Page 2564 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2564
Chapter 158 Hematologic Aspects of Parasitic Diseases 2287
procedure is examination of thick and thin blood films by an expert Artemisinin-based combination treatments have been the main-
to detect and speciate the malarial parasites. However, P. falciparum stay of treatment for falciparum malaria in Southeast Asia for more
and P. vivax malaria can be diagnosed almost as accurately using rapid than 10 years and are now recommended as first-line treatment
122
diagnostic tests (RDTs) that detect plasmodial antigens, depending throughout the rest of the world. However, resistance to these drugs
upon the product. However, RDTs for other Plasmodium species are is emerging, and very young children (particularly those underweight
not as reliable. 116 for age), patients with high parasitemias, and patients in very low
Amplification of circulating parasite DNA using the repeated transmission intensity areas with emerging parasite resistance are at
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes is an extremely sensitive method of risk for treatment failure and should be monitored closely. 120,121 The
117
malaria diagnosis. The sensitivity may be as low as 0.005 hematologic side effects of antimalarial drugs in use today are few.
parasites/µL or 5 parasites/mL. 118,119 Undoubtedly, this is a useful tool Amodiaquine is associated with neutropenia and agranulocytosis.
for reference laboratories and epidemiologic surveys. Artemisinin-based treatments may cause reticulocytopenia and
hemolysis in approximately 10% to 15% patients following intrave-
nous artesunate treatment. Hemoglobin concentrations should be
Treatment checked approximately 14 days following treatment in those treated
with intravenous artemisinins. 116
Malaria requires urgent effective chemotherapy to prevent progres- In severely ill patients, good nursing care is vital. Monitoring and
sion of disease and may be the most crucial public health intervention treatment of fits and hypoglycemia are essential, and antipyretics
123
to reduce global mortality from malaria. The drug treatment of should be given. Certainly, blood transfusion is in principle a
malaria must take account of the expected pattern of drug resistance straightforward solution to the treatment of severe malarial anemia,
in the area where infection was contracted, the severity of clinical although controversy exists over the trigger for transfusion and the
disease, and the species of parasite. The spread of drug-resistant para- rate of administration of blood. The standard regimens of cautious
sites and the optimal use of affordable, effective drugs are of continual and slow delivery of blood have been challenged by the demonstra-
concern, and these have recently been reviewed (Table 158.2). 116,120,121 tion that rapid initial flow rates may correct lactic acidosis and
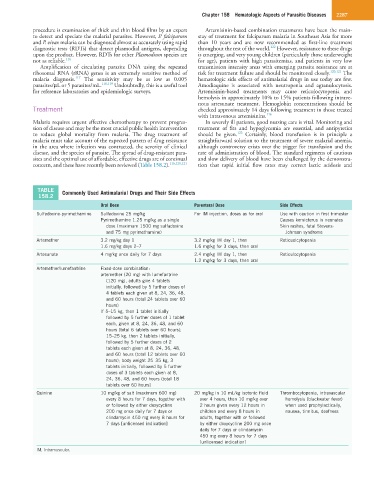
TABLE Commonly Used Antimalarial Drugs and Their Side Effects
158.2
Oral Dose Parenteral Dose Side Effects
Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine Sulfadoxine 25 mg/kg For IM injection, doses as for oral Use with caution in first trimester
Pyrimethamine 1.25 mg/kg as a single Causes kernicterus in neonates
dose (maximum 1500 mg sulfadoxine Skin rashes, fatal Stevens-
and 75 mg pyrimethamine) Johnson syndrome
Artemether 3.2 mg/kg day 1 3.2 mg/kg IM day 1, then Reticuolcytopenia
1.6 mg/kg days 2–7 1.6 mg/kg for 3 days, then oral
Artesunate 4 mg/kg once daily for 7 days 2.4 mg/kg IM day 1, then Reticulocytopenia
1.2 mg/kg for 3 days, then oral
Artemether/lumefantrine Fixed-dose combination:
artemether (20 mg) with lumefantrine
(120 mg), adults give 4 tablets
initially, followed by 5 further doses of
4 tablets each given at 8, 24, 36, 48,
and 60 hours (total 24 tablets over 60
hours)
If 5–15 kg, then 1 tablet initially
followed by 5 further doses of 1 tablet
each, given at 8, 24, 36, 48, and 60
hours (total 6 tablets over 60 hours);
15–25 kg, then 2 tablets initially,
followed by 5 further doses of 2
tablets each given at 8, 24, 36, 48,
and 60 hours (total 12 tablets over 60
hours); body weight 25–35 kg, 3
tablets initially, followed by 5 further
doses of 3 tablets each given at 8,
24, 36, 48, and 60 hours (total 18
tablets over 60 hours)
Quinine 10 mg/kg of salt (maximum 600 mg) 20 mg/kg in 10 mL/kg isotonic fluid Thrombocytopenia, intravascular
every 8 hours for 7 days, together with over 4 hours, then 10 mg/kg over hemolysis (blackwater fever)
or followed by either doxycycline 2 hours given every 12 hours in when used prophylactically,
200 mg once daily for 7 days or children and every 8 hours in nausea, tinnitus, deafness
clindamycin 450 mg every 8 hours for adults, together with or followed
7 days [unlicensed indication] by either doxycycline 200 mg once
daily for 7 days or clindamycin
450 mg every 8 hours for 7 days
[unlicensed indication]
IM, Intramuscular.