Page 1187 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1187
1162 Part IX: Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells Chapter 75: Functions of B Lymphocytes and Plasma Cells in Immunoglobulin Production 1163
Another nephritis associated with glomerular IgA deposits is
Henoch-Schönlein purpura, a condition that most commonly presents
with a characteristic pruritic skin rash, arthritis, and abdominal pain in
children or young adults (Chap. 122).
IgM
In a normal adult, approximately 6 percent of the total plasma immu-
noglobulins belong to the IgM class (see Tables 75–1 and 75–2). IgM
molecules classically are termed macroglobulins because of their large
molecular weight. Circulating IgM molecules contain 12 percent car-
bohydrate and are formed through the linkage of five identical immu-
noglobulin units by disulfide bonds and by a J chain (Fig. 75–2). IgM
14
represents the predominant immunoglobulin class formed during a
primary immune response. IgM macroglobulins do not penetrate eas-
ily into extravascular spaces or readily cross the placenta. Compared to
monomeric IgG antibodies, pentavalent IgM antibodies fix complement
more efficiently. A single IgM molecule on the surface of a red blood
cell can initiate complement-mediated hemolysis. IgM is catabolized
rapidly, with a plasma half-life of only 6 days. The monomeric form of
IgM, with only two heavy and two light chains, is the major immuno-
globulin expressed on the B-cell surface (Fig. 75–3). The IgM mono-
mer represents the ligand-binding part of the receptor. The component
that is responsible for signal transduction consists of two glycoproteins,
CD79a and CD79b. The cytoplasmic domains of CD79a (Ig-α) and
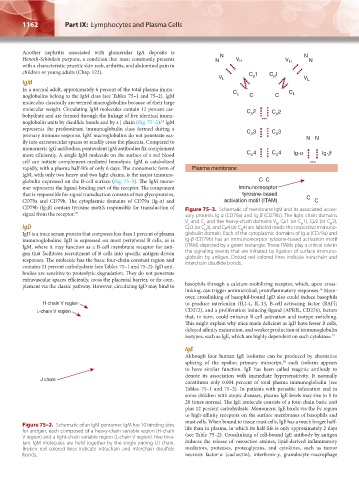
CD79b (Ig-β) contain tyrosine motifs responsible for transduction of Figure 75–3. Schematic of membrane IgM and its associated acces-
signal from the receptor. 15 sory proteins Ig-α (CD79a) and Ig-β (CD79b). The light-chain domains
V and C and the heavy-chain domains V , Cμ1 (or C 1), Cμ2 (or C 2),
H
L
L
H
H
IgD Cμ3 (or C 3), and Cμ4 (or C 4) are labeled inside the respective immuno-
H
H
IgD is a trace serum protein that composes less than 1 percent of plasma globulin domain. Each of the cytoplasmic domains of Ig-α (CD79a) and
immunoglobulins. IgD is expressed on most peripheral B cells, as is Ig-β (CD79b) has an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
IgM, where it may function as a B-cell membrane receptor for anti- (ITAM) depicted by a green rectangle. These ITAMs play a critical role in
gen that facilitates recruitment of B cells into specific antigen-driven the signaling events that are initiated by ligation of surface immuno-
responses. The molecule has the basic four-chain constant region and globulin by antigen. Dotted red colored lines indicate intrachain and
contains 11 percent carbohydrate (see Tables 75–1 and 75–2). IgD anti- interchain disulfide bonds.
bodies are sensitive to proteolytic degradation. They do not penetrate
extravascular spaces efficiently, cross the placental barrier, or fix com-
plement via the classic pathway. However, circulating IgD may bind to basophils through a calcium-mobilizing receptor, which, upon cross-
16
linking, can trigger antimicrobial, proinflammatory responses. More-
over, crosslinking of basophil-bound IgD also could induce basophils
H-chain V region to produce interleukin (IL)-4, IL-13, B-cell activating factor (BAFF,
L-chain V region CD272), and a proliferation inducing-ligand (APRIL, CD276), factors
that, in turn, could enhance B-cell activation and isotype switching.
This might explain why mice made deficient in IgD have fewer B cells,
delayed affinity maturation, and weaker production of immunoglobulin
isotypes, such as IgE, which are highly dependent on such cytokines. 17
IgE
Although four human IgE isoforms can be produced by alternative
18
splicing of the epsilon primary transcript, each isoform appears
to have similar function. IgE has been called reaginic antibody to
denote its association with immediate hypersensitivity. It normally
J chain
constitutes only 0.004 percent of total plasma immunoglobulin (see
Tables 75–1 and 75–2). In patients with parasitic infestation and in
some children with atopic diseases, plasma IgE levels may rise to 5 to
20 times normal. The IgE molecule consists of a four-chain basic unit
plus 12 percent carbohydrate. Monomeric IgE binds via the Fc region
to high-affinity receptors on the surface membranes of basophils and
mast cells. When bound to tissue mast cells, IgE has a much longer half-
Figure 75–2. Schematic of an IgM pentamer. IgM has 10 binding sites life than in plasma, in which its half-life is only approximately 2 days
for antigen, each composed of a heavy-chain variable region (H-chain
V region) and a light-chain variable region (L-chain V region). Five biva- (see Table 75–2). Crosslinking of cell-bound IgE antibody by antigen
lent IgM molecules are held together by the single joining (J) chain. induces the release of vasoactive amines, lipid-derived inflammatory
Broken red colored lines indicate intrachain and interchain disulfide mediators, proteases, proteoglycans, and cytokines, such as tumor
bonds. necrosis factor-α (cachectin), interferon-γ, granulocyte-macrophage
Kaushansky_chapter 75_p1159-1174.indd 1162 9/21/15 12:10 PM