Page 475 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 475
396 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
100 30
90 Seattle NIH
Chronic
80
Acute
70
20
60
Number 50 Number Median age, 25 years
40
10
30
20
10 Median age, 20 years
0 0
0-4 5-9 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 65-69 70-74 0-4 5-9 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 65-69 70-74 75-79
Age Age
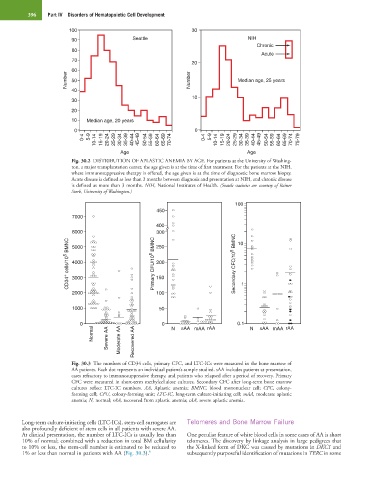
Fig. 30.2 DISTRIBUTION OF APLASTIC ANEMIA BY AGE. For patients at the University of Washing-
ton, a major transplantation center, the age given is at the time of first treatment. For the patients at the NIH,
where immunosuppressive therapy is offered, the age given is at the time of diagnostic bone marrow biopsy.
Acute disease is defined as less than 3 months between diagnosis and presentation at NIH, and chronic disease
is defined as more than 3 months. NIH, National Institutes of Health. (Seattle statistics are courtesy of Rainer
Storb, University of Washington.)
100
450
7000
400
6000 300 10
CD34 + cells/10 5 BMNC 4000 Primary CFU/10 5 BMNC 150 Secondary CFC/10 5 BMNC
5000
250
200
3000
2000 100 1
1000 50
0 0 N sAA mAA rAA 0.1 N sAA mAA rAA
Normal Severe AA Moderate AA Recovered AA
Fig. 30.3 The numbers of CD34 cells, primary CFC, and LTC-ICs were measured in the bone marrow of
AA patients. Each dot represents an individual patient’s sample studied. sAA includes patients at presentation,
cases refractory to immunosuppressive therapy, and patients who relapsed after a period of recovery. Primary
CFC were measured in short-term methylcellulose cultures. Secondary CFC after long-term bone marrow
cultures reflect LTC-IC numbers. AA, Aplastic anemia; BMNC, blood mononuclear cell; CFC, colony-
forming cell; CFU, colony-forming unit; LTC-IC, long-term culture-initiating cell; mAA, moderate aplastic
anemia; N, normal; rAA, recovered from aplastic anemia; sAA, severe aplastic anemia.
Long-term culture-initiating cells (LTC-ICs), stem-cell surrogates are Telomeres and Bone Marrow Failure
also profoundly deficient of stem cells in all patients with severe AA.
At clinical presentation, the number of LTC-ICs is usually less than One peculiar feature of white blood cells in some cases of AA is short
10% of normal; combined with a reduction in total BM cellularity telomeres. The discovery by linkage analysis in large pedigrees that
to 10% or less, the stem-cell number is estimated to be reduced to the X-linked form of DKC was caused by mutations in DKC1 and
1% or less than normal in patients with AA (Fig. 30.3). 6 subsequently purposeful identification of mutations in TERC in some