated” HIT, i.e., HIT without apparent thrombosis), or when thrombosis
is documented.
b Adjust IV danaparoid bolus for body weight: <60 kg, 1500 units; 60–75 kg, 2250 units; 75–90 kg, 3000 units; >90 kg, 3750 units.
c Prophylactic-dose regimen, 750 units subcutaneous every 8 h (for renal failure, reduce to 750 units every 12 h).
d Five milligrams for body weight <50 kg and 10 mg for body weight >100 kg; the author sometimes gives 10 mg as the first and/or second dose (rather than 7.5 mg) for
severe HIT. Because HIT treatment is usually started in the afternoon, the author usually gives the second dose (and subsequent doses) at 8 AM (i.e., the interval
between first and second doses is often only 14–20 h rather than 24 h), which helps to achieve steady-state therapy more quickly. Dose reduction and antifactor Xa
monitoring (if available) is appropriate if being used in a patient with renal insufficiency.
e Prophylactic-dose regimen, 2.5 mg subcutaneous every day (assumes normal renal function).
HIT, Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; IV, intravenous.
TABLE Treatment Schedules for Lepirudin, Desirudin, Bivalirudin, and Argatroban
133.7
Dosing Protocol for HIT- Anticoagulant
Anticoagulant Associated Thrombosis Monitoring a Clearance Half-Life (min) Comment
Lepirudin No bolus; initial infusion rate: 1.5–2.5 × baseline Renal c 80 Approved dosing regimen (not shown)
0.05–0.10 mg/kg/h b,c aPTT is too high; no longer available
(withdrawn by manufacturer
Desirudin Not established aPTT Renal 120 Half-life shown is for subcutaneous
administration; minimal experience
for treating HIT
Bivalirudin No bolus; initial infusion rate: 1.5–2.5 × baseline Enzymic (80%); 25 Off-label treatment for HIT (although
0.15–0.20 mg/kg/h aPTT renal (20%) approved for PCI in patient with
HIT); minor prolongation of INR
(compared with argatroban)
Argatroban No bolus; initial infusion rate: 1.5–3.0 × baseline Hepatobiliary 40–50 Initial dose 0.5 µg/kg/min in hepatic
2 µg/kg/min aPTT insufficiency ; moderate or marked
d
prolongation of INR, which
complicates overlap with warfarin
anticoagulation
Dosing protocols shown are appropriate for most patients with strongly suspected or confirmed HIT whether or not complicated by thrombosis. (Dosing for bivalirudin and
argatroban is substantially different when given for PCI.)
a In general, the patient’s baseline aPTT should be used for calculating target range, when appropriate; otherwise the mean laboratory normal range can be used.
b This dosing protocol differs from the package insert (which advises initial bolus of 0.4 mg/kg and initial infusion rate [assuming normal renal function] of 0.15 mg/kg/h);
however, this dosing regimen is now considered too high. 26
c Major dose reduction in renal insufficiency is required. 26
d Reduced initial dosing (e.g., 0.5–1.2 µg/kg/min) is also appropriate in patients in intensive care units, with cardiac failure, or postcardiac surgery).
aPTT, Activated partial thromboplastin time; HIT, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; INR, international normalized ratio; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention.
26
more than lepirudin or bivalirudin, and a higher-than-usual target from 34.8% to 19.4% and 13.1%, respectively. In patients with
INR during warfarin co-therapy (which depends on the thromboplas- isolated HIT, argatroban reduced the rate of new thrombosis from
tin reagent used to measure the INR) can be expected (see Caveats 22.4% to 6.9%, and the combined event rate of new thrombosis,
26
in Treatment of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia). Argatroban limb amputation, and all-cause mortality from 38.8% to 26.9%.
reduced the frequency of a composite end point (new thrombosis, Dosing information for the parenteral DTIs is shown in Table 133.7.
limb amputation, and all-cause mortality) from 56.5% (in historical In theory, dabigatran, an oral thrombin inhibitor, should also be
controls) to 43.8% and 41.5% in two studies of patients with HIT effective for treatment of HIT. To date, experience for treating HIT
complicated by thrombosis; new thrombosis event rates were reduced has been minimal.