Page 421 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 421
342 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
A B C
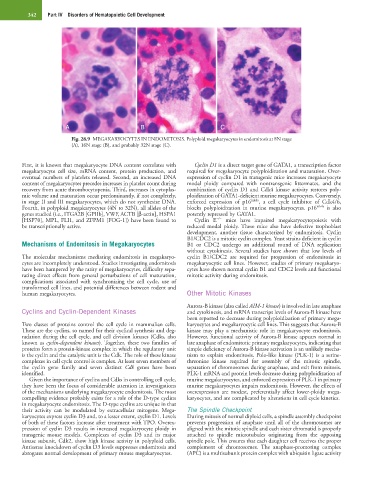
Fig. 28.9 MEGAKARYOCYTES IN ENDOMITOSIS. Polyploid megakaryocytes in endomitosis at 8N stage
(A), 16N stage (B), and probably 32N stage (C).
First, it is known that megakaryocyte DNA content correlates with Cyclin D1 is a direct target gene of GATA1, a transcription factor
megakaryocyte cell size, mRNA content, protein production, and required for megakaryocyte polyploidization and maturation. Over-
eventual numbers of platelets released. Second, an increased DNA expression of cyclin D1 in transgenic mice increases megakaryocyte
content of megakaryocytes precedes increases in platelet count during modal ploidy compared with nontransgenic littermates, and the
recovery from acute thrombocytopenia. Third, increases in cytoplas- combination of cyclin D1 and Cdk4 kinase activity restores poly-
mic volume and maturation occur predominantly, if not completely, ploidization of GATA1-deficient murine megakaryocytes. Conversely,
in stage II and III megakaryocytes, which do not synthesize DNA. enforced expression of p16 ink4a , a cell cycle inhibitor of Cdk4/6,
Fourth, in polyploid megakaryocytes (4N to 32N), all alleles of the blocks polyploidization in murine megakaryocytes. p16 ink4a is also
genes studied (i.e., ITGA2B [GPIIb], VWF, ACTB [β-actin], HSPA1 potently repressed by GATA1.
−/−
[HSP70], MPL, FLI1, and ZFPM1 [FOG-1]) have been found to Cyclin E mice have impaired megakaryocytopoiesis with
be transcriptionally active. reduced modal ploidy. These mice also have defective trophoblast
development, another tissue characterized by endomitosis. Cyclin
B1/CDC2 is a mitotic cyclin complex. Yeast strains deficient in cyclin
Mechanisms of Endomitosis in Megakaryocytes B1 or CDC2 undergo an additional round of DNA replication
without cytokinesis. Several studies have shown that low levels of
The molecular mechanisms mediating endomitosis in megakaryo- cyclin B1/CDC2 are required for progression of endomitosis in
cytes are incompletely understood. Studies investigating endomitosis megakaryocytic cell lines. However, studies of primary megakaryo-
have been hampered by the rarity of megakaryocytes, difficulty sepa- cytes have shown normal cyclin B1 and CDC2 levels and functional
rating direct effects from general perturbations of cell maturation, mitotic activity during endomitosis.
complications associated with synchronizing the cell cycle, use of
transformed cell lines, and potential differences between rodent and
human megakaryocytes. Other Mitotic Kinases
Aurora-B kinase (also called AIM-1 kinase) is involved in late anaphase
Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases and cytokinesis, and mRNA transcript levels of Aurora-B kinase have
been reported to decrease during polyploidization of primary mega-
Two classes of proteins control the cell cycle in mammalian cells. karyocytes and megakaryocytic cell lines. This suggests that Aurora-B
These are the cyclins, so named for their cyclical synthesis and deg- kinase may play a mechanistic role in megakaryocyte endomitosis.
radation during the cell cycle, and cell division kinases (Cdks, also However, functional activity of Aurora-B kinase appears normal in
known as cyclin-dependent kinases). Together, these two families of late anaphase of endomitotic primary megakaryocytes, indicating that
proteins form a protein-kinase complex in which the regulatory unit simple deficiency of Aurora-B kinase activation is an unlikely mecha-
is the cyclin and the catalytic unit is the Cdk. The role of these kinase nism to explain endomitosis. Polo-like kinase (PLK-1) is a serine-
complexes in cell cycle control is complex. At least seven members of threonine kinase required for assembly of the mitotic spindle,
the cyclin gene family and seven distinct Cdk genes have been separation of chromosomes during anaphase, and exit from mitosis.
identified. PLK-1 mRNA and protein levels decrease during polyploidization of
Given the importance of cyclins and Cdks in controlling cell cycle, murine megakaryocytes, and enforced expression of PLK-1 in primary
they have been the focus of considerable attention in investigations murine megakaryocytes impairs endomitosis. However, the effects of
of the mechanisms underlying megakaryocyte endomitosis. The most overexpression are modest, preferentially affect lower-ploidy mega-
compelling evidence probably exists for a role of the D-type cyclins karyocytes, and are complicated by alterations in cell cycle kinetics.
in megakaryocyte endomitosis. The D-type cyclins are unique in that
their activity can be modulated by extracellular mitogens. Mega- The Spindle Checkpoint
karyocytes express cyclin D3 and, to a lesser extent, cyclin D1. Levels During mitosis of normal diploid cells, a spindle assembly checkpoint
of both of these factors increase after treatment with TPO. Overex- prevents progression of anaphase until all of the chromosomes are
pression of cyclin D3 results in increased megakaryocyte ploidy in aligned with the mitotic spindle and each sister chromatid is properly
transgenic mouse models. Complexes of cyclin D3 and its major attached to spindle microtubules originating from the opposing
kinase subunit, Cdk2, show high kinase activity in polyploid cells. spindle pole. This ensures that each daughter cell receives the proper
Antisense knockdown of cyclin D3 levels suppresses endomitosis and complement of chromosomes. The anaphase-promoting complex
abrogates normal development of primary mouse megakaryocytes. (APC) is a multisubunit protein complex with ubiquitin ligase activity