Page 328 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 328
270 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
SCR1
C3d SCR2
Ag
CR2
κ
BCR complex
µ CD19
CD81
β α
P Y Y P
lyn Y Y Y P PI3K
P P syk Augmented signaling Y
syk Y
P
Y vav
A
Cytosol
FDC plasma membrane SCR1
FcγR
S18
L44 K57
V26
Y16 Q50
CD21/CR2
R28
E166 R49
K108 D163 R13
C3d S30
Ag
SCR2 K41
SCR2 SCR1
κ E37
R83
E39
BCR complex D92
µ K251
β α
B cell centrocyte plasma membrane
lyn P Y Y P Cytosol
B P Y Y P syk C
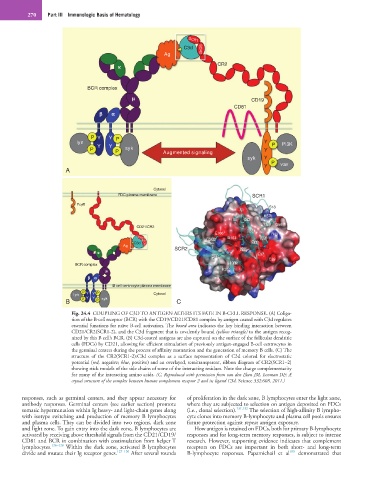
Fig. 24.4 COUPLING OF C3D TO ANTIGEN ALTERS ITS FATE IN B-CELL RESPONSE. (A) Coliga-
tion of the B-cell receptor (BCR) with the CD19/CD21/CD81 complex by antigen coated with C3d regulates
essential functions for naïve B-cell activation. The boxed area indicates the key binding interaction between
CD21/CR2(SCR1-2), and the C3d fragment that is covalently bound (yellow triangle) to the antigen recog-
nized by this B cell’s BCR. (B) C3d-coated antigens are also captured on the surface of the follicular dendritic
cells (FDCs) by CD21, allowing for efficient stimulation of previously antigen-engaged B-cell centrocytes in
the germinal centers during the process of affinity maturation and the generation of memory B cells. (C) The
structure of the CR2(SCR1-2):C3d complex as a surface representation of C3d colored for electrostatic
potential (red, negative; blue, positive) and an overlayed, semitransparent, ribbon diagram of CR2(SCR1–2)
showing stick models of the side chains of some of the interacting residues. Note the charge complementarity
for many of the interacting amino acids. (C, Reproduced with permission from van den Elsen JM, Isenman DE: A
crystal structure of the complex between human complement receptor 2 and its ligand C3d. Science 332:608, 2011.)
responses, such as germinal centers, and they appear necessary for of proliferation in the dark zone, B lymphocytes enter the light zone,
antibody responses. Germinal centers (see earlier section) promote where they are subjected to selection on antigen deposited on FDCs
somatic hypermutation within Ig heavy- and light-chain genes along (i.e., clonal selection). 131,132 The selection of high-affinity B lympho-
with isotype switching and production of memory B lymphocytes cyte clones into memory B-lymphocyte and plasma cell pools ensures
and plasma cells. They can be divided into two regions, dark zone future protection against repeat antigen exposure.
and light zone. To gain entry into the dark zone, B lymphocytes are How antigen is retained on FDCs, both for primary B-lymphocyte
activated by receiving above threshold signals from the CD21/CD19/ responses and for long-term memory responses, is subject to intense
CD81 and BCR in combination with costimulation from helper T research. However, supporting evidence indicates that complement
lymphocytes. 126–128 Within the dark zone, activated B lymphocytes receptors on FDCs are important in both short- and long-term
105
divide and mutate their Ig receptor genes. 127–130 After several rounds B-lymphocyte responses. Papamichail et al demonstrated that