Page 807 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 807
Chapter 50 Disorders of Phagocyte Function 693
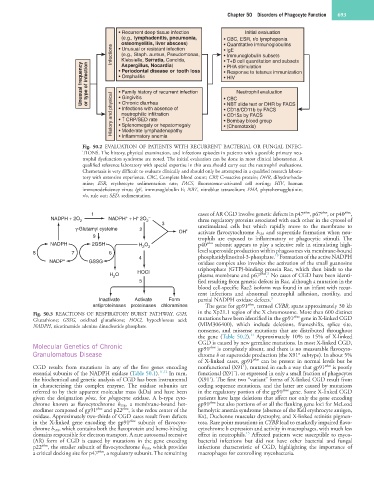
• Recurrent deep tissue infection Initial evaluation
(e.g., lymphadenitis, pneumonia, • CBC, ESR, r/o lymphopenia
osteomyelitis, liver abscess) • Quantitative immunoglobulins
Infections (e.g., Staph. aureus, Pseudomonas, • lgE
• Unusual or resistant infection
• Immunoglobulin subsets
Klebsiella, Serratia, Candida,
• T+B cell quantitation and subsets
Unusual frequency or type of infection • Periodontal disease or tooth loss • Response to tetanus immunization
Aspergillus, Nocardia)
• PHA stimulation
• Omphalitis
• HIV
Neutrophil evaluation
• Family history of recurrent infection
History and physical • Chronic diarrhea • NBT slide test or DHR by FACS
• Gingivitis
• CBC
• Infections with absence of
• CD18/CD11b by FACS
neutrophilic infiltration
• CD15a by FACS
• ↑ CRP/SED rate
• Bombay blood group
• Splenomegaly or hepatomegaly
• (Chemotaxis)
• Moderate lymphadenopathy
• Inflammatory anemia
Fig. 50.2 EVALUATION OF PATIENTS WITH RECURRENT BACTERIAL OR FUNGAL INFEC-
TIONS. The history, physical examination, and infections episodes in patients with a possible primary neu-
trophil dysfunction syndrome are noted. The initial evaluation can be done in most clinical laboratories. A
qualified reference laboratory with special expertise in this area should carry out the neutrophil evaluations.
Chemotaxis is very difficult to evaluate clinically and should only be attempted in a qualified research labora-
tory with extensive experience. CBC, Complete blood count; CRP, C-reactive protein; DHR, dihydrorhoda-
mine; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; HIV, human
immunodeficiency virus; IgE, immunoglobulin E; NBT, nitroblue tetrazolium; PHA, phytohemagglutinin;
r/o, rule out; SED, sedimentation.
1 cases of AR CGD involve genetic defects in p47 phox , p67 phox , or p40 phox ,
+
+
NADPH + 2O NADPH + H 2O –
2 2 three regulatory proteins associated with each other in the cytosol of
3
γ-Glutamyl cysteine 2 OH • unstimulated cells but which rapidly move to the membrane to
activate flavocytochrome b 558 and superoxide formation when neu-
9 trophils are exposed to inflammatory or phagocytic stimuli. The
NADPH 2GSH H O 2 p40 phox subunit appears to play a selective role in stimulating high-
2
8 7 6 level superoxide production within phagosomes via membrane-bound
10
4 phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Formation of the active NADPH
NADP + GSSG oxidase complex also involves the activation of the small guanosine
triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein Rac, which then binds to the
H O HOCI plasma membrane and p67 phox 3
. No cases of CGD have been identi-
2
5 fied resulting from genetic defects in Rac, although a mutation in the
blood cell-specific Rac2 isoform was found in an infant with recur-
rent infections and abnormal neutrophil adhesion, motility, and
Inactivate Activate Form partial NADPH oxidase defects. 3
antiproteinases proteinases chloramines The gene for gp91 phox , termed CYBB, spans approximately 30 kb
Fig. 50.3 REACTIONS OF RESPIRATORY BURST PATHWAY. GSH, in the Xp21.1 region of the X chromosome. More than 600 distinct
phox
Glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; HOCl, hypochlorous acid; mutations have been identified in the gp91 gene in X-linked CGD
NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. (MIM306400), which include deletions, frameshifts, splice site,
nonsense, and missense mutations that are distributed throughout
11
the gene (Table 50.2). Approximately 10% to 15% of X-linked
Molecular Genetics of Chronic CGD is caused by new germline mutations. In most X-linked CGD,
phox
is completely absent, and there is no measurable flavocyto-
gp91
Granulomatous Disease chrome b or superoxide production (the X91° subtype). In about 5%
of X-linked cases, gp91 phox can be present in normal levels but be
+
CGD results from mutations in any of the five genes encoding nonfunctional (X91 ), mutated in such a way that gp91 phox is poorly
−
essential subunits of the NADPH oxidase (Table 50.1). 11,12 In turn, functional (X91 ), or expressed in only a small fraction of phagocytes
+
the biochemical and genetic analysis of CGD has been instrumental (X91 ). The first two “variant” forms of X-linked CGD result from
in characterizing this complex enzyme. The oxidase subunits are coding sequence mutations, and the latter are caused by mutations
referred to by their apparent molecular mass (kDa) and have been in the regulatory portion of the gp91 phox gene. Some X-linked CGD
given the designation phox, for phagocyte oxidase. A b-type cyto- patients have large deletions that affect not only the gene encoding
chrome known as flavocytochrome b 558, a membrane-bound het- gp91 phox but also portions of or all the flanking gene loci for McLeod
erodimer composed of gp91 phox and p22 phox , is the redox center of the hemolytic anemia syndrome (absence of the Kell erythrocyte antigen,
oxidase. Approximately two-thirds of CGD cases result from defects Kx), Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and X-linked retinitis pigmen-
in the X-linked gene encoding the gp91 phox subunit of flavocyto- tosa. Rare point mutations in CYBB lead to markedly impaired flavo-
chrome b 558, which contains both the flavoprotein and heme-binding cytochrome b expression and activity in macrophages, with much less
13
domains responsible for electron transport. A rare autosomal recessive effect in neutrophils. Affected patients were susceptible to myco-
(AR) form of CGD is caused by mutations in the gene encoding bacterial infections but did not have other bacterial and fungal
p22 phox , the smaller subunit of flavocytochrome b 558, which provides infections characteristic of CGD, highlighting the importance of
a critical docking site for p47 phox , a regulatory subunit. The remaining macrophages for controlling mycobacteria.