Page 1523 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1523
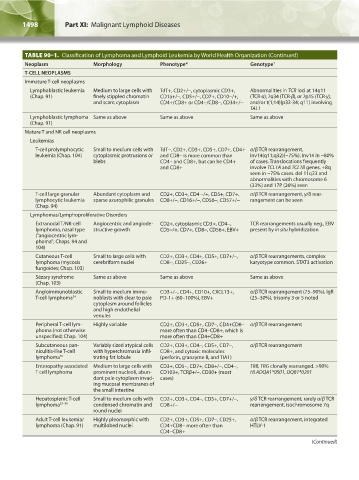
1498 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 90: Classification of Malignant Lymphoid Disorders 1499
TABLE 90–1. Classification of Lymphoma and Lymphoid Leukemia by World Health Organization (Continued)
Neoplasm Morphology Phenotype* Genotype †
T-CELL NEOPLASMS
Immature T-cell neoplasms
Lymphoblastic leukemia Medium to large cells with TdT+, CD2+/-, cytoplasmic CD3+, Abnormalities in TCR loci at 14q11
(Chap. 91) finely stippled chromatin CD1a+/-, CD5+/-, CD7+, CD10-/+, (TCR-α), 7q34 (TCR-β), or 7p15 (TCR-γ),
and scant cytoplasm CD4+/CD8+ or CD4-/CD8-, CD34+/- and/or t(1;14)(p32-34; q11) involving
TAL1
Lymphoblastic lymphoma Same as above Same as above Same as above
(Chap. 91)
Mature T and NK cell neoplasms
Leukemias
T-cell prolymphocytic Small to medium cells with TdT-, CD2+, CD3+, CD5+, CD7+, CD4+ α/β TCR rearrangement,
leukemia (Chap. 104) cytoplasmic protrusions or and CD8- is more common than inv14(q11;q32)(~75%). Inv14 in ~80%
blebs CD4- and CD8+, but can be CD4+ of cases. Translocations frequently
and CD8+ involve TCL1A and TCL1B genes. +8q
seen in ~75% cases. del 11q23 and
abnormalities with chromosome 6
(33%) and 17P (26%) seen
T-cell large granular Abundant cytoplasm and CD2+, CD3+, CD4 -/+, CD5+, CD7+, α/β TCR rearrangement, γ/δ rear-
lymphocytic leukemia sparse azurophilic granules CD8+/-, CD16+/-, CD56-, CD57+/- rangement can be seen
(Chap. 94)
Lymphomas/Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Extranodal T/NK-cell Angiocentric and angiode- CD2+, cytoplasmic CD3+, CD4-, TCR rearrangements usually neg., EBV
lymphoma, nasal type structive growth CD5-/+, CD7+, CD8-, CD56+, EBV+ present by in situ hybridization
(“angiocentric lym-
phoma”; Chaps. 94 and
104)
Cutaneous T-cell Small to large cells with CD2+, CD3+, CD4+, CD5+, CD7+/-, α/β TCR rearrangements, complex
lymphoma (mycosis cerebriform nuclei CD8-, CD25-, CD26+ karyotype common. STAT3 activation
fungoides; Chap. 103)
Sézary syndrome Same as above Same as above Same as above
(Chap. 103)
Angioimmunoblastic Small to medium immu- CD3+/-, CD4+, CD10+, CXCL13+, α/β TCR rearrangement (75–90%), IgR
T-cell lymphoma 34 noblasts with clear to pale PD-1+ (60–100%), EBV+ (25–30%), trisomy 3 or 5 noted
cytoplasm around follicles
and high endothelial
venules
Peripheral T-cell lym- Highly variable CD2+, CD3+, CD5+, CD7-, CD4+CD8- α/β TCR rearrangement
phoma (not otherwise more often than CD4-CD8+, which is
unspecified; Chap. 104) more often than CD4+CD8+
Subcutaneous pan- Variably sized atypical cells CD2+, CD3+, CD4-, CD5+, CD7-, α/β TCR rearrangement
niculitis-like T-cell with hyperchromasia infil- CD8+, and cytoxic molecules
lymphoma 35 trating fat lobule (perforin, granzyme B, and TIA1)
Enteropathy associated Medium to large cells with CD3+, CD5-, CD7+, CD8+/-, CD4-, TRB, TRG clonally rearranged. >90%
T cell lymphoma prominent nucleoli, abun- CD103+, TCRβ+/-. CD30+ (most HLADQA1*0501, DQB1*0201
dant pale cytoplasm invad- cases)
ing mucosal membranes of
the small intestine
Hepatosplenic T-cell Small to medium cells with CD2+, CD3+, CD4-, CD5+, CD7+/-, γ/δ TCR rearrangement, rarely α/β TCR
lymphoma 37–39 condensed chromatin and CD8+/- rearrangement, isochromosome 7q
round nuclei
Adult T-cell leukemia/ Highly pleomorphic with CD2+, CD3+, CD5+, CD7-, CD25+, α/β TCR rearrangement, integrated
lymphoma (Chap. 91) multilobed nuclei CD4+CD8- more often than HTLV-1
CD4-CD8+
(Continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 90_p1491-1504.indd 1498 9/21/15 4:07 PM