Page 274 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 274
Chapter 21 T-Cell Immunity 225
TCR complex
α β
PKC θ DAG
PIP 2 Hydrolysis
RasGRP
NK-κB IP 3 LAT
activation Ras Itk PLCγ1 P
P P
Erk Ca 2+ Vav P P
Nck SLP-76 Gads
PTK
AP-1 Activation
activation NFAT P
activation ADAP
Cytoskeletal Integrin activation
Reorganization
Transcriptional
activation
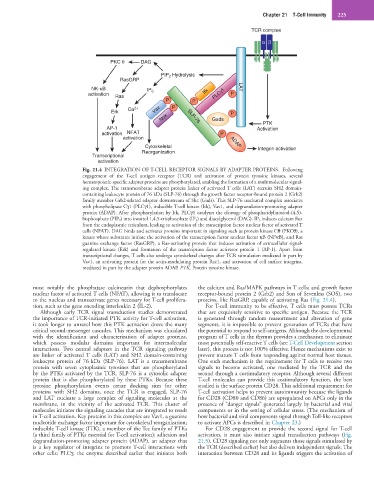
Fig. 21.4 INTEGRATION OF T-CELL RECEPTOR SIGNALS BY ADAPTER PROTEINS. Following
engagement of the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) and activation of protein tyrosine kinases, several
hematopoietic-specific adapter proteins are phosphorylated, enabling the formation of a multimolecular signal-
ing complex. The transmembrane adapter protein linker of activated T cells (LAT) recruits SH2 domain-
containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76) through the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2)
family member Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc (Gads). This SLP-76 nucleated complex associates
with phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1), inducible T-cell kinase (Itk), Vav1, and degranulation-promoting adapter
protein (ADAP). After phosphorylation by Itk, PLCγ1 catalyzes the cleavage of phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-
bisphosphate (PIP 2) into inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP 3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP 3 induces calcium flux
from the endoplasmic reticulum, leading to activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T
cells (NFAT). DAG binds and activates proteins important in signaling such as protein kinase Cθ (PKCθ), a
kinase whose substrates initiate the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NFκB), and Ras
guanine exchange factor (RasGRP), a Ras-activating protein that induces activation of extracellular signal-
regulated kinase (Erk) and formation of the transcription factor activator protein 1 (AP-1). Apart from
transcriptional changes, T cells also undergo cytoskeletal changes after TCR stimulation mediated in part by
Vav1, an activating protein for the actin-modulating protein Rac1, and activation of cell surface integrins,
mediated in part by the adapter protein ADAP. PTK, Protein tyrosine kinase.
most notably the phosphatase calcineurin that dephosphorylates the calcium and Ras/MAPK pathways in T cells; and growth factor
nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), allowing it to translocate receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) and Son of Sevenless (SOS), two
to the nucleus and transactivate genes necessary for T-cell prolifera- proteins, like RasGRP, capable of activating Ras (Fig. 21.4).
tion, such as the gene encoding interleukin 2 (IL-2). For T-cell immunity to be effective, T cells must possess TCRs
Although early TCR signal transduction studies demonstrated that are exquisitely sensitive to specific antigen. Because the TCR
the importance of TCR-initiated PTK activity for T-cell activation, is generated through random reassortment and alteration of gene
it took longer to unravel how this PTK activation drove the many segments, it is impossible to prevent generation of TCRs that have
critical second-messenger cascades. This mechanism was elucidated the potential to respond to self-antigens. Although the developmental
with the identification and characterization of adapter proteins, program of T cells in the thymus provides a mechanism to eliminate
which possess modular domains important for intermolecular most potentially self-reactive T cells (see T-Cell Development section
interactions. Two central adapters in the TCR signaling pathway later), this process is not 100% effective. Hence mechanisms exist to
are linker of activated T cells (LAT) and SH2 domain-containing prevent mature T cells from responding against normal host tissues.
leukocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76). LAT is a transmembrane One such mechanism is the requirement for T cells to receive two
protein with seven cytoplasmic tyrosines that are phosphorylated signals to become activated, one mediated by the TCR and the
by the PTKs activated by the TCR. SLP-76 is a cytosolic adapter second through a costimulatory receptor. Although several different
protein that is also phosphorylated by these PTKs. Because these T-cell molecules can provide this costimulatory function, the best
tyrosine phosphorylation events create docking sites for other studied is the surface protein CD28. This additional requirement for
proteins with SH2 domains, once the TCR is engaged, SLP-76 T-cell activation helps to prevent autoimmunity because the ligands
and LAT nucleate a large complex of signaling molecules at the for CD28 (CD80 and CD86) are upregulated on APCs only in the
membrane, in the vicinity of the activated TCR. This cluster of presence of “danger signals” generated largely by bacterial and viral
molecules initiates the signaling cascades that are integrated to result components or in the setting of cellular stress. (The mechanism of
in T-cell activation. Key proteins in this complex are Vav1, a guanine how bacterial and viral components signal through Toll-like receptors
nucleotide exchange factor important for cytoskeletal reorganization; to activate APCs is described in Chapter 23.)
inducible T-cell kinase (ITK), a member of the Tec family of PTKs For CD28 engagement to provide the second signal for T-cell
(a third family of PTKs essential for T-cell activation); adhesion and activation, it must also initiate signal transduction pathways (Fig.
degranulation-promoting adapter protein (ADAP), an adapter that 21.5). CD28 signaling not only augments those signals stimulated by
is a key regulator of integrins to promote T-cell interactions with the TCR (described earlier) but also delivers independent signals. The
other cells; PLCγ, the enzyme described earlier that initiates both interaction between CD28 and its ligands triggers the activation of