Page 1167 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1167
1142 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells
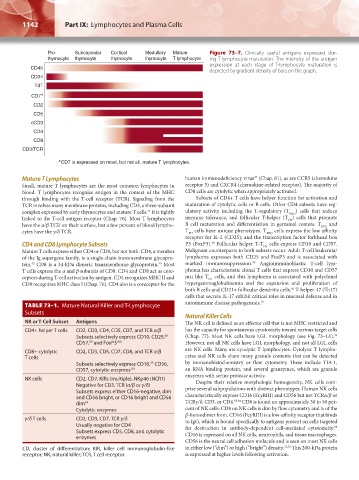
Pro- Subcapsular Cortical Medullary Mature Figure 73–7. Clinically useful antigens expressed dur-
thymocyte thymocyte thymocyte thymocyte T lymphocyte ing T-lymphocyte maturation. The intensity of the antigen
expression at each stage of T-lymphocyte maturation is
CD45
depicted by gradient density of bars on the graph.
CD34
TdT
CD7 ∗
CD2
CD5
cCD3
CD4
CD8
CD3/TCR
∗ CD7 is expressed on most, but not all, mature T lymphocytes.
Mature T Lymphocytes human immunodeficiency virus (Chap. 81), as are CCR5 (chemokine
47
Small, mature T lymphocytes are the most common lymphocytes in receptor 5) and CXCR4 (chemokine-related receptor). The majority of
blood. T lymphocytes recognize antigen in the context of the MHC CD8 cells are cytolytic when appropriately activated.
through binding with the T-cell receptor (TCR). Signaling from the Subsets of CD4+ T cells have helper function for activation and
TCR involves many membrane proteins, including CD3, a three- subunit maturation of cytolytic cells or B cells. Other CD4 subsets have reg-
complex expressed by early thymocytes and mature T cells. It is tightly ulatory activity including the T-regulatory (T REG ) cells that induce
44
linked to the T-cell antigen receptor (Chap. 76). Most T lymphocytes immune tolerance, and follicular T-helper (T ) cells that promote
FH
have the α/β TCR on their surface, but a few percent of blood lympho- B cell maturation and differentiation in germinal centers. T REG and
cytes have the γ/δ TCR. T cells have unique phenotypes. T REG cells express the low affinity
FH
receptor for IL-2 (CD25); and the transcription factor forkhead box
CD4 and CD8 Lymphocyte Subsets P3 (FoxP3). Follicular helper T-T cells express CD10 and CD57.
48
FH
Mature T cells express either CD4 or CD8, but not both. CD4, a member Malignant counterparts to both subsets occur. Adult T-cell leukemia/
of the Ig supergene family, is a single-chain transmembrane glycopro- lymphoma expresses both CD25 and FoxP3 and is associated with
49
tein. CD8 is a 34-kDa dimeric transmembrane glycoprotein. Most marked immunosuppression. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lym-
46
45
T cells express the α and β subunits of CD8. CD4 and CD8 act as core- phoma has characteristic clonal T cells that express CD10 and CD57
ceptors during T-cell activation by antigen. CD4 recognizes MHC II and just like T cells, and this lymphoma is associated with polyclonal
FH
CD8 recognizes MHC class I (Chap. 76). CD4 also is a coreceptor for the hypergammaglobulinemia and the expansion and proliferation of
both B cells and CD21+ follicular dendritic cells. T-helper-17 (Th17)
50
cells that secrete IL-17 exhibit critical roles in mucosal defense and in
autoimmune disease pathogenesis. 51
TABLE 73–1. Mature Natural Killer and T-Lymphocyte
Subsets
Natural Killer Cells
NK or T-Cell Subset Antigens The NK cell is defined as an effector cell that is not MHC restricted and
CD4+ helper T cells CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, and TCR α/β has the capacity for spontaneous cytotoxicity toward various target cells
52
49
Subsets selectively express CD10, CD25, (Chap. 77). Most NK cells have LGL morphology (see Fig. 73–1E).
CD57, and FoxP3 100 However, not all NK cells have LGL morphology, and not all LGL cells
99
CD8+ cytolytic CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD8, and TCR α/β are NK cells. Many are cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cytolytic T lympho-
T cells cytes and NK cells share many granule contents that can be detected
Subsets selectively express CD16, CD56, by immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry. These include TIA-1,
55
CD57, cytolytic enzymes 101 an RNA binding protein, and several granzymes, which are granule
enzymes with serine protease activity.
NK cells CD2, CD7, KIRs (multiple), NKp46 (NCR1) Despite their relative morphologic homogeneity, NK cells com-
Negative for CD3, TCR (α/β or γ/δ) prise several subpopulations with distinct phenotypes. Human NK cells
Subsets express either CD16-negative, dim
and CD56 bright, or CD16 bright and CD56 characteristically express CD16 (FcγRIII) and CD56 but not TCRα/β or
dim 54 TCRγ/δ, CD3, or CD4. 53,54 CD8 is found on approximately 30 to 50 per-
Cytolytic enzymes cent of NK cells. CD8 on NK cells is dim by flow cytometry and is of the
β-homodimer form. CD16 (FcγRIII) is a low-affinity receptor that binds
γ/δ T cells CD2, CD3, CD7, TCR γ/δ to IgG, which is bound specifically to antigens present on cells targeted
Usually negative for CD4 for destruction in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
55
Subsets express CD5, CD8, and cytolytic CD16 is expressed on all NK cells, neutrophils, and tissue macrophages.
enzymes
CD56 is the neural cell adhesion molecule and is seen on most NK cells
CD, cluster of differentiation; KIR, killer cell immunoglobulin-like in either low (“dim”) or high (“bright”) density. 53,56 This 200-kDa protein
receptor; NK, natural killer; TCR, T cell receptor. is expressed at higher levels following activation.
Kaushansky_chapter 73_p1135-1148.indd 1142 9/21/15 4:44 PM