Page 272 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 272
Chapter 21 T-Cell Immunity 223
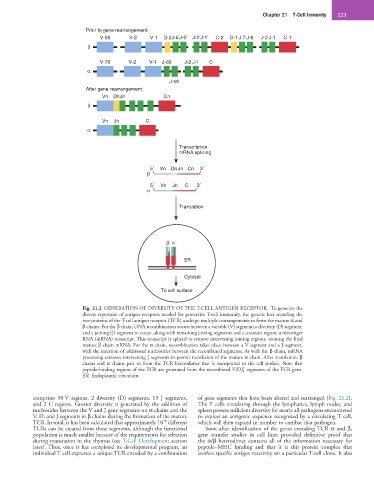
Prior to gene rearrangement:
V-50 V-2 V-1 D-2J-6 J-5 J-2 J-1 C-2 D-1 J-7 J-6 J-2 J-1 C-1
β
V-70 V-2 V-1 J-60 J-2 J-1 C
α
J-59
After gene rearrangement:
Vn DnJn Cn
β
Vn Jn C
α
Transcription
mRNA splicing
5 Vn DnJn Cn 3
β
5 Vn Jn C 3
α
Translation
β α
ER
Cytosol
To cell surface
Fig. 21.2 GENERATION OF DIVERSITY OF THE T-CELL ANTIGEN RECEPTOR. To generate the
diverse repertoire of antigen receptors needed for protective T-cell immunity, the genetic loci encoding the
two proteins of the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) undergo multiple rearrangements to form the mature α and
β chains. For the β chain, DNA recombination occurs between a variable (V) segment, a diversity (D) segment,
and a joining (J) segment to create, along with remaining joining segments and a constant region, a messenger
RNA (mRNA) transcript. This transcript is spliced to remove intervening joining regions, creating the final
mature β chain mRNA. For the α chain, recombination takes place between a V segment and a J segment,
with the insertion of additional nucleotides between the recombined segments. As with the β chain, mRNA
processing removes intervening J segments to permit translation of the mature α chain. After translation, β
chains and α chains pair to form the TCR heterodimer that is transported to the cell surface. Note that
peptide-binding regions of the TCR are generated from the recombined V(D)J segments of the TCR gene.
ER, Endoplasmic reticulum.
comprises 50 V regions, 2 diversity (D) segments, 13 J segments, of gene segments that have been altered and rearranged (Fig. 21.2).
and 2 C regions. Greater diversity is generated by the addition of The T cells circulating through the lymphatics, lymph nodes, and
nucleotides between the V and J gene segments on α chains and the spleen possess sufficient diversity for nearly all pathogens encountered
V, D, and J segments in β chains during the formation of the mature to express an antigenic sequence recognized by a circulating T cell,
18
TCR. In total, it has been calculated that approximately 10 different which will then expand in number to combat that pathogen.
TCRs can be created from these segments, although the functional Soon after identification of the genes encoding TCR α and β,
population is much smaller because of the requirements for selection gene transfer studies in cell lines provided definitive proof that
during maturation in the thymus (see T-Cell Development section the α/β heterodimer contains all of the information necessary for
later). Thus, once it has completed its developmental program, an peptide–MHC binding and that it is this protein complex that
individual T cell expresses a unique TCR encoded by a combination confers specific antigen reactivity on a particular T-cell clone. It also