Page 420 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 420
Chapter 28 Thrombocytopoiesis 341
4N 4N 4N 4N 4N
2N early prophase late prophase metaphase anaphase A anaphase B
Normal
mitosis
4N
8N 8N 4N Endomitosis cytokinesis
late prophase early prophase Gap phase
2N 2N
8N 8N 8N
metaphase Uneven anaphase A (gap phase)
chromosome
segregation
16N and etc.
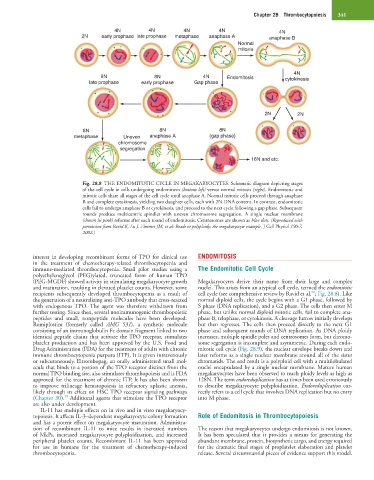
Fig. 28.8 THE ENDOMITOTIC CYCLE IN MEGAKARYOCYTES. Schematic diagram depicting stages
of the cell cycle in cells undergoing endomitosis (bottom left) versus normal mitosis (right). Endomitotic and
mitotic cells share all stages of the cell cycle until anaphase A. Normal mitotic cells proceed through anaphase
B and complete cytokinesis, yielding two daughter cells, each with 2N DNA content. In contrast, endomitotic
cells fail to undergo anaphase B or cytokinesis, and proceed to the next cycle following a gap phase. Subsequent
rounds produce multicentric spindles with uneven chromosome segregation. A single nuclear membrane
(shown in pink) reforms after each round of endomitosis. Centrosomes are shown as blue dots. (Reproduced with
permission from Ravid K, Lu J, Zimmet JM, et al: Roads to polyploidy: the megakaryocyte example. J Cell Physiol 190:7,
2002.)
interest in developing recombinant forms of TPO for clinical use ENDOMITOSIS
in the treatment of chemotherapy-related thrombocytopenia and
immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. Small pilot studies using a The Endomitotic Cell Cycle
polyethyleneglycol (PEG)ylated, truncated form of human TPO
(PEG-MGDF) showed activity in stimulating megakaryocyte growth Megakaryocytes derive their name from their large and complex
and maturation, resulting in elevated platelet counts. However, some nuclei. This arises from an atypical cell cycle, termed the endomitotic
20
recipients subsequently developed thrombocytopenia as a result of cell cycle (see comprehensive review by Ravid et al. ; Fig. 28.8). Like
the generation of a neutralizing anti-TPO antibody that cross-reacted normal diploid cells, the cycle begins with a G1 phase, followed by
with endogenous TPO. The agent was therefore withdrawn from S phase (DNA replication), and a G2 phase. The cells then enter M
further testing. Since then, several nonimmunogenic thrombopoietic phase, but unlike normal diploid mitotic cells, fail to complete ana-
peptides and small, nonpeptide molecules have been developed. phase B, telophase, or cytokinesis. A cleavage furrow initially develops
Romiplostim (formerly called AMG 531), a synthetic molecule but then regresses. The cells then proceed directly to the next G1
consisting of an immunoglobulin Fc domain fragment linked to two phase and subsequent rounds of DNA replication. As DNA ploidy
identical peptide chains that activate the TPO receptor, stimulates increases, multiple spindle poles and centrosomes form, but chromo-
platelet production and has been approved by the U.S. Food and some segregation is incomplete and asymmetric. During each endo-
Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adults with chronic mitotic cell cycle (Fig. 28.9), the nuclear envelope breaks down and
immune thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP). It is given intravenously later reforms as a single nuclear membrane around all of the sister
or subcutaneously. Eltrombopag, an orally administered small mol- chromatids. The end result is a polyploid cell with a multilobulated
ecule that binds to a portion of the TPO receptor distinct from the nuclei encapsulated by a single nuclear membrane. Mature human
normal TPO binding site, also stimulates thrombopoiesis and is FDA megakaryocytes have been observed to reach ploidy levels as high as
approved for the treatment of chronic ITP. It has also been shown 128N. The term endoreduplication has at times been used erroneously
to improve trilineage hematopoiesis in refractory aplastic anemia, to describe megakaryocyte polyploidization. Endoreduplication cor-
likely through its effect on HSC TPO receptor signaling pathways rectly refers to a cell cycle that involves DNA replication but no entry
19
(Chapter 30). Additional agents that stimulate the TPO receptor into M phase.
are also under development.
IL-11 has multiple effects on in vivo and in vitro megakaryocy-
topoiesis. It affects IL-3–dependent megakaryocyte colony formation Role of Endomitosis in Thrombocytopoiesis
and has a potent effect on megakaryocyte maturation. Administra-
tion of recombinant IL-11 to mice results in increased numbers The reason that megakaryocytes undergo endomitosis is not known.
of MkPs, increased megakaryocyte polyploidization, and increased It has been speculated that it provides a means for generating the
peripheral platelet counts. Recombinant IL-11 has been approved abundant membrane, protein, biosynthetic cargo, and energy required
for use in humans for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced for the dramatic final stages of proplatelet elaboration and platelet
thrombocytopenia. release. Several circumstantial pieces of evidence support this model.