Page 1189 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1189
1164 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 75: Functions of B Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells in Immunoglobulin Production 1165
7-4-1 1-38-4 Golgin 3-64 5' Telomeric
3-63
44 3.21 3-41 (II)-62-1
1-3 (11)-40-1 3-62
4-61
G3
(III)-2-1 7-40 3-38-3 (II)-60-1 (III)-62
(II)-20-1 4-39 3-60 7-81
26
3-20 (III)-38-1 4-59 4-80
1-2 1-58 3-79
S8 3-38 3-43D 3-57 (III)-78-1
3-19 3-37
G1
MDC 3-36 7-56
D1-1 1-18 3-35 4-55 5-78
19
D2-2 GLVR1 7-34-1 4-38-2 3-54
(II)-53-1
D3-3 1-17 4-34 3-53 7-77
EP1
D4-4 (III)-16-1 3-33-2 3-52 (III)-76-1
13
A1
(II)1-1 D5-5 3-16 (II)-33-1 3-30-5 (II)-51-2 (III)-51-1 3-76
D6-6
6-1 D1-7 (II)-15-1 Golgin 3-33 5-51 3-75
3-32
D2-8 3-15 (II)-31-1 4-30-4 3-50 (II)-74-1
25
KIAA D3-10 D3-9 1-14 4-31 (II)-49-1 3-74
D5-12 D4-11 (III)-13-1 3-30-2 4-30-3 3-49 3-73
(II)-30-1
D6-13
Enhancer
D1-14 3-13 Golgin 3-30 4-30-2
D2-15 1-12 3-29 3-72
(II)-38-1
D3-18 (III)-11-1 4-28 4-30-1 3-48 1-69D
3-11
D5-18 D4-17 7-27 (III)-47-1
D6-19 2-10 (II)-26-2 3-47 3-71
D1-20 (III)-26-1 (II)-46-1 2-70
GP
~55
D2-21 3-9 2-26 1-46 1-69-2
D3-22 1-8 1-45 1-69
D4-23 (III)-25-1 3-69-1
D5-24 3-25 1-68 2-70D
D6-25 (II)-44-2 (III)-67-4
D1-26 (IV)-44-1 (III)-67-3 (III)-67-2
3-7 1-24
G2
3-6 3-23 3-23D (III)-44 GLVR1 (II)-67-1
1-67
18
(III)-22-2 (II)-22-1 (II)-43-1
4.5
M D
(III)-5-2 3-22 3-43 3-66
G4
J1 to JB Enhancer
(III)-5-1 3-42 (II)-65-1
2-5 3-65
23
J1P
D7-27 800 kb 600 kb 400 kb 200 kb
~60
E
10
A2
1 000 kb
25
3'
Enhancer
Centromeric
1 250 kb
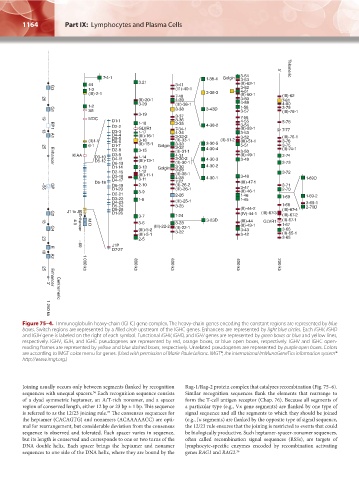
Figure 75–4. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IGHC) gene complex. The heavy-chain genes encoding the constant regions are represented by blue
boxes. Switch regions are represented by a filled circle upstream of the IGHC genes. Enhancers are represented by light blue circles. Each IGHV, IGHD
and IGJH gene is labeled on the right of each symbol. Functional IGHV, IGHD, and IGHJ genes are represented by green boxes or blue and yellow lines,
respectively. IGHV, IGJH, and IGHC pseudogenes are represented by red, orange boxes, or blue open boxes, respectively. IGHV and IGHC open-
reading frames are represented by yellow and blue dashed boxes, respectively. Unrelated pseudogenes are represented by purple open boxes. Colors
are according to IMGT color menu for genes. (Used with permission of Marie-Paule Lefranc. IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system®
http://www.imgt.org.)
Joining usually occurs only between segments flanked by recognition Rag-1/Rag-2 protein complex that catalyzes recombination (Fig. 75–6).
sequences with unequal spacers. Each recognition sequence consists Similar recognition sequences flank the elements that rearrange to
36
of a dyad symmetric heptamer, an A/T-rich nonamer, and a spacer form the T-cell antigen receptor (Chap. 76). Because all segments of
region of conserved length, either 12 bp or 23 bp ± 1 bp. This sequence a particular type (e.g., Vκ gene segments) are flanked by one type of
is referred to as the 12/23 joining rule. The consensus sequences for signal sequence and all the segments to which they should be joined
37
the heptamer (CACAGTG) and nonamers (ACAAAAACC) are opti- (e.g., Jκ segments) are flanked by the opposite type of signal sequence,
mal for rearrangement, but considerable deviation from the consensus the 12/23 rule ensures that the joining is restricted to events that could
sequence is observed and tolerated. Each spacer varies in sequence, be biologically productive. Such heptamer-spacer-nonamer sequences,
but its length is conserved and corresponds to one or two turns of the often called recombination signal sequences (RSSs), are targets of
DNA double helix. Each spacer brings the heptamer and nonamer lymphocyte-specific enzymes encoded by recombination activating
sequences to one side of the DNA helix, where they are bound by the genes RAG1 and RAG2. 36
Kaushansky_chapter 75_p1159-1174.indd 1164 9/21/15 12:11 PM