Page 664 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 664
566 Part V Red Blood Cells
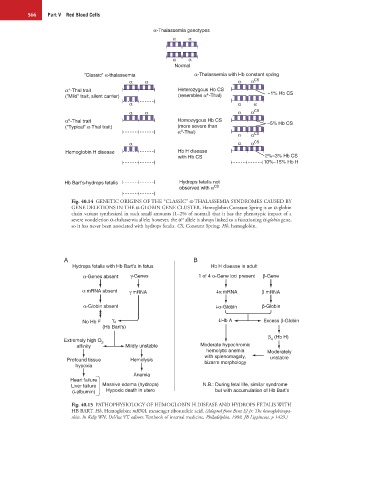
α-Thalassemia genotypes
α α
α α
Normal
“Classic” α-thalassemia α-Thalassemia with Hb constant spring
α α α α CS
+
α -Thal trait Heterozygous Hb CS ~1% Hb CS
+
(”Mild” trait, silent carrier) (resembles α -Thal)
α α α
α α α α CS
o
α -Thal trait Homozygous Hb CS ~5% Hb CS
(“Typical” α-Thal trait) (more severe than
o
α -Thal)
α α CS
α α α CS
Hemoglobin H disease Hb H disease
with Hb CS 2%–3% Hb CS
10%–15% Hb H
Hb Bart’s-hydrops fetalis Hydrops fetalis not
observed with α CS
Fig. 40.14 GENETIC ORIGINS OF THE “CLASSIC” α-THALASSEMIA SYNDROMES CAUSED BY
GENE DELETIONS IN THE α-GLOBIN GENE CLUSTER. Hemoglobin Constant Spring is an α-globin
chain variant synthesized in such small amounts (1–2% of normal) that it has the phenotypic impact of a
cs
severe nondeletion α-thalassemia allele; however, the α allele is always linked to a functioning α-globin gene,
so it has never been associated with hydrops fetalis. CS, Constant Spring; Hb, hemoglobin.
A B
Hydrops fetalis with Hb Bart’s in fetus Hb H disease in adult
α-Genes absent γ-Genes 1 of 4 α-Gene loci present β-Gene
α mRNA absent γ mRNA α mRNA β mRNA
α-Globin absent α-Globin β-Globin
No Hb F γ 4 Hb A Excess β-Globin
(Hb Bart’s)
β (Hb H)
Extremely high O 2 4
affinity Mildly unstable Moderate hypochromic
hemolytic anemia Moderately
with splenomagaly, unstable
Profound tissue Hemolysis bizarre morphology
hypoxia
Anemia
Heart failure
Liver failure Massive edema (hydrops) N.B.: During fetal life, similar syndrome
( albumin) Hypoxic death in utero but with accumulation of Hb Bart’s
Fig. 40.15 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HEMOGLOBIN H DISEASE AND HYDROPS FETALIS WITH
HB BART. Hb, Hemoglobin; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid. (Adapted from Benz EJ Jr: The hemoglobinopa-
thies. In Kelly WN, DeVita VT, editors: Textbook of internal medicine, Philadelphia, 1988, JB Lippincott, p 1423.)