Page 1149 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1149
1124 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 72: Gaucher Disease and Related Lysosomal Storage Diseases 1125
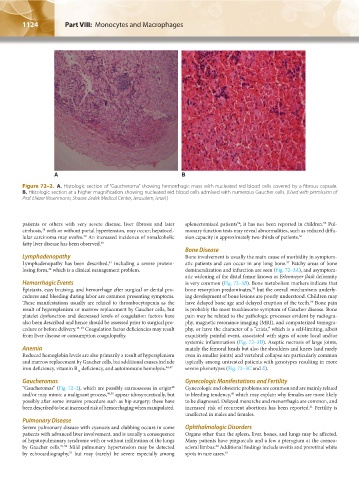
A B
Figure 72–2. A. Histologic section of “Gaucheroma” showing hemorrhagic mass with nucleated red blood cells covered by a fibrous capsule.
B. Histologic section at a higher magnification showing nucleated red blood cells admixed with numerous Gaucher cells. (Used with permission of
Prof. Eliezer Rosenmann, Shaare Zedek Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel.)
patients or others with very severe disease, liver fibrosis and later splenectomized patients ; it has not been reported in children. Pul-
55
54
cirrhosis, with or without portal hypertension, may occur; hepatocel- monary function tests may reveal abnormalities, such as reduced diffu-
38
lular carcinoma may evolve. An increased incidence of nonalcoholic sion capacity in approximately two-thirds of patients. 56
39
fatty liver disease has been observed. 40
Bone Disease
Lymphadenopathy Bone involvement is usually the main cause of morbidity in symptom-
Lymphadenopathy has been described, including a severe protein- atic patients and can occur in any long bone. Patchy areas of bone
57
41
losing form, which is a clinical management problem. demineralization and infarction are seen (Fig. 72–3A), and asymptom-
42
atic widening of the distal femur known as Erlenmeyer flask deformity
Hemorrhagic Events is very common (Fig. 72–3B). Bone metabolism markers indicate that
Epistaxis, easy bruising, and hemorrhage after surgical or dental pro- bone resorption predominates, but the overall mechanisms underly-
58
cedures and bleeding during labor are common presenting symptoms. ing development of bone lesions are poorly understood. Children may
These manifestations usually are related to thrombocytopenia as the have delayed bone age and delayed eruption of the teeth. Bone pain
59
result of hypersplenism or marrow replacement by Gaucher cells, but is probably the most troublesome symptom of Gaucher disease. Bone
platelet dysfunction and decreased levels of coagulation factors have pain may be related to the pathologic processes evident by radiogra-
also been described and hence should be assessed prior to surgical pro- phy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computerized tomogra-
cedure or before delivery. 43–45 Coagulation factor deficiencies may result phy, or have the character of a “crisis,” which is a self-limiting, albeit
from liver disease or consumption coagulopathy. exquisitely painful event, associated with signs of acute local and/or
systemic inflammation (Fig. 72–3D). Aseptic necrosis of large joints,
Anemia mainly the femoral heads but also the shoulders and knees (and rarely
Reduced hemoglobin levels are also primarily a result of hypersplenism even in smaller joints) and vertebral collapse are particularly common
and marrow replacement by Gaucher cells, but additional causes include typically among untreated patients with genotypes resulting in more
iron deficiency, vitamin B deficiency, and autoimmune hemolysis. 46,47 severe phenotypes (Fig. 72–3C and E).
12
Gaucheromas Gynecologic Manifestations and Fertility
“Gaucheromas” (Fig. 72–2), which are possibly extraosseous in origin Gynecologic and obstetric problems are common and are mainly related
48
and/or may mimic a malignant process, 49,50 appear idiosyncratically, but to bleeding tendency, which may explain why females are more likely
60
possibly after some invasive procedure such as hip surgery; these have to be diagnosed. Delayed menarche and menorrhagia are common, and
been described to be at increased risk of hemorrhaging when manipulated. increased risk of recurrent abortions has been reported. Fertility is
61
unaffected in males and females.
Pulmonary Disease
Severe pulmonary disease with cyanosis and clubbing occurs in some Ophthalmologic Disorders
patients with advanced liver involvement, and is usually a consequence Organs other than the spleen, liver, bones, and lungs may be affected.
of hepatopulmonary syndrome with or without infiltration of the lungs Many patients have pinguecula and a few a pterygium at the corneo-
by Gaucher cells. 51,52 Mild pulmonary hypertension may be detected scleral limbus. Additional findings include uveitis and preretinal white
62
by echocardiography, but may (rarely) be severe especially among spots in rare cases. 63
53
Kaushansky_chapter 72_p1121-1134.indd 1124 9/17/15 3:53 PM