Page 273 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 273
224 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
became apparent that although sufficient to bind peptide–MHC, the T cells. Exactly how TCR engagement initiates PTK activation
the α/β heterodimer was not capable of transmitting an intracellular remains unclear; however, clustering of TCRs on the cell surface
signal once ligand was bound. A series of studies, first in cell lines with resultant conformational changes in the CD3 proteins appears
and then in mouse models, demonstrated that the signal transduction critical in the process. Src family (Lck and Fyn) PTKs are activated
function of the TCR complex resides in a protein complex that first following TCR stimulation, and the tyrosines within the CD3
associates noncovalently with the α/β dimer. This complex, CD3, is and ζ ITAMs are substrates of these kinases. Phosphorylation of the
required both for stable expression of the ligand-binding components ITAM tyrosines makes these residues able to bind to Src homology 2
of the TCR and for signal transduction. CD3 is composed of three (SH2) domains of other proteins. The most important SH2 domain-
subunits, δ, ε, and γ, expressed as heterodimers (γ/ε and δ/ε) along containing protein that is recruited to the ITAMs is ζ-associated
with the ζ subunit, which is present as a homodimer. Each subunit protein of 70 kDa (ZAP-70), a PTK itself and a member of the Syk
contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs), family of proteins. Thus binding of the TCR by ligand converts an
a stretch of amino acids with discretely placed tyrosine residues: one enzymatically inactive receptor complex into an active PTK through
ITAM in δ, ε, and γ and three ITAMS in ζ. The ITAM tyrosines recruitment and activation of cytosolic proteins.
are key for the CD3 and ζ chains to transduce signals and are Activation of ZAP-70 leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of a
inducibly phosphorylated upon engagement of the α/β TCR chains number of substrates, including enzymes that catalyze reactions
by peptide–MHC. Upon their phosphorylation, the ITAMs become generating second messengers important for T-cell activation. Phos-
docking sites for other proteins that initiate the signaling cascade for pholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) is activated by its tyrosine phosphorylation to
T-cell activation. Notably, the CD4 or CD8 protein also plays a role cleave phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP 2) into the second
in mediating signal transduction. These coreceptors bind both the messengers diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-(1,4,5)-triphosphate
appropriate MHC complex (MHC I for CD8, MHC II for CD4) (IP 3). DAG is a lipid second messenger that binds to and activates
and, via their cytoplasmic tails, the signaling molecule Lck, one of the downstream signaling components, including protein kinase C θ
kinases capable of phosphorylating the ITAMs (Fig. 21.3). (PKCθ) and the Ras guanine exchange factor RasGRP. PKCθ, a serine/
threonine kinase, regulates numerous effectors of gene transcription
and T-cell effector function development, including the transcription
T-Cell Receptor Signal Transduction factors nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and activator protein 1 (AP-1).
RasGRP is responsible for activating the small molecular weight
Once the genes were cloned for each TCR complex component, guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein Ras by enhancing
it became clear that, unlike many other cell surface receptors that Ras release of GDP, allowing it to assume its activated GTP-bound
transduce activating signals, neither the ligand-binding domains nor form. Active Ras collaborates with PKC family members to stimulate
the CD3 proteins of the complex have intrinsic enzymatic function. transcription of new genes by activating mitogen-activated protein
Engagement of the TCR by the peptide–MHC was found to result kinase (MAPK) family members. IP 3 mobilizes calcium stores from
in the rapid activation of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) within the ER. This increase in calcium is important for enzyme function,
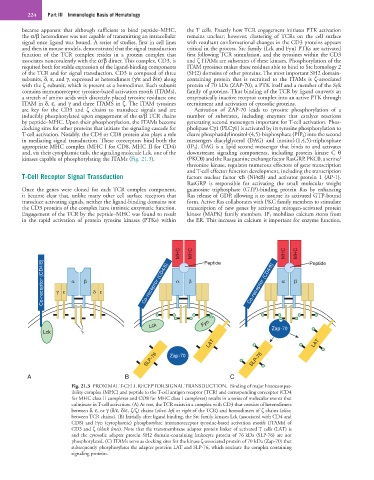
MHC MHC Peptide MHC MHC Peptide
Co-receptor (CD4/8) γ ε α β δ ε Co-receptor (CD4/8) α β Co-receptor (CD4/8) α β
Lck Fyn Zap-70
Lck ζ
LAT LAT
SLP-76 Zap-70 SLP-76
A B C
Fig. 21.3 PROXIMAL T-CELL RECEPTOR SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION. Binding of major histocompat-
ibility complex (MHC) and peptide to the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) and corresponding coreceptor (CD4
for MHC class II complexes and CD8 for MHC class I complexes) results in a series of molecular events that
culminate in T-cell activation. (A) At rest, the TCR exists in a complex with CD3 that consists of heterodimers
between δ, ε, or γ (δ/ε, δ/ε, ζ/ζ) chains (olive, left or right of the TCR) and homodimers of ζ chains (olive,
between TCR chains). (B) Initially after ligand binding, the Src family kinases Lck (associated with CD4 and
CD8) and Fyn (cytoplasmic) phosphorylate immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) of
CD3 and ζ (black lines). Note that the transmembrane adapter protein linker of activated T cells (LAT) is
and the cytosolic adapter protein SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76) are not
phosphorylated. (C) ITAMs serve as docking sites for the kinase ζ-associated protein of 70 kDa (Zap-70) that
subsequently phosphorylates the adapter proteins LAT and SLP-76, which nucleate the complex containing
signaling proteins.