Page 330 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 330
272 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
Spleen/bone marrow
B-cell Spleen Germinal
compartment center lgG lo
T-cell
compartment B B CD21 hi
−
B B T FDC CD23 Antigen
Memory selection
B compartment
Mature
µ+ Expansion Long-term Short-term
δ+ effector cells effector cells
CD21+ Antigen T
CD23+ B B B selection
B B
CD21/ CD19 FcγR MHC
TCR BCR antigen C3d CD35 peptide
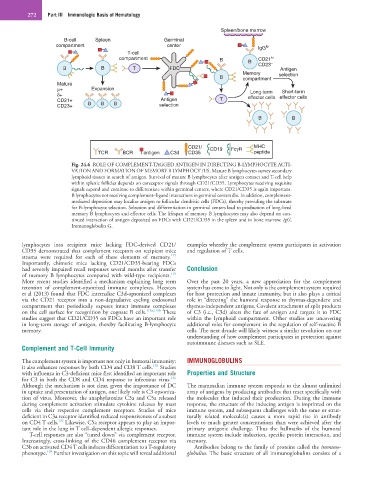
Fig. 24.6 ROLE OF COMPLEMENT-TAGGED ANTIGEN IN DIRECTING B-LYMPHOCYTE ACTI-
VATION AND FORMATION OF MEMORY B LYMPHOCYTES. Mature B lymphocytes survey secondary
lymphoid tissues in search of antigen. Survival of mature B lymphocytes after antigen contact and T-cell help
within splenic follicles depends on coreceptor signals through CD21/CD35. Lymphocytes receiving requisite
signals expand and continue to differentiate within germinal centers, where CD21/CD35 is again important.
B lymphocytes not receiving complement–ligand interactions in germinal centers die. In addition, complement-
mediated deposition may localize antigen to follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), thereby providing the substrate
for B-lymphocyte selection. Selection and differentiation in germinal centers lead to production of long-lived
memory B lymphocytes and effector cells. The lifespan of memory B lymphocytes may also depend on con-
tinued interaction of antigen deposited on FDCs with CD21/CD35 in the spleen and in bone marrow. IgG,
Immunoglobulin G.
lymphocytes into recipient mice lacking FDC-derived CD21/ examples whereby the complement system participates in activation
CD35 demonstrated that complement receptors on recipient mice and regulation of T cells.
115
stroma were required for each of these elements of memory.
Importantly, chimeric mice lacking CD21/CD35-bearing FDCs
had severely impaired recall responses several months after transfer Conclusion
115
of memory B lymphocytes compared with wild-type recipients.
More recent studies identified a mechanism explaining long term Over the past 20 years, a new appreciation for the complement
retention of complement-opsonized immune complexes. Heesters system has come to light. Not only is the complement system required
et al (2013) found that FDC internalize C3d-opsonized complexes for host protection and innate immunity, but it also plays a critical
via the CD21 receptor into a non-degradative cycling endosomal role in “directing” the humoral response to thymus-dependent and
compartment that periodically exposes intact immune complexes thymus-independent antigens. Covalent attachment of split products
on the cell surface for recognition by cognate B cells. 115a,115b These of C3 (i.e., C3d) alters the fate of antigen and targets it to FDC
studies suggest that CD21/CD35 on FDCs have an important role within the lymphoid compartment. Other studies are uncovering
in long-term storage of antigen, thereby facilitating B-lymphocyte additional roles for complement in the regulation of self-reactive B
memory. cells. The next decade will likely witness a similar revolution on our
understanding of how complement participates in protection against
autoimmune diseases such as SLE.
Complement and T-Cell Immunity
The complement system is important not only in humoral immunity; IMMUNOGLOBULINS
135
it also enhances responses by both CD4 and CD8 T cells. Studies
with influenza in C3-deficient mice first identified an important role Properties and Structure
136
for C3 in both the CD8 and CD4 response to infectious virus.
Although the mechanism is not clear, given the importance of DC The mammalian immune system responds to the almost unlimited
in uptake and presentation of antigen, one likely role is C3 opsoniza- array of antigens by producing antibodies that react specifically with
tion of virus. Moreover, the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a released the molecules that induced their production. During the immune
during complement activation stimulate cytokine releases by mast response, the structure of the inducing antigen is imprinted on the
cells via their respective complement receptors. Studies of mice immune system, and subsequent challenges with the same or struc-
deficient in C3a receptor identified reduced responsiveness of a subset turally related molecule(s) causes a more rapid rise in antibody
137
on CD4 T cells. Likewise, C5a receptor appears to play an impor- levels to much greater concentrations than were achieved after the
tant role in the lung in T cell–dependent allergic responses. primary antigenic challenge. Thus the hallmarks of the humoral
T-cell responses are also “tuned down” via complement receptor. immune system include induction, specific protein interaction, and
Interestingly, cross-linking of the CD46 complement receptor via memory.
C3b on activated CD4 T cells induces differentiation to a T-regulatory Antibodies belong to the family of proteins called the immuno-
138
phenotype. Further investigation on this topic will reveal additional globulins. The basic structure of all immunoglobulins consists of a