Page 329 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 329
Chapter 24 Complement and Immunoglobulin Biology Leading to Clinical Translation 271
Strain HD-2 Strain HD-2
100 100
90 Wild type 90 Wild type
C3–/– C3–/–
80 C4–/– 80 Cr2–/–
Anti HSV-I lgG titer (×10 –3 ) 60 Anti HSV-I lgG titer (×10 –3 ) 60
70
70
50
50
40
40
30
20
20 30
10 10
0 0
0 2 4 6 0 2 4 6
A Week B Week
Strain HD-2 Strain KOS 1.1
100 100
90 Wild type 90 Wild type
C3–/– C3–/–
80 Cr2–/– 80 C4–/–
Anti βgal IgG titer (×10 –3 ) 60 Anti HSV-I lgG titer (×10 –3 ) 60
70
70
50
50
40
40
30
20 30
20
10 10
0 0
0 2 4 6 0 2 4 6
C Week D Week
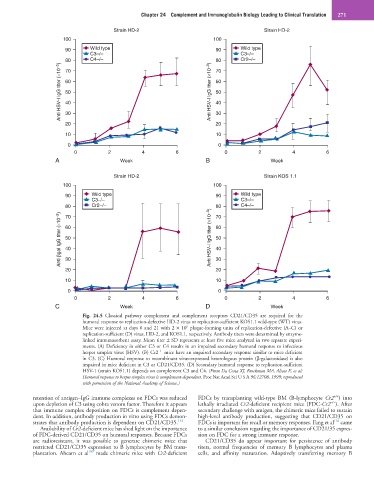
Fig. 24.5 Classical pathway complement and complement receptors CD21/CD35 are required for the
humoral response to replication-defective HD-2 virus or replication-sufficient KOS1.1 wild-type (WT) virus.
Mice were injected at days 0 and 21 with 2 × 10 plaque-forming units of replication-defective (A–C) or
6
replication-sufficient (D) virus, HD-2, and KOS1.1, respectively. Antibody titers were determined by enzyme-
linked immunosorbent assay. Mean titer ± SD represents at least five mice analyzed in two separate experi-
ments. (A) Deficiency in either C3 or C4 results in an impaired secondary humoral response to infectious
−/−
herpes simplex virus (HSV). (B) Cr2 mice have an impaired secondary response similar to mice deficient
in C3. (C) Humoral response to recombinant virus-expressed heterologous protein (β-galactosidase) is also
impaired in mice deficient in C3 or CD21/CD35. (D) Secondary humoral response to replication-sufficient
HSV-1 (strain KOS1.1) depends on complement C3 and C4. (From Da Costa XJ, Brockman MA, Alicot E, et al:
Humoral response to herpes simplex virus is complement-dependent. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 96:12708, 1999; reproduced
with permission of the National Academy of Science.)
+/+
retention of antigen–IgG immune complexes on FDCs was reduced FDCs by transplanting wild-type BM (B-lymphocyte Cr2 ) into
−/−
upon depletion of C3 using cobra venom factor. Therefore it appears lethally irradiated Cr2-deficient recipient mice (FDC-Cr2 ). After
that immune complex deposition on FDCs is complement depen- secondary challenge with antigen, the chimeric mice failed to sustain
dent. In addition, antibody production in vitro using FDCs demon- high-level antibody production, suggesting that CD21/CD35 on
134
strates that antibody production is dependent on CD21/CD35. 133 FDCs is important for recall or memory responses. Fang et al came
Availability of Cr2-deficient mice has shed light on the importance to a similar conclusion regarding the importance of CD21/35 expres-
of FDC-derived CD21/CD35 on humoral responses. Because FDCs sion on FDC for a strong immune response.
are radioresistant, it was possible to generate chimeric mice that CD21/CD35 do appear important for persistence of antibody
restricted CD21/CD35 expression to B lymphocytes by BM trans- titers, normal frequencies of memory B lymphocytes and plasma
109
plantation. Ahearn et al made chimeric mice with Cr2-deficient cells, and affinity maturation. Adoptively transferring memory B