Page 415 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 415
336 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
A B C
D E F G H
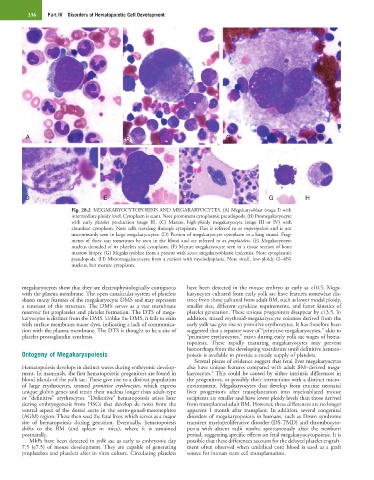
Fig. 28.2 MEGAKARYOCYTOPOEISIS AND MEGAKARYOCYTES. (A) Megakaryoblast (stage I) with
intermediate ploidy level. Cytoplasm is scant. Note prominent cytoplasmic pseudopods. (B) Promegakaryocyte
with early platelet production (stage II). (C) Mature, high-ploidy megakaryocyte (stage III or IV) with
abundant cytoplasm. Note cells traveling through cytoplasm. This is referred to as emperipolesis and is not
uncommonly seen in large megakaryocytes. (D) Portion of megakaryocyte cytoplasm in a long strand. Frag-
ments of these can sometimes be seen in the blood and are referred to as proplatelets. (E) Megakaryocyte
nucleus denuded of its platelets and cytoplasm. (F) Mature megakaryocyte seen in a tissue section of bone
marrow biopsy. (G) Megakaryoblast from a patient with acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Note cytoplasmic
pseudopods. (H) Micromegakaryocyte from a patient with myelodysplasia. Note small, low-ploidy (2−4N)
nucleus, but mature cytoplasm.
megakaryocytes show that they are electrophysiologically contiguous have been detected in the mouse embryo as early as e10.5. Mega-
with the plasma membrane. The open canalicular system of platelets karyocytes cultured from early yolk sac have features somewhat dis-
shares many features of the megakaryocyte DMS and may represent tinct from those cultured from adult BM, such as lower modal ploidy,
a remnant of this structure. The DMS serves as a vast membrane smaller size, different cytokine requirements, and faster kinetics of
reservoir for proplatelet and platelet formation. The DTS of mega- platelet generation. These unique progenitors disappear by e13.5. In
karyocytes is distinct from the DMS. Unlike the DMS, it fails to stain addition, mixed erythroid-megakaryocyte colonies derived from the
with surface membrane tracer dyes, indicating a lack of communica- early yolk sac give rise to primitive erythrocytes. It has therefore been
tion with the plasma membrane. The DTS is thought to be a site of suggested that a separate wave of “primitive megakaryocytes,” akin to
platelet prostaglandin synthesis. “primitive erythrocytes,” exists during early yolk sac stages of hema-
topoiesis. These rapidly maturing megakaryocytes may prevent
hemorrhage from the developing vasculature until definitive hemato-
Ontogeny of Megakaryopoiesis poiesis is available to provide a steady supply of platelets.
Several pieces of evidence suggest that fetal liver megakaryocytes
Hematopoiesis develops in distinct waves during embryonic develop- also have unique features compared with adult BM–derived mega-
4
ment. In mammals, the first hematopoietic progenitors are found in karyocytes. This could be caused by either intrinsic differences in
blood islands of the yolk sac. These give rise to a distinct population the progenitors, or possibly their interactions with a distinct micro-
of large erythrocytes, termed primitive erythrocytes, which express environment. Megakaryocytes that develop from murine neonatal
unique globin genes and retain their nucleus longer than adult-type liver progenitors after transplantation into myeloablated mouse
or “definitive” erythrocytes. “Definitive” hematopoiesis arises later recipients are smaller and have lower ploidy levels than those derived
during embryogenesis from HSCs that develop de novo from the from transplanted adult BM. However, these differences are no longer
ventral aspect of the dorsal aorta in the aorto-gonad-mesonephros apparent 1 month after transplant. In addition, several congenital
(AGM) region. These then seed the fetal liver, which serves as a major disorders of megakaryopoiesis in humans, such as Down syndrome
site of hematopoiesis during gestation. Eventually, hematopoiesis transient myeloproliferative disorder (DS-TMD) and thrombocyto-
shifts to the BM (and spleen in mice), where it is sustained penia with absent radii resolve spontaneously after the newborn
postnatally. period, suggesting specific effects on fetal megakaryocytopoiesis. It is
MkPs have been detected in yolk sac as early as embryonic day possible that these differences account for the delayed platelet engraft-
7.5 (e7.5) of mouse development. They are capable of generating ment often observed when umbilical cord blood is used as a graft
proplatelets and platelets after in vitro culture. Circulating platelets source for human stem cell transplantation.