Page 479 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 479
400 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
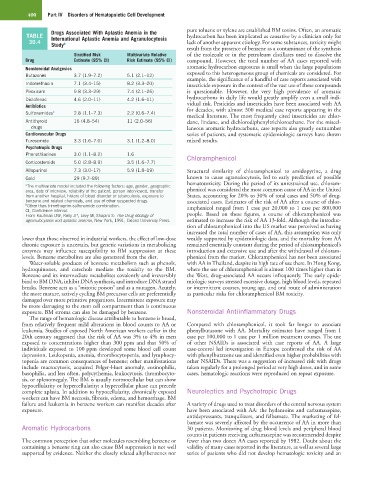
Drugs Associated With Aplastic Anemia in the pure toluene or xylene are established BM toxins. Often, an aromatic
TABLE International Aplastic Anemia and Agranulocytosis hydrocarbon has been implicated as causative by a clinician only for
30.4 Study a lack of another apparent etiology. For some substances, toxicity might
result from the presence of benzene as a contaminant of the synthesis
Stratified Risk Multivariate Relative of the molecule or in the petroleum distillates used to dissolve the
Drug Estimate (95% CI) Risk Estimate (95% CI) compound. However, the total number of AA cases reported with
Nonsteroidal Analgesics aromatic hydrocarbon exposures is small when the large populations
Butazones 3.7 (1.9–7.2) 5.1 (2.1–12) exposed to this heterogeneous group of chemicals are considered. For
example, the significance of a handful of case reports associated with
Indomethacin 7.1 (3.4–15) 8.2 (3.3–20) insecticide exposure in the context of the vast use of these compounds
Piroxicam 9.8 (3.3–29) 7.4 (2.1–26) is questionable. However, the very high prevalence of aromatic
Diclofenac 4.6 (2.0–11) 4.2 (1.6–11) hydrocarbons in daily life would greatly amplify even a small indi-
Antibiotics vidual risk. Pesticides and insecticides have been associated with AA
for decades, with almost 300 medical case reports appearing in the
Sulfonamides b 2.8 (1.1–7.3) 2.2 (0.6–7.4)
medical literature. The most frequently cited insecticides are chlor-
Antithyroid 16 (4.8–54) 11 (2.0–56) dane, lindane, and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. For the miscel-
drugs laneous aromatic hydrocarbons, case reports also greatly outnumber
Cardiovascular Drugs series of patients, and systematic epidemiologic surveys have shown
Furosemide 3.3 (1.6–7.0) 3.1 (1.2–8.0) mixed results.
Psychotropic Drugs
Phenothiazines 3.0 (1.1–8.2) 1.6 Chloramphenicol
Corticosteroids 5.0 (2.8–8.9) 3.5 (1.6–7.7)
Allopurinol 7.3 (3.0–17) 5.9 (1.8–19) Structural similarity of chloramphenicol to amidopyrine, a drug
Gold 29 (9.7–89) known to cause agranulocytosis, led to early prediction of possible
hematotoxicity. During the period of its unrestrained use, chloram-
a The multivariate model included the following factors: age, gender, geographic
area, date of interview, reliability of the patient, person interviewed, transfer phenicol was considered the most common cause of AA in the United
from another hospital, history of blood disorder or tuberculosis, exposure to States, accounting for 20% to 30% of total cases and 50% of drug-
benzene and related chemicals, and use of other suspected drugs. associated cases. Estimates of the risk of AA after a course of chlor-
b Other than trimethoprim-sulfonamide combination. amphenicol ranged from 1 case per 20,000 to 1 case per 800,000
CI, Confidence interval.
From Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Levy M, Shapiro S: The Drug etiology of people. Based on these figures, a course of chloramphenicol was
agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia, New York, 1991, Oxford University Press. estimated to increase the risk of AA 13-fold. Although the introduc-
tion of chloramphenicol into the US market was perceived as having
increased the total number of cases of AA, this assumption was only
lower than those observed in industrial workers, the effect of low-dose weakly supported by epidemiologic data, and the mortality from AA
chronic exposure is uncertain, but genetic variations in metabolizing remained essentially constant during the period of chloramphenicol’s
enzymes may influence susceptibility to BM suppression at these introduction and extensive use and after the withdrawal of chloram-
levels. Benzene metabolites are also generated from the diet. phenicol from the market. Chloramphenicol has not been associated
Water-soluble products of benzene metabolism such as phenols, with AA in Thailand, despite its high rate of use there. In Hong Kong,
hydroquinones, and catechols mediate the toxicity to the BM. where the use of chloramphenicol is almost 100 times higher than in
Benzene and its intermediate metabolites covalently and irreversibly the West, drug-associated AA occurs infrequently. The early epide-
bind to BM DNA, inhibit DNA synthesis, and introduce DNA strand miologic surveys stressed excessive dosage, high blood levels, repeated
breaks. Benzene acts as a “mitotic poison” and as a mutagen. Acutely, or intermittent courses, young age, and oral route of administration
the more mature, actively cycling BM precursor cells are preferentially as particular risks for chloramphenicol BM toxicity.
damaged over more primitive progenitors. Intermittent exposure may
be more damaging to the stem cell compartment than is continuous
exposure. BM stroma can also be damaged by benzene. Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs
The range of hematologic disease attributable to benzene is broad,
from relatively frequent mild alterations in blood counts to AA or Compared with chloramphenicol, it took far longer to associate
leukemia. Studies of exposed North American workers earlier in the phenylbutazone with AA. Mortality estimates have ranged from 1
20th century suggested that the risk of AA was 3% to 4% in men case per 100,000 to 1 case per 1 million treatment courses. The use
exposed to concentrations higher than 300 ppm and that 50% of of other NSAIDs is associated with case reports of AA. A large
individuals exposed to 100 ppm developed some blood cell count case-control led investigation in Europe confirmed the risk of AA
depression. Leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and lymphocy- with phenylbutazone use and identified even higher probabilities with
topenia are common consequences of benzene; other manifestations other NSAIDs. There was a suggestion of increased risk with drugs
include macrocytosis, acquired Pelger-Huet anomaly, eosinophilia, taken regularly for a prolonged period at very high doses, and in some
basophilia, and less often, polycythemia, leukocytosis, thrombocyto- cases, hematologic reactions were reproduced on repeat exposure.
sis, or splenomegaly. The BM is usually normocellular but can show
hypocellularity or hypercellularity; a hypercellular phase can precede
complete aplasia. In addition to hypocellularity, chronically exposed Neuroleptics and Psychotropic Drugs
workers can have BM necrosis, fibrosis, edema, and hemorrhage. BM
failure and leukemia in benzene workers can manifest decades after A variety of drugs used to treat disorders of the central nervous system
exposure. have been associated with AA: the hydantoins and carbamazepine,
antidepressants, tranquilizers, and felbamate. The marketing of fel-
bamate was severely affected by the occurrence of AA in more than
Aromatic Hydrocarbons 30 patients. Monitoring of drug blood levels and peripheral blood
counts in patients receiving carbamazepine was recommended despite
The common perception that other molecules resembling benzene or fewer than two dozen AA cases reported by 1982. Doubt about the
containing a benzene ring can also cause BM suppression is not well validity of many cases reported in the literature, as well as several large
supported by evidence. Neither the closely related alkylbenzenes nor series of patients who did not develop hematologic toxicity and an