Page 1150 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1150
1124 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 72: Gaucher Disease and Related Lysosomal Storage Diseases 1125
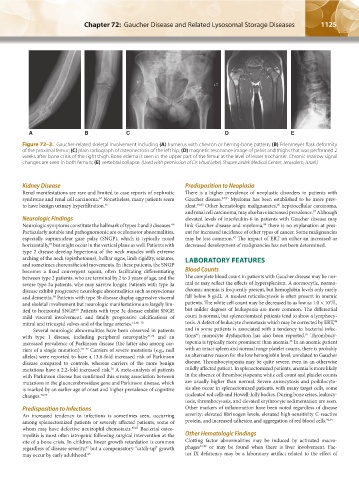
A B C D E
Figure 72–3. Gaucher-related skeletal involvement including (A) humerus with chevron or herring-bone pattern; (B) Erlenmeyer flask deformity
of the proximal femur; (C) plain radiograph of osteonecrosis of the left hip; (D) magnetic resonance image of pelvis and thighs that was performed 2
weeks after bone crisis of the right thigh. Bone edema is seen in the upper part of the femur at the level of lesser trochanter. Chronic marrow signal
changes are seen in both femurs; (E) vertebral collapse. (Used with permission of Dr. Ehud Lebel, Shaare Zedek Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel.)
Kidney Disease Predisposition to Neoplasia
Renal manifestations are rare and limited to case reports of nephrotic There is a higher prevalence of neoplastic disorders in patients with
64
syndrome and renal cell carcinoma. Nonetheless, many patients seem Gaucher disease. 84,85 Myeloma has been established to be more prev-
86
to have benign urinary hyperfiltration. 65 alent. 84,85 Other hematologic malignancies, hepatocellular carcinoma,
and renal cell carcinoma, may also have increased prevalence. Although
87
Neurologic Findings elevated levels of interleukin-6 in patients with Gaucher disease may
88
Neurologic symptoms constitute the hallmark of types 2 and 3 diseases. link Gaucher disease and myeloma, there is no explanation at pres-
66
Particularly notable and pathognomonic are oculomotor abnormalities, ent for increased incidence of other types of cancer. Some malignancies
especially supranuclear gaze palsy (SNGP), which is typically noted may be less common. The impact of ERT on either an increased or
87
67
horizontally, but might occur in the vertical plane as well. Patients with decreased development of malignancies has not been determined.
type 2 disease develop hypertonia of the neck muscles with extreme
arching of the neck (opisthotonus), bulbar signs, limb rigidity, seizures, LABORATORY FEATURES
and sometimes choreoathetoid movements. In these patients, the SNGP
becomes a fixed convergent squint, often facilitating differentiating Blood Counts
between type 2 patients, who are terminal by 2 to 3 years of age, and the The complete blood count in patients with Gaucher disease may be nor-
severe type 3a patients, who may survive longer. Patients with type 3a mal or may reflect the effects of hypersplenism. A normocytic, normo-
disease exhibit progressive neurologic abnormalities such as myoclonus chromic anemia is frequently present, but hemoglobin levels only rarely
68
and dementia. Patients with type 3b disease display aggressive visceral fall below 8 g/dL. A modest reticulocytosis is often present in anemic
9
and skeletal involvement but neurologic manifestations are largely lim- patients. The white cell count may be decreased to as low as 1.0 × 10 /L,
68
ited to horizontal SNGP. Patients with type 3c disease exhibit SNGP, but milder degrees of leukopenia are more common. The differential
mild visceral involvement, and fatally progressive calcifications of count is normal, but splenectomized patients tend to show a lymphocy-
89
mitral and tricuspid valves and of the large arteries. 12,68–70 tosis. A defect of leukocyte chemotaxis which may be corrected by ERT,
Several neurologic abnormalities have been observed in patients and in some patients is associated with a tendency to bacterial infec-
81
80
with type 1 disease, including peripheral neuropathy 71,72 and an tions ; monocyte dysfunction has also been reported. Thrombocy-
46
increased prevalence of Parkinson disease (the latter also among car- topenia is typically more prominent than anemia. In an anemic patient
riers of a single mutation). 73–77 Carriers of severe mutations (e.g., null with an intact spleen and normal range platelet counts, there is probably
alleles) were reported to have a 13.6-fold increased risk of Parkinson an alternative reason for the low hemoglobin level, unrelated to Gaucher
disease compared to controls, whereas carriers of the more benign disease. Thrombocytopenia may be quite severe, even in an otherwise
78
mutations have a 2.2-fold increased risk. A meta-analysis of patients mildly affected patient. In splenectomized patients, anemia is more likely
with Parkinson disease has confirmed this strong association between in the absence of thrombocytopenia; white cell count and platelet counts
mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and Parkinson disease, which are usually higher than normal. Severe anisocytosis and poikilocyto-
is marked by an earlier age of onset and higher prevalence of cognitive sis also occur in splenectomized patients, with many target cells, some
changes. 78,79 nucleated red cells and Howell-Jolly bodies. During bone crises, leukocy-
tosis, thrombocytosis, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation are seen.
Predisposition to Infections Other markers of inflammation have been noted regardless of disease
An increased tendency to infections is sometimes seen, occurring severity: elevated fibrinogen levels, elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive
among splenectomized patients or severely affected patients, some of protein, and increased adhesion and aggregation of red blood cells. 90,91
whom may have defective neutrophil chemotaxis. 80,81 Bacterial osteo-
myelitis is most often iatrogenic following surgical intervention at the Other Hematologic Findings
site of a bone crisis. In children, linear growth retardation is common Clotting factor abnormalities may be induced by activated macro-
82
regardless of disease severity, but a compensatory “catch-up” growth phages 41,42 or may be found when there is liver involvement. Fac-
may occur by early adulthood. 83 tor IX deficiency may be a laboratory artifact related to the effect of
Kaushansky_chapter 72_p1121-1134.indd 1125 9/17/15 3:53 PM