Page 810 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 810
696 Part VI Non-Malignant Leukocytes
Resting Stimulated with PMA
80 80
M1
Counts Counts
0 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
D DHR 123 (resting) DHR 123 (resting)
80 80
M2
Counts Counts
A M1
0 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
E DHR 123 (resting) DHR 123 (resting)
80
60
50
M1
Counts Counts 40
30
B 20
10
0 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
F DHR 123 (resting) DHR 123 (resting)
500 200
400 160
Counts 300 Counts 120
80
200
100 40
C
0 0
10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
G Unstimulated PMA stimulated
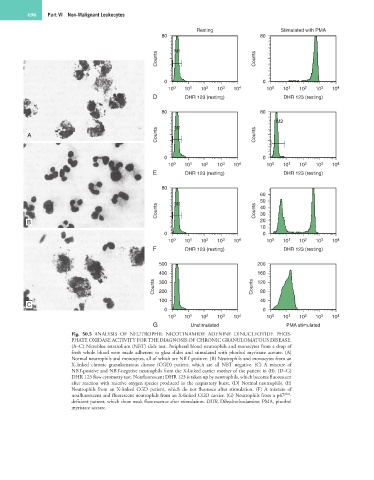
Fig. 50.5 ANALYSIS OF NEUTROPHIL NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE PHOS-
PHATE OXIDASE ACTIVITY FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC GRANULOMATOUS DISEASE.
(A–C) Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) slide test. Peripheral blood neutrophils and monocytes from a drop of
fresh whole blood were made adherent to glass slides and stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate. (A)
Normal neutrophils and monocytes, all of which are NBT positive. (B) Neutrophils and monocytes from an
X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) patient, which are all NBT negative. (C) A mixture of
NBT-positive and NBT-negative neutrophils from the X-linked carrier mother of the patient in (B). (D–G)
DHR 123 flow cytometry test. Nonfluorescent DHR 123 is taken up by neutrophils, which become fluorescent
after reaction with reactive oxygen species produced in the respiratory burst. (D) Normal neutrophils. (E)
Neutrophils from an X-linked CGD patient, which do not fluoresce after stimulation. (F) A mixture of
nonfluorescent and fluorescent neutrophils from an X-linked CGD carrier. (G) Neutrophils from a p47 phox -
deficient patient, which show weak fluorescence after stimulation. DHR, Dihydrorhodamine; PMA, phorbol
myristate acetate.